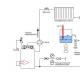
Ultraviolet light is beneficial for the body because... What is Ultraviolet Light: UV radiation. Use in filters
I remember disinfection with UV lamps from childhood - in kindergartens, sanatoriums and even in summer camps there were somewhat frightening structures that glowed with a beautiful purple light in the dark and from which teachers drove us away. So what exactly is ultraviolet radiation and why does a person need it?
Perhaps the first question that needs to be answered is what ultraviolet rays are and how they work. This is usually the name for electromagnetic radiation, which is in the range between visible and x-ray radiation. Ultraviolet is characterized by a wavelength from 10 to 400 nanometers.
It was discovered back in the 19th century, and this happened thanks to the discovery of infrared radiation. Having discovered the IR spectrum, in 1801 I.V. Ritter turned his attention to the opposite end of the light spectrum during experiments with silver chloride. And then several scientists immediately came to the conclusion that ultraviolet radiation is heterogeneous.
Today it is divided into three groups:
- UVA radiation – near ultraviolet;
- UV-B – medium;
- UV-C - far.
This division is largely due to the impact of rays on humans. The natural and main source of ultraviolet radiation on Earth is the Sun. In fact, it is this radiation that we protect ourselves from with sunscreens. In this case, far ultraviolet radiation is completely absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, and UV-A just reaches the surface, causing a pleasant tan. And on average, 10% of UV-B provokes those same sunburns, and can also lead to the formation of mutations and skin diseases.

Artificial ultraviolet sources are created and used in medicine, agriculture, cosmetology and various sanitary institutions. Ultraviolet radiation can be generated in several ways: by temperature (incandescent lamps), by the movement of gases (gas lamps) or metal vapors (mercury lamps). Moreover, the power of such sources varies from several watts, usually small mobile emitters, to kilowatts. The latter are mounted in large stationary installations. The areas of application of UV rays are determined by their properties: the ability to accelerate chemical and biological processes, the bactericidal effect and the luminescence of certain substances.
Ultraviolet is widely used to solve a wide variety of problems. In cosmetology, the use of artificial UV radiation is used primarily for tanning. Solariums create fairly mild ultraviolet-A according to the introduced standards, and the share of UV-B in tanning lamps is no more than 5%. Modern psychologists recommend solariums for the treatment of “winter depression,” which is mainly caused by a deficiency of vitamin D, as it is formed under the influence of UV rays. UV lamps are also used in manicure, since it is in this spectrum that especially resistant gel polishes, shellac and the like dry.
Ultraviolet lamps are used to create photographs in unusual situations, for example, to capture space objects that are invisible through a regular telescope.
Ultraviolet light is widely used in expert activities. With its help, the authenticity of paintings is verified, since fresher paints and varnishes look darker in such rays, which means the real age of the work can be established. Forensic scientists also use UV rays to detect traces of blood on objects. In addition, ultraviolet light is widely used for the development of hidden seals, security elements and threads confirming the authenticity of documents, as well as in the lighting design of shows, signs of establishments or decorations.

In medical institutions, ultraviolet lamps are used to sterilize surgical instruments. In addition, air disinfection using UV rays is still widespread. There are several types of such equipment.

This is the name given to high- and low-pressure mercury lamps, as well as xenon flash lamps. The bulb of such a lamp is made of quartz glass. The main advantage of bactericidal lamps is their long service life and immediate ability to work. Approximately 60% of their rays are in the bactericidal spectrum. Mercury lamps are quite dangerous to operate; if the housing is accidentally damaged, thorough cleaning and demercurization of the room is necessary. Xenon lamps are less dangerous if damaged and have higher bactericidal activity. Germicidal lamps are also divided into ozone and ozone-free. The former are characterized by the presence in their spectrum of a wave with a length of 185 nanometers, which interacts with oxygen in the air and turns it into ozone. High concentrations of ozone are dangerous to humans, and the use of such lamps is strictly limited in time and recommended only in a ventilated area. All this led to the creation of ozone-free lamps, the bulb of which was coated with a special coating that did not transmit a wave of 185 nm to the outside.
Regardless of the type, bactericidal lamps have common disadvantages: they operate in complex and expensive equipment, the average operating life of the emitter is 1.5 years, and the lamps themselves, after burning out, must be stored packaged in a separate room and disposed of in a special way in accordance with current regulations.

Consist of a lamp, reflectors and other auxiliary elements. There are two types of such devices - open and closed, depending on whether UV rays pass out or not. Open ones release ultraviolet radiation, enhanced by reflectors, into the space around them, capturing almost the entire room at once if installed on the ceiling or wall. It is strictly prohibited to treat a room with such an irradiator in the presence of people.
Closed irradiators operate on the principle of a recirculator, inside of which a lamp is installed, and a fan draws air into the device and releases the already irradiated air outside. They are placed on the walls at a height of at least 2 m from the floor. They can be used in the presence of people, but long-term exposure is not recommended by the manufacturer, since some of the UV rays may pass out.
The disadvantages of such devices include immunity to mold spores, as well as all the difficulties of recycling lamps and strict regulations for use depending on the type of emitter.
Bactericidal installations
A group of irradiators combined into one device used in one room is called a bactericidal installation. They are usually quite large and have high energy consumption. Air treatment with bactericidal installations is carried out strictly in the absence of people in the room and is monitored according to the Commissioning Certificate and the Registration and Control Log. Used only in medical and hygienic institutions to disinfect both air and water.
Disadvantages of ultraviolet air disinfection
In addition to what has already been listed, the use of UV emitters has other disadvantages. First of all, ultraviolet radiation itself is dangerous for the human body; it can not only cause skin burns, but also affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system and is dangerous for the retina. In addition, it can cause the appearance of ozone, and with it the unpleasant symptoms inherent in this gas: irritation of the respiratory tract, stimulation of atherosclerosis, exacerbation of allergies.
The effectiveness of UV lamps is quite controversial: inactivation of pathogens in the air by permitted doses of ultraviolet radiation occurs only when these pests are static. If microorganisms move and interact with dust and air, then the required radiation dose increases by 4 times, which a conventional UV lamp cannot create. Therefore, the efficiency of the irradiator is calculated separately, taking into account all parameters, and it is extremely difficult to select those suitable for influencing all types of microorganisms at once.
The penetration of UV rays is relatively shallow, and even if immobile viruses are under a layer of dust, the upper layers protect the lower ones by reflecting ultraviolet radiation from themselves. This means that after cleaning, disinfection must be carried out again.
UV irradiators cannot filter the air; they only fight microorganisms, keeping all mechanical pollutants and allergens in their original form.
Constant exposure to ultraviolet radiation on microorganisms causes mutation in the latter, so that after several irradiations, viruses and infections become resistant to UV treatment and survive it.
The concept of ultraviolet rays was first encountered by an Indian philosopher of the 13th century in his work. The atmosphere of the area he described Bhootakasha contained violet rays that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Soon after infrared radiation was discovered, the German physicist Johann Wilhelm Ritter began searching for radiation at the opposite end of the spectrum, with a wavelength shorter than that of violet. In 1801, he discovered that silver chloride, which decomposes faster when exposed to light decomposes under the influence of invisible radiation outside the violet region of the spectrum. Silver chloride, which is white in color, darkens in the light within a few minutes. Different parts of the spectrum have different effects on the rate of darkening. This happens most quickly in front of the violet region of the spectrum. Many scientists, including Ritter, then agreed that light consists of three distinct components: an oxidative or thermal (infrared) component, an illuminant (visible light) component, and a reducing (ultraviolet) component. At that time, ultraviolet radiation was also called actinic radiation. Ideas about the unity of three different parts of the spectrum were first voiced only in 1842 in the works of Alexander Becquerel, Macedonio Melloni and others.
Subtypes
Degradation of polymers and dyes
Scope of application
Black light
Chemical analysis
UV spectrometry
UV spectrophotometry is based on irradiating a substance with monochromatic UV radiation, the wavelength of which changes over time. The substance absorbs UV radiation at different wavelengths to varying degrees. A graph, the ordinate axis of which shows the amount of transmitted or reflected radiation, and the abscissa axis the wavelength, forms a spectrum. The spectra are unique for each substance, which is the basis for the identification of individual substances in a mixture, as well as their quantitative measurement.
Mineral Analysis
Many minerals contain substances that, when illuminated by ultraviolet light, begin to emit visible light. Each impurity glows in its own way, which makes it possible to determine the composition of a given mineral by the nature of the glow. A. A. Malakhov in his book “Interesting about Geology” (Moscow, “Young Guard”, 1969. 240 pp) talks about it this way: “An unusual glow of minerals is caused by cathode, ultraviolet, and x-rays. In the world of dead stone, those minerals that light up and shine most brightly are those that, once in the zone of ultraviolet light, tell about the smallest impurities of uranium or manganese included in the rock. Many other minerals that do not contain any impurities also flash a strange “unearthly” color. I spent the whole day in the laboratory, where I observed the luminescent glow of minerals. Ordinary colorless calcite became miraculously colored under the influence of various light sources. Cathode rays made the crystal ruby red; in ultraviolet light it lit up with crimson-red tones. The two minerals, fluorite and zircon, were indistinguishable in X-rays. Both were green. But as soon as the cathode light was connected, the fluorite became purple, and the zircon turned lemon yellow.” (p. 11).
Qualitative chromatographic analysis
Chromatograms obtained by TLC are often viewed under ultraviolet light, which makes it possible to identify a number of organic substances by their glow color and retention index.
Catching insects
Ultraviolet radiation is often used when catching insects with light (often in combination with lamps emitting in the visible part of the spectrum). This is due to the fact that in most insects the visible range is shifted, compared to human vision, to the short-wave part of the spectrum: insects do not see what humans perceive as red, but see soft ultraviolet light.
Artificial tanning and “Mountain sun”
At certain dosages, artificial tanning can improve the condition and appearance of human skin and promotes the formation of vitamin D. Fotaria are currently popular, which in everyday life are often called solariums.
Ultraviolet in restoration
One of the main tools of experts is ultraviolet, x-ray and infrared radiation. Ultraviolet rays make it possible to determine the aging of a varnish film - fresher varnish looks darker in ultraviolet light. In the light of a large laboratory ultraviolet lamp, restored areas and hand-written signatures appear as darker spots. X-rays are blocked by the heaviest elements. In the human body this is bone tissue, but in a painting it is whitewash. The basis of white in most cases is lead; in the 19th century, zinc began to be used, and in the 20th century, titanium. All these are heavy metals. Ultimately, on film we get an image of the whitewash underpainting. Underpainting is the individual “handwriting” of the artist, an element of his own unique technique. To analyze the underpainting, a database of X-ray photographs of paintings by great masters is used. These photographs are also used to determine the authenticity of a painting.
Notes
- ISO 21348 Process for Determining Solar Irradiances. Archived from the original on June 23, 2012.
- Bobukh, Evgeniy On animal vision. Archived from the original on November 7, 2012. Retrieved November 6, 2012.
- Soviet encyclopedia
- V. K. Popov // UFN. - 1985. - T. 147. - P. 587-604.
- A. K. Shuaibov, V. S. Shevera Ultraviolet nitrogen laser at 337.1 nm in frequent repetition mode // Ukrainian Physical Journal. - 1977. - T. 22. - No. 1. - P. 157-158.
- A. G. Molchanov Lasers in the vacuum ultraviolet and x-ray regions of the spectrum // UFN. - 1972. - T. 106. - P. 165-173.
- V. V. Fadeev Ultraviolet lasers based on organic scintillators // UFN. - 1970. - T. 101. - P. 79-80.
- Ultraviolet laser // Scientific network nature.web.ru
- Laser Twinkles in Rare Color (Russian) , Science Daily(Dec. 21, 2010). Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- R. V. Lapshin, A. P. Alekhin, A. G. Kirilenko, S. L. Odintsov, V. A. Krotkov (2010). “Smoothing of nanoroughness of polymethyl methacrylate surface with vacuum ultraviolet light” (PDF). Surface. X-ray, synchrotron and neutron research(MAIK) (1): 5-16.
The influence of sun light on a person is difficult to overestimate - under its influence, the most important physiological and biochemical processes are launched in the body. The solar spectrum is divided into infrared and visible parts, as well as the most biologically active ultraviolet part, which has a great influence on all living organisms on our planet. Ultraviolet radiation is a short-wave part of the solar spectrum that is not perceived by the human eye, has an electromagnetic nature and photochemical activity.
Due to its properties, ultraviolet light is successfully used in various areas of human life. UV radiation is widely used in medicine because it can change the chemical structure of cells and tissues, having different effects on humans.
Ultraviolet wavelength range
The main source of UV radiation is the sun. The share of ultraviolet radiation in the total flux of sunlight is not constant. It depends on:
- time of day;
- time of year;
- solar activity;
- geographical latitude;
- state of the atmosphere.
Despite the fact that the celestial body is far from us and its activity is not always the same, a sufficient amount of ultraviolet radiation reaches the Earth's surface. But this is only its small long-wavelength part. Short waves are absorbed by the atmosphere at a distance of about 50 km from the surface of our planet.
The ultraviolet range of the spectrum, which reaches the earth's surface, is conventionally divided by wavelength into:
- far (400 – 315 nm) – UV – A rays;
- medium (315 – 280 nm) – UV – B rays;
- near (280 – 100 nm) – UV – C rays.
The effect of each UV range on the human body is different: the shorter the wavelength, the deeper it penetrates through the skin. This law determines the positive or negative effects of ultraviolet radiation on the human body.
Near-range UV radiation has the most adverse effect on health and carries the threat of serious diseases.
UV-C rays should be scattered in the ozone layer, but due to poor ecology they reach the surface of the earth. Ultraviolet rays of the A and B ranges are less dangerous; with strict dosage, far- and mid-range radiation has a beneficial effect on the human body.
Artificial sources of ultraviolet radiation
The most significant sources of UV waves affecting the human body are: 
- bactericidal lamps - sources of UV - C waves, used to disinfect water, air or other environmental objects;
- industrial welding arc – sources of all waves in the range of the solar spectrum;
- erythemal fluorescent lamps - sources of UV waves in the A and B ranges, used for therapeutic purposes and in solariums;
- industrial lamps are powerful sources of ultraviolet waves used in manufacturing processes to cure paints, inks, or cure polymers.
The characteristics of any UV lamp are its radiation power, wavelength range, type of glass, and service life. These parameters determine how useful or harmful the lamp will be to humans.
Before irradiation with ultraviolet waves from artificial sources for the treatment or prevention of diseases, you should consult with a specialist to select the necessary and sufficient erythema dose, which is individual for each person, taking into account his skin type, age, and existing diseases.
It should be understood that ultraviolet is electromagnetic radiation, which has not only a positive effect on the human body.
A germicidal ultraviolet lamp used for tanning will cause significant harm rather than benefit to the body. Only a professional who is well versed in all the nuances of such devices should use artificial sources of UV radiation.
Positive effects of UV radiation on the human body
Ultraviolet radiation is widely used in the field of modern medicine. And this is not surprising, because UV rays produce analgesic, sedative, antirachitic and antispastic effects. Under their influence occurs: 
- formation of vitamin D, necessary for the absorption of calcium, development and strengthening of bone tissue;
- decreased excitability of nerve endings;
- increased metabolism, as it causes activation of enzymes;
- dilation of blood vessels and improvement of blood circulation;
- stimulating the production of endorphins - “hormones of happiness”;
- increasing the speed of regenerative processes.
The beneficial effect of ultraviolet waves on the human body is also expressed in a change in its immunobiological reactivity - the body’s ability to exhibit protective functions against pathogens of various diseases. Strictly dosed ultraviolet irradiation stimulates the production of antibodies, thereby increasing the human body's resistance to infections.
Exposure of the skin to UV rays causes a reaction called erythema (redness). Vasodilation occurs, expressed by hyperemia and swelling. The breakdown products formed in the skin (histamine and vitamin D) enter the blood, which causes general changes in the body when irradiated with UV waves.
The degree of development of erythema depends on:
- ultraviolet dose values;
- range of ultraviolet rays;
- individual sensitivity.
With excessive UV irradiation, the affected area of the skin is very painful and swollen, a burn occurs with the appearance of a blister and further convergence of the epithelium.
But skin burns are far from the most serious consequences of prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation on humans. Unreasonable use of UV rays causes pathological changes in the body.
Negative effects of UV radiation on humans
 Despite its important role in medicine, The harm of ultraviolet radiation on health outweighs the benefits. Most people are not able to accurately control the therapeutic dose of ultraviolet radiation and resort to protection methods in a timely manner, so an overdose often occurs, which causes the following phenomena:
Despite its important role in medicine, The harm of ultraviolet radiation on health outweighs the benefits. Most people are not able to accurately control the therapeutic dose of ultraviolet radiation and resort to protection methods in a timely manner, so an overdose often occurs, which causes the following phenomena:
- headaches appear;
- body temperature rises;
- fatigue, apathy;
- memory impairment;
- cardiopalmus;
- decreased appetite and nausea.
Excessive tanning affects the skin, eyes and immune (defense) system. The tangible and visible consequences of excessive UV irradiation (burns of the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes, dermatitis and allergic reactions) disappear within a few days. Ultraviolet radiation accumulates over a long period of time and causes very serious diseases.
The effect of ultraviolet radiation on the skin
A beautiful, even tan is the dream of every person, especially the fairer sex. But it should be understood that skin cells darken under the influence of the coloring pigment released in them - melanin in order to protect against further ultraviolet irradiation. That's why tanning is a protective reaction of our skin to damage to its cells by ultraviolet rays. But it does not protect the skin from the more serious effects of UV radiation: 
- Photosensitivity – increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. Even a small dose of it causes severe burning, itching and sunburn of the skin. This is often associated with the use of medications or the consumption of cosmetics or certain foods.
- Photoaging. UV rays of spectrum A penetrate into the deep layers of the skin, damaging the structure of connective tissue, which leads to the destruction of collagen, loss of elasticity, and early wrinkles.
- Melanoma - skin cancer. The disease develops after frequent and prolonged exposure to the sun. Under the influence of an excessive dose of ultraviolet radiation, malignant formations appear on the skin or old moles degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
- Basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma are non-melanoma skin cancers that are not fatal but require surgical removal of the affected areas. It has been noticed that the disease occurs much more often in people who work in the open sun for a long time.
Any dermatitis or phenomena of skin sensitization under the influence of ultraviolet radiation are provoking factors for the development of skin cancer.
Effect of UV waves on the eyes
Ultraviolet rays, depending on the depth of penetration, can also negatively affect the condition of a person’s eyes: 
- Photoophthalmia and electroophthalmia. Expressed in redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the eyes, lacrimation, photophobia. Occurs when safety rules are not followed when working with welding equipment or in people who are in bright sunlight in a snow-covered area (snow blindness).
- Growth of the conjunctiva of the eye (pterygium).
- Cataract (clouding of the lens of the eye) is a disease that occurs to varying degrees in the vast majority of people in old age. Its development is associated with exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the eyes, which accumulates throughout life.
Excess UV rays can lead to various forms of eye and eyelid cancer.
The effect of ultraviolet radiation on the immune system
If the dosed use of UV radiation helps to increase the body’s defenses, then Excessive exposure to ultraviolet light suppresses the immune system. This has been proven in scientific studies by US scientists on the herpes virus. Ultraviolet radiation changes the activity of cells responsible for immunity in the body; they cannot restrain the proliferation of viruses or bacteria, cancer cells.
Basic safety precautions and protection against exposure to ultraviolet radiation
To avoid the negative effects of UV rays on the skin, eyes and health, every person needs protection from ultraviolet radiation. If you are forced to spend a long time in the sun or in a workplace exposed to high doses of ultraviolet rays, you must find out whether the UV radiation index is normal. In enterprises, a device called a radiometer is used for this.
When calculating the index at meteorological stations, the following are taken into account: 
- ultraviolet wavelength;
- ozone layer concentration;
- solar activity and other indicators.
The UV index is an indicator of the potential risk to the human body as a result of the influence of ultraviolet radiation on it. The index value is assessed on a scale from 1 to 11+. The norm for the UV index is considered to be no more than 2 units.
At high index values (6 – 11+), the risk of adverse effects on human eyes and skin increases, so protective measures must be taken.
- Use sunglasses (special masks for welders).
- In the open sun, you should definitely wear a hat (if the index is very high, a wide-brimmed hat).
- Wear clothing that covers your arms and legs.
- On areas of the body not covered by clothing Apply sunscreen with a protection factor of at least 30.
- Avoid being in an open space not protected from direct sunlight from noon to 4 p.m.
Following simple safety rules will reduce the harmfulness of UV radiation for humans and avoid the occurrence of diseases associated with the adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation on the body.
For whom ultraviolet irradiation is contraindicated?
The following categories of people should be careful with exposure to ultraviolet radiation: 
- with very fair and sensitive skin and albinos;
- children and teenagers;
- those who have many birthmarks or nevi;
- suffering from systemic or gynecological diseases;
- those who have had skin cancer among their close relatives;
- taking certain medications for a long time (consult a doctor).
UV radiation is contraindicated for such people even in small doses; the degree of protection from sunlight should be maximum.
The effect of ultraviolet radiation on the human body and its health cannot be clearly called positive or negative. Too many factors must be taken into account when it affects humans under different environmental conditions and with radiation from different sources. The main thing to remember is the rule: any exposure to ultraviolet radiation on a person should be minimal before consulting a specialist and strictly dosed according to the doctor’s recommendations after examination and examination.
In spring, nature awakens, and people say goodbye to winter depression. And the main reason for this is the warmer and longer days that the Sun gives to those around us - the main natural source of ultraviolet radiation on Earth. Namely, ultraviolet radiation is one of the main sources of a full and healthy human life. However, not all people manage to spend enough time outside. Therefore, an ultraviolet lamp for the home today is an excellent solution for many.
The essence of home ultraviolet lamps.
An ultraviolet lamp for the home is a type of lighting lamp used in everyday life, the light source of which is rays invisible to the human eye, located on the border of the violet spectrum and x-ray radiation.
This radiation is the most beneficial for health. Examples of household appliances of this kind include: fluorescent, tungsten-halogen, LED ultraviolet lamps and many others.
Benefits of home ultraviolet lamps.
Ultraviolet radiation lamps promote the production of vitamin D. This vitamin is actively involved in the synthesis and absorption of calcium by the body, which is involved in the construction and strengthening of bones, teeth, hair and nails. With enough vitamin D, the body is able to obtain calcium from the food it eats. However, if there is a deficiency of the vitamin in question, then calcium ceases to be absorbed, and the body is immediately replenished by consuming this useful microelement directly from its own bone tissue. As a result of this, the skeleton becomes fragile, teeth may begin to crumble, nails break, and so on.
In the future, a person acquires such a difficult-to-treat disease as osteoporosis. It is important to note that the synthesis of vitamin D when exposed to ultraviolet radiation is independently regulated by the body, that is, the possibility of hypervitaminization and side effects is completely absent. The benefit of the vitamin in question lies not only in the prevention and treatment of rickets and other diseases associated with a lack of calcium in the body, but also in the ability to prevent the growth of cancer cells. All types of lamps under consideration, including a fluorescent ultraviolet lamp, have this property.
Additionally, the following useful properties of such lamps can be noted:
General immune-strengthening effect
It has long been proven that UV radiation has a beneficial effect on all systems of the human and animal body, contributing to the development of a powerful protective system against viral and infectious diseases, including such as seasonal colds.
Possibility of disinfection and disinfection of the premises
All UV lamps have this effect, helping to destroy pathogenic bacteria in the house or apartment and other harmful microorganisms.
Development of resistance of human skin to sunburn
Benefits for Pets
First of all, we are talking about exotic pets from warm countries, where the sun shines brightly all year round. In temperate zone conditions, these animals experience stress and are provoked to develop a number of diseases, often with fatal outcomes. Additional artificial UV radiation completely helps solve this problem.
Are ultraviolet lamps harmful?
To the question: is the ultraviolet lamp used in everyday life harmful? We can say unequivocally - no. Indeed, UV radiation is often harmful to human health and has contraindications for many diseases. But the harm is directly related to the amount of solar radiation consumed. And it is extremely dangerous to be uncontrolled under the scorching Sun. With lamps this is completely impossible. The fact is that the amount of radiation produced by a home ultraviolet lamp is minimal (significantly lower than solar radiation), and, therefore, completely safe for health.
Their positive effect is noticeable, as a rule, only after a few months. In this regard, special ultraviolet lamps are used for therapy, which allow achieving a therapeutic result after two to three days of use. Such procedures can only be carried out as directed and under the guidance of a qualified specialist.
In conclusion, we need to say how to choose ultraviolet lamps. For general purposes and prevention, emphasis should be placed on lamps with radiation in the range of 280 - 410 nm. Unless, of course, we are talking about specialized devices. For example, such as an ultraviolet lamp for water disinfection. There, the radiation range may differ from the average.
Source:
The use of ultraviolet radiation in medicine, everyday life, and educational institutions includes the disinfection of premises without the use of chemical compounds. A quartz lamp is an effective preventive anti-epidemic agent that combats pathogenic microorganisms in the air, water and on various surfaces. This device reduces the spread of infections and viruses in the room being treated.
Quartz lamps are used in:
- hospital wards;
- operating rooms;
- kindergartens and schools;
- everyday life
The use of ultraviolet irradiation simultaneously with ozonation in retail premises and food warehouses makes it possible to preserve the freshness of food products, prevent the processes of rotting and the development of harmful microflora.
Indoor quartzingThe principle of operation of the lamp
A quartz lamp is an electric gas-discharge mercury device with a bulb consisting of quartz glass. When heated, the lamp begins to emit ultraviolet light. This radiation actively fights harmful bacteria and microbes.
However, ultraviolet rays do not penetrate deep into furniture or through wall plaster; they kill germs only on the surface. To combat different types of microorganisms, different intensity and duration of operation of disinfection devices is required.
First of all, rods and cocci die under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, and the most resistant during irradiation are fungi, spore bacteria and protozoa. Carrying out quartz treatment gives a positive result in the fight against the influenza virus. After 20 minutes from the start of operation of the device, the room becomes almost sterile.
Expert opinion
Alexey Bartosh
Specialist in repair and maintenance of electrical equipment and industrial electronics.
Ask a question to an expert
Attention! During operation of the quartz lamp, oxygen is ionized, due to which it turns into ozone. In high concentrations, this gas is poisonous to all living organisms. Therefore, while the quartz generator is working, the room should be empty. The person and pets must leave the room. If there are plants, it is better to take them out too.
Ozone, like ultraviolet light, fights harmful bacteria. But in order not to harm a person, after quartz treatment it is necessary to ventilate the room.
Ventilation after quartzing is a must. Features of quartzing
To use quartz for disinfecting purposes, in accordance with regulatory sanitary requirements, an indicator of bactericidal effectiveness is determined. This parameter evaluates the degree to which bacterial contamination of the air is reduced under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The indicator is expressed as a percentage, as the ratio of the number of dead microorganisms to their original number. For premises for various purposes with mandatory air disinfection, their own values for the required degree of bactericidal effect have been established.
Since direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation on human skin and eyes is dangerous, the following quartz treatment rules are required:
- First of all, make sure that there are no people, plants or other living creatures in the room before disinfecting.
- Depending on the size of the room and the number of operating quartz devices, the required irradiation time and operating mode are set.
- During quartzing, a sign with the inscription “Do not enter” turns on at the entrance to the room. After the session is completed, the light display turns off.
It is also possible to quartz rooms in the presence of a person if closed ultraviolet irradiators - recirculators - are used. In this case, the air is disinfected inside the device, entering through the ventilation passage. After disinfection, the air is sent back into the room.
Special cabinets are used to disinfect medical instruments, cutlery, dishes, children's toys and other items. There are lattice shelves installed inside. This design allows the objects being processed to be irradiated with ultraviolet light from all sides.
Before using quartzizer at home, consult your family doctor. There are a number of diseases for which quartz air disinfection is prohibited.
Version of household quartz lamp with contents Precautions
When using a quartz lamp, the following precautions are observed:
- Use of safety glasses. They will protect your eyes from burns.
- Do not look at the working lamp or touch the heating surfaces of the device.
- You cannot sit next to a working light bulb.
- It is prohibited to sunbathe under germicidal ultraviolet lamps.
- Radiation should not be allowed to enter exposed areas of the skin - this leads to burns and dangerous skin diseases, including cancer.
- Do not disinfect a room if there is a sick person with a high body temperature in the house.
- Observe fire safety when using devices.
- If after quartzing you notice a specific smell of ozone, be sure to ventilate the room.
At home, use quartz irradiators with extreme caution. Ultraviolet radiation can destroy not only harmful microbes, but also cells of the human body. Do not forget to replace lamps promptly.
If the air is not effectively disinfected with a low-quality lamp, or if it breaks due to mercury inside or breaks, the risk of the spread of harmful bacteria increases. This situation is unacceptable. Therefore, when determining the serviceability of the device, the user should be wary of the following aspects:
- The device does not turn on.
- The timer is malfunctioning - the lamp does not turn off on time.
- The device is flashing.
- The ends of the lamp darkened.
- There is an unpleasant smell near the device, as if something is burning.
- The device makes noise during operation.
Compact device for home use
What to do with a faulty device?
If you suspect that the device is malfunctioning, immediately disconnect it from the power supply. Do not try to repair the lamp yourself and do not open the housing of the device. If the device is under warranty, take it to a service center. If the warranty period has expired, find a quartz lamp repair specialist.
If the lamp accidentally breaks, then there will be not only vapor in the room, but also small droplets of mercury. If this happens, you will need to demercurize the room.
Quartz lamp: harm and benefit
The benefits of an ultraviolet lamp for disinfecting premises are undeniable. Are there any negative aspects to this device?
In this context, the following nuances can be mentioned. Potential harm occurs when:
- the lamp is not used for its intended purpose;
- instructions and precautions are not followed;
- there are contraindications for health reasons among family members;
- the lamp is incorrectly selected.
Manufacturers offer two types of devices:
- Open.
- Closed.
When using the first option, the room is freed from the presence of all living creatures, including flowers. These devices are too aggressive for domestic use. They are more often used in laboratories, clinics, and offices.
Violation of safety rules is fraught with dangerous consequences for human health:
- Eye burn.
- Skin burn.
- Melanoma - cancer.
Quartz lamp burn
Homemade irradiators pose a danger. After all, it is unknown how correctly a person followed the manufacturing technology, what the impact of such a device is, and whether its use will harm people. When using such devices, you must not be in the room where disinfection is taking place. After turning off the device, the room is ventilated for at least half an hour.
Important! It should be remembered that excessive disinfection of living spaces is harmful to the human body. Even a child’s body must independently form its own immunity and cope with certain bacteria. A child who grew up in sterile conditions begins to get sick often when entering kindergarten or school.
But if there is mold in the house, one of the household members falls ill with an infectious pathology, and cold season begins outside the window, then quartz treatment will be very useful.
There are two types of quartz lamps:
- Ozone (open).
- Ozone-free (closed).
Devices of the first type are used only in the complete absence of living beings in the room. They are widely used in hospitals, catering establishments, laboratories, educational institutions, and offices. In the fight against pathogenic flora, viruses and infections, they are more effective than closed devices, but also more aggressive.
Combination devices that combine the advantages of open and closed devices deserve special attention. With their help, direct irradiation of space is carried out (when an open lamp is turned on) and diffused (when a shielded device is operating). Lamps for direct and reflected irradiation have separate switches and can operate independently of each other.
What should you consider when choosing?
When choosing a quartz irradiator, consider the lamp power and room size:
- 15 W lamps are suitable for rooms with an area of 15–35 square meters.
- Devices from 36 W are intended for rooms from 40 square meters.
If you are going to carry out disinfection inside closed spaces: in a refrigerator, closet, medicine drawer, then pay attention to the size of the lamp. A compact model is best suited for this. Bulky devices are inconvenient to carry and use in such conditions.
The design and installation method of the lamp are also taken into account:
- Wall-mounted.
- Ceiling.
- Mobile or portable.
- Wall-ceiling.
When purchasing a lamp, give preference to trusted manufacturers. Do not buy devices in the market from street vendors who do not even provide a warranty on their products.
To summarize, it should be noted that bactericidal devices are used to disinfect surfaces and indoor air. They have become an effective means for disinfecting drinking water and sterilizing objects and instruments. A properly selected lamp can neutralize viruses, infectious agents, fungi, spores and mold, preventing their reproduction. To ensure that the operation of such a device does not harm human health, it is important to follow the instructions and precautions.
The sun gives life to our planet and provides a sea of ultraviolet radiation for the beauty and health of humanity. It has been noted that people living in countries where there is more natural light, due to location and climate, are happier compared, for example, to northern countries, where there can be bad weather and cloudiness for many months of the year.
More recently, by historical standards, people began to spend a huge amount of time indoors, which resulted in a lack of solar heat and a lack of ultraviolet rays. City dwellers rarely spend time in the fresh air, but progress does not stand still and responds to emerging difficulties with simple technical solutions.
An ultraviolet lamp is a device that emits radiation in a range invisible to the eye, between the X-ray and violet spectrum.
Ultraviolet lamp: benefits and harms
The radiation of a lamp or exposure to the sun is a necessary condition for the health of both humans and animals and plants; few creatures inhabiting our planet can do without this component completely.
A UV lamp, replacing natural light, promotes the production of vitamin D, the deficiency of which is known to lead to diseases such as rickets. However, vitamin D is known for another important property - it promotes the absorption of calcium by the body, and calcium, in turn, is one of the most basic elements for the functioning and growth of many human tissues and is even a protector against cancer.
Ultraviolet radiation helps get rid of pathogenic organisms that surround us all in abundance, ranging from common cold pathogens to more serious “comrades”, like Koch’s bacillus. Koch's bacillus is the causative agent of tuberculosis, the breeding ground for which are places of detention, where not only ventilation is poorly organized, but where even a ray of light does not penetrate.
The beneficial effects of UV can be observed on the skin - a bactericidal and drying effect, which helps to cope with many skin problems faster and more effectively. Typical examples are acne, fungi and dermatitis.
As already mentioned, ultraviolet rays lift your spirits, prevent depression, and charge you with optimism.
Don't expect immediate results. The beneficial effect is cumulative and weeks and months may pass before the first positive changes are noticeable to the eye.
Harm from ultraviolet lamps
Everything is good in moderation. If you do not abuse the use of such a lamp and follow the instructions, then there will be no problems. If the device is used ineptly, quite serious consequences can occur: burns (eyes and skin), exacerbation of heart disease. You can provoke the growth of epidermal cancer cells - skin cancer. Note that prolonged sunbathing also has these side effects, therefore, the lamp itself is not harmful, the harm appears only in conjunction with the human factor.
How to use an ultraviolet lamp?
Mainly, carefully read the instructions and strictly follow its recommendations, especially carefully observing the parameters for safe use.
How to choose an ultraviolet lamp?
If the question is asked which lamp to buy, ultraviolet or quartz (as a type: home solarium), then it should be taken into account that the latter can only be used after a doctor’s permission. The choice should be based on the desired beneficial effect, for example, for a preventive function, you should find a device emitting 280 - 410 nm.
The rest of the choice depends on quality indicators, the capabilities of the purchaser and the trust of the manufacturer’s brand.
Home » Benefits and harm » Quartz lamp harm and benefit
The benefits and harms of home quartzing
Quartzization is a process of treating air with ultraviolet rays to destroy bacteria, viruses and microbes. Bactericidal treatment of the room and enrichment of the air with ozone made the process relevant in the cold season. Artificial quartz does not replace sunlight, but it makes it possible to strengthen the body, increase immunity, ensure the production of vitamin D with biologically active substances, and compensate for sunlight.
The benefits of quartzing
Quartz lamps are used for general and local irradiation. For a long time they were used for intracavitary treatment and disinfection of domestic premises. It is necessary to disinfect rooms not only in hospitals and laboratories, but also at home. Home quartzing is used to treat children's rooms.
Before using quartz treatment at home, find out what the benefits and harms of the procedure are. Positive changes from quartz lamps are provided by an antibacterial effect. The benefits of quartzing are as follows:
- Prevention of colds and flu. If there is an infected person, quartzing will reduce the risk of further infection of family members.
- The condition of chronic bronchitis, adenoids and persistent runny nose is alleviated because the lamp kills bacteria.
- Treatment of otitis media or ear inflammation. Is a quick and easy way.
- Treatment of skin diseases, from psoriasis, eczema, rashes to acne.
- Toothache and stomatitis can be effectively treated with home quartz treatment.
- Relief of pain in joints and osteochondrosis during inflammatory processes.
- Prevention of rickets. The lamp is useful for families with children.
- Treatment of inflammatory processes.
When recovering from major operations, quartz treatment is used for prevention.
It is not surprising that quartzing a room has positive effects. This is due to the qualities of ultraviolet rays. By periodically turning on a quartz lamp, the air becomes sterile because there are no harmful microorganisms in it.
Harm of quartz treatment
Before purchasing and using a lamp, find out what harm quartz treatment brings to humans.
Quartz treatment can be harmful due to improper use of the device. Modern options can be turned on even if there are residents in the room. Read the instructions carefully before using the device.
The lamp will cause harm if family members suffer:
- Individual intolerance. Use the lamp carefully.
- Tumors. Using a quartz lamp can lead to accelerated tumor formation.
- High blood pressure. If you suffer from vascular problems, then do not use quartz treatment at home - the harm will be greater than the benefit.
For maximum safety of the procedure, consult your doctor. After concluding that there are no contraindications for using home quartz, feel free to start using the device. There are many benefits from the procedure, but potential harm may not appear.
How to choose lamps
When choosing a lamp, remember the variety of designs and options produced by different factories. Consider several options, compare, and then make a choice.
There are two types of quartz lamps - open and closed. The use of the first type is possible only in the absence of living organisms in the room, including flowers. Such lamps for quartzing rooms are used in hospitals, offices and laboratories.
In apartment conditions, it is preferable to use universal closed quartz lamps.
Device characteristics:
- versatility;
- closed type;
- compact size.
The device looks like a structure with tubes. The main purpose is disinfection of rooms or intracavitary irradiation.
When you purchase a lamp for home quartzing, check each tube for integrity and completeness.
How is quartzing carried out?
Use safety glasses when quartzing to protect your eyes from exposure to the rays. Touching the surface of the lamp is prohibited. In case of accidental touching, treat the area with alcohol solutions.
The instructions for the lamp indicate the exact time for home quartzing. The first times should be carried out at minimal parameters to check individual tolerance to ultraviolet radiation.
When carrying out quartz treatment at home, remember that:
- You cannot disinfect a living space if there is a patient with an elevated body temperature;
- for dry skin, consultation with a specialist before the procedure is required;
- It is prohibited to use quartz lamps as a means of tanning;
- Do not leave pets and plants in the room while quartzing;
- It is necessary to observe fire safety in the house when using a quartz lamp.
If you correctly follow the operating rules and doctor's instructions, you will fully experience the beneficial effect of a quartz lamp on the air in your apartment and improve your well-being.
polzavred.ru>
Quartz lamps for the home - benefit or harm
Using quartz lamps
It is no secret that the air we breathe in some way determines the state of our body. If you and I inhale dust, hundreds of bacteria, we shouldn’t be surprised that we feel bad. But, if you can get rid of dust using wet cleaning and avoiding carpets (find out where the dust in the house comes from) and objects that collect this dust, then you can clear the air of bacteria, viruses and microbes using a quartz lamp for the home .
About the benefits and harms of quartzing, how to choose a quartz lamp for your home and how to properly quartz a room - we will tell you about all this right now...
What is a quartz lamp used for?
A quartz lamp is a special lamp that is used to carry out the quartzization process, as a result of which the air is treated with ultraviolet rays and viruses, bacteria and microbes are destroyed. In addition, during such bactericidal treatment of the air, it is enriched with ozone, which is very useful for the cold season. However, you should not think that thanks to quartz lamps you will be able to replace sunlight. It will not happen. But to strengthen your body, increase its defenses, as well as ensure the production of vitamin D and biologically active substances, and at least somehow compensate for the lack of sunlight - a quartz lamp will cope with these tasks perfectly.
At the same time, you can use a quartz lamp both to provide targeted irradiation and for general irradiation.
Surely, those who have been in the hospital at least once will remember that the daily routine indicated the time during which the wards were quartzed.
But it is necessary to disinfect the air not only in the hospital, but also in our homes, especially in children's rooms.
The benefits of quartzing
Benefits of using quartz lamps
Considering that medical institutions actively use quartz lamps to quartz wards and rooms with increased sterility, it can be assumed that this procedure is not only necessary, but also useful. This is true. Today, experts have compiled a whole list of useful aspects of quartzing, and World Without Harm invites you to familiarize yourself with it.
So, quartzing will be useful for:
- Prophylaxis of colds and viral diseases. If one of the family members is already sick, then regular quartzing will reduce the risk of infection to other family members.
- Relief from diseases such as chronic bronchitis, adenoids, chronic runny nose, due to the fact that quartz lamps will kill bacteria that contribute to the development of the disease.
- Treatment of ear diseases, in particular otitis media.
- Treatment of stomatitis and toothache.
- For inflammatory processes in osteochondrosis, as well as to relieve pain in the joints.
- For the prevention of rickets in the case of newborn children.
- Treatment of inflammatory diseases.
- During the period of rehabilitation and recovery after serious illnesses.
Considering the quality of ultraviolet rays and the spectrum of their influence, periodically turning on quartz lamps and quartzing the room with their help will help clean the air and make it sterile, and relieve you of the presence of harmful microorganisms in it that cause dangerous diseases.
Harm from quartz lamps
Follow safety precautions when quartzing
However, in the wrong hands, quartz lamps, and even quartzing itself, as a preventive procedure, can cause more harm than good. First of all, this applies to situations when the device - a quartz lamp - is used for other purposes, and without following the recommendations in the instructions. In particular, if it says that it is not worth quartzing a room when there are people in it, it would not be appropriate to ignore this recommendation.
Also, some people may experience individual intolerance to quartz treatment. So, even if the instructions indicate that you can be in the room while it is quartzing, but you feel unwell, you should not tempt fate, it is better to leave the room while it is quartzing.
The presence of neoplasms, both malignant and benign, in the case of irradiation with a quartz lamp can lead to intensive growth of tumors. Therefore, if you have been diagnosed with a tumor or cyst, you are strictly prohibited from being in the room when it is quartzed.
People suffering from high blood pressure should also be extremely careful when using quartz lamps. The same can be said about patients with cardiovascular diseases.
Only after making sure that you have no direct contraindications to the use of quartz lamps, having studied the instructions for them, and having consulted about this with your doctor, can you begin the quartz procedure without worrying that it may be harmful to you .
How to choose a quartz lamp for your home
If you have no contraindications for using quartz lamps, and you are interested in ensuring that you and your loved ones get sick less often, you should consider purchasing your own quartz lamp for your home.
Types of quartz lamps
Today there are enough options, they differ in their appearance, but in general they can be divided into 2 main types. Quartz lamps can be open or closed.
Open quartz lamps can only be used when there are no living organisms, pets or indoor plants in the room. As a rule, it would be appropriate to install such quartz lamps in hospital wards, offices, or laboratories, where they can be turned on for a period while all staff are absent.
But for home use, closed-type quartz lamps are better suited. They can be used even if you don't plan to leave the room. You will not get any harm from quartzing with them.
What else to look for when choosing a quartz lamp for your home
Also, pay attention to the versatility of such quartz lamps, their size, and what they are intended for. Having decided on a specific model, carefully study its characteristics, read the instructions, and only after making sure that all the lamp parts are in place and the quartz lamp is fully equipped with them, make the purchase.
How to properly quartz a room
- In order for the use of quartz lamps to benefit you, follow the recommendations from the instructions for such lamps, and also do not forget that even if you have closed-type lamps, in order to protect your eyes from exposure to quartz rays, you will need special glasses.
- Avoid careless touching the surface of a heated lamp, as this can cause a severe burn; if you were not careful, carefully treat the area of contact with the lamp.
- In order to make sure that you do not suffer from individual intolerance to quartzing, the first quartzing sessions should be at minimal parameters and not long in time so that you can establish that you can tolerate ultraviolet radiation normally. In the future, adhere to the recommended quartzing times.
- If there is a person with a high temperature in the room, then it is not worth quartzing the room while the patient is in it.
- The ultraviolet rays of a quartz lamp tend to dry out the skin, and the air in the room after their use is dry. Take care of the condition of your skin by specially nourishing and moisturizing it, as well as additional air humidification, if necessary.
- And now, pay attention, a quartz lamp is not a mini solarium; with its help, you should not try to get an even chocolate tan that you will keep for a long time. Read more about the dangers of solariums and how to maintain a tan.
- Do not leave small children, animals or plants alone with operating quartz lamps.
- When operating a quartz lamp, do not forget to comply with fire safety regulations.
Video about quartz lamps for the home
Today we talked about quartz lamps for the home, their benefits and harms, how to choose the right lamps, and how to use them to quartz a room.
We will be interested to know your opinion about the benefits and harms of quartz lamps. Do you use them to disinfect rooms and air in your home?
Shevtsova Olga, World without Harm
Water, sunlight and oxygen contained in the earth’s atmosphere are the main conditions for the emergence and factors that ensure the continuation of life on our planet. At the same time, it has long been proven that the spectrum and intensity of solar radiation in the vacuum of space are unchanged, and on Earth the impact of ultraviolet radiation depends on many reasons: time of year, geographic location, altitude above sea level, thickness of the ozone layer, cloudiness and the level of concentration of natural and industrial impurities in the air.
What are ultraviolet rays
The sun emits rays in ranges visible and invisible to the human eye. The invisible spectrum includes infrared and ultraviolet rays.
Infrared radiation is electromagnetic waves with a length of 7 to 14 nm, which carry a colossal flow of thermal energy to the Earth, and therefore they are often called thermal. The share of infrared rays in solar radiation is 40%.
Ultraviolet radiation is a spectrum of electromagnetic waves, the range of which is divided conventionally into near and far ultraviolet rays. Distant or vacuum rays are completely absorbed by the upper layers of the atmosphere. Under terrestrial conditions, they are artificially generated only in vacuum chambers.
Near ultraviolet rays are divided into three subgroups of ranges:
- long – A (UVA) from 400 to 315 nm;
- medium – B (UVB) from 315 to 280 nm;
- short – C (UVC) from 280 to 100 nm.
How is ultraviolet radiation measured? Today, there are many special devices, both for domestic and professional use, that allow you to measure the frequency, intensity and magnitude of the received dose of UV rays, and thereby assess their likely harmfulness to the body.
Despite the fact that ultraviolet radiation makes up only about 10% of sunlight, it was thanks to its influence that a qualitative leap occurred in the evolutionary development of life - the emergence of organisms from water to land.
Main sources of ultraviolet radiation
The main and natural source of ultraviolet radiation is, of course, the Sun. But man has also learned to “produce ultraviolet light” using special lamp devices:
- high-pressure mercury-quartz lamps operating in the general range of UV radiation - 100-400 nm;
- vital fluorescent lamps generating wavelengths from 280 to 380 nm, with a maximum emission peak between 310 and 320 nm;
- ozone and non-ozone (with quartz glass) bactericidal lamps, 80% of ultraviolet rays of which are at a length of 185 nm.
Both ultraviolet radiation from the sun and artificial ultraviolet light have the ability to affect the chemical structure of cells of living organisms and plants, and at the moment, only some species of bacteria are known that can do without it. For everyone else, the lack of ultraviolet radiation will lead to inevitable death.
So what is the real biological effect of ultraviolet rays, what are the benefits and is there any harm from ultraviolet radiation for humans? 
The effect of ultraviolet rays on the human body
The most insidious ultraviolet radiation is short-wave ultraviolet radiation, since it destroys all types of protein molecules.
So why is terrestrial life possible and continuing on our planet? What layer of the atmosphere blocks harmful ultraviolet rays?
Living organisms are protected from hard ultraviolet radiation by the ozone layers of the stratosphere, which completely absorb rays in this range, and they simply do not reach the surface of the Earth.
Therefore, 95% of the total mass of solar ultraviolet comes from long waves (A), and approximately 5% from medium waves (B). But it’s important to clarify here. Despite the fact that there are many more long UV waves and they have great penetrating power, affecting the reticular and papillary layers of the skin, it is the 5% of medium waves that cannot penetrate beyond the epidermis that have the greatest biological impact.
It is mid-range ultraviolet radiation that intensively affects the skin, eyes, and also actively affects the functioning of the endocrine, central nervous and immune systems.
On the one hand, ultraviolet irradiation can cause:
- severe sunburn of the skin - ultraviolet erythema;
- clouding of the lens leading to blindness - cataracts;
- skin cancer – melanoma.
In addition, ultraviolet rays have a mutagenic effect and cause disruptions in the functioning of the immune system, which cause the occurrence of other oncological pathologies. 
On the other hand, it is the effect of ultraviolet radiation that has a significant impact on the metabolic processes occurring in the human body as a whole. The synthesis of melatonin and serotonin increases, the level of which has a positive effect on the functioning of the endocrine and central nervous systems. Ultraviolet light activates the production of vitamin D, which is the main component for the absorption of calcium, and also prevents the development of rickets and osteoporosis.
Ultraviolet irradiation of the skin
Skin lesions can be both structural and functional in nature, which, in turn, can be divided into:
- Acute injuries– arise due to high doses of solar radiation from mid-range rays received in a short time. These include acute photodermatosis and erythema.
- Delayed damage– occur against the background of prolonged irradiation with long-wave ultraviolet rays, the intensity of which, by the way, does not depend on the time of year or the time of daylight. These include chronic photodermatitis, photoaging of the skin or solar geroderma, ultraviolet mutagenesis and the occurrence of neoplasms: melanoma, squamous cell and basal cell skin cancer. Among the list of delayed injuries is herpes.
It is important to note that both acute and delayed damage can be caused by excessive exposure to artificial sunbathing, not wearing sunglasses, as well as by visiting solariums that use uncertified equipment and/or do not carry out special preventive calibration of ultraviolet lamps. 
Skin protection from ultraviolet radiation
If you do not abuse any “sunbathing”, then the human body will cope with protection from radiation on its own, because more than 20% is retained by a healthy epidermis. Today, protection from ultraviolet radiation of the skin comes down to the following techniques that minimize the risk of the formation of malignant neoplasms:
- limiting time spent in the sun, especially during midday summer hours;
- wearing light but closed clothing, because to receive the necessary dose that stimulates the production of vitamin D, it is not at all necessary to cover yourself with a tan;
- selection of sunscreens depending on the specific ultraviolet index characteristic of the area, time of year and day, as well as your own skin type.
Attention! For indigenous residents of central Russia, a UV index above 8 not only requires the use of active protection, but also poses a real threat to health. Radiation measurements and solar indices forecasts can be found on leading weather websites.
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the eyes
Damage to the structure of the eye cornea and lens (electro-ophthalmia) is possible with visual contact with any source of ultraviolet radiation. Despite the fact that a healthy cornea does not transmit and reflects 70% of hard ultraviolet radiation, there are many reasons that can become a source of serious diseases. Among them:
- unprotected observation of flares, solar eclipses;
- a casual glance at a star on the sea coast or in high mountains;
- photo injury from camera flash;
- observing the operation of a welding machine or neglecting safety precautions (lack of a protective helmet) when working with it;
- long-term operation of the strobe light in discos;
- violation of the rules for visiting a solarium;
- long-term stay in a room in which quartz bactericidal ozone lamps operate.
What are the first signs of electroophthalmia? Clinical symptoms, namely redness of the eye sclera and eyelids, pain when moving the eyeballs and the sensation of a foreign body in the eye, as a rule, occur 5-10 hours after the above circumstances. However, means of protection against ultraviolet radiation are available to everyone, because even ordinary glass lenses do not transmit most UV rays. 
The use of safety glasses with a special photochromic coating on the lenses, the so-called “chameleon glasses,” will be the best “household” option for eye protection. You won't have to worry about wondering what color and shade level of UV filter actually provides effective protection in specific circumstances.
And of course, if you expect eye contact with ultraviolet flashes, it is necessary to wear protective glasses in advance or use other devices that block rays harmful to the cornea and lens.
Application of ultraviolet radiation in medicine
Ultraviolet light kills fungus and other microbes in the air and on the surface of walls, ceilings, floors and objects, and after exposure to special lamps, mold is removed. People use this bactericidal property of ultraviolet light to ensure the sterility of manipulation and surgical rooms. But ultraviolet radiation in medicine is used not only to combat hospital-acquired infections.
The properties of ultraviolet radiation have found their application in a wide variety of diseases. At the same time, new techniques are emerging and constantly being improved. For example, ultraviolet blood irradiation, invented about 50 years ago, was initially used to suppress the growth of bacteria in the blood during sepsis, severe pneumonia, extensive purulent wounds and other purulent-septic pathologies.
Today, ultraviolet irradiation of blood or blood purification helps fight acute poisoning, drug overdose, furunculosis, destructive pancreatitis, obliterating atherosclerosis, ischemia, cerebral atherosclerosis, alcoholism, drug addiction, acute mental disorders and many other diseases, the list of which is constantly expanding. .
Diseases for which the use of ultraviolet radiation is indicated, and when any procedure with UV rays is harmful:
| INDICATIONS | CONTRAINDICATIONS |
| sun starvation, rickets | individual intolerance |
| wounds and ulcers | oncology |
| frostbite and burns | bleeding |
| neuralgia and myositis | hemophilia |
| psoriasis, eczema, vitiligo, erysipelas | ONMK |
| respiratory diseases | photodermatitis |
| diabetes | renal and liver failure |
| adnexitis | malaria |
| osteomyelitis, osteoporosis | hyperthyroidism |
| non-systemic rheumatic lesions | heart attacks, strokes |
In order to live without pain, people with joint damage will benefit from an ultraviolet lamp as an invaluable aid in general complex therapy.
The influence of ultraviolet radiation in rheumatoid arthritis and arthrosis, the combination of ultraviolet therapy techniques with the correct selection of biodose and a competent antibiotic regimen is a 100% guarantee of achieving a systemic health effect with a minimal drug load.
In conclusion, we note that the positive effect of ultraviolet radiation on the body and just one single procedure of ultraviolet irradiation (purification) of the blood + 2 sessions in a solarium will help a healthy person look and feel 10 years younger.