Build the right greenhouse. Building a greenhouse on your own: How? Of what? What is the price? Manufacturing technology of a gable wooden greenhouse
Every gardener can independently and correctly, and most importantly, economically and quickly produce a greenhouse structure at his dacha. Construction requires a good plan, competent step-by-step instructions and minimal experience in handling basic construction tools.
Advantages of making your own greenhouse
Currently, in the conditions of home and country vegetable growing, a huge number of varieties of greenhouse structures, both factory-produced and handicraft, are used. You can make a greenhouse of any size yourself.
What a homemade greenhouse or hothouse building will be like depends largely on the materials available to the summer resident. The undeniable advantages of this design are its low cost and the possibility of construction at a convenient time and time frame. In addition, you can make quite unusual or original, but very functional greenhouses or greenhouses with your own hands.

Winter and summer designs
It is quite possible to build both winter and summer versions yourself. However, before making a project and bringing it to life, you should understand how these types of greenhouses differ and why the design requires additional costs.
- The main difference lies in the material from which the structure is built. For example, polyethylene film is used in the manufacture of summer structures, but it is not suitable for winter ones. As a covering for a winter greenhouse, you should choose high-quality glass or translucent polycarbonate. Thin sheet polycarbonate can also be used in the manufacture of a summer greenhouse.
- If we are building a winter greenhouse, then it is very important to pay special attention to the foundation, since this part has a direct impact on the efficiency of the heating system.
- The frame of a winter greenhouse building should be as powerful and reliable as possible, and for a summer structure it can be made lighter.
These are the most important seasonal features that need to be taken into account to create a high-quality and durable greenhouse.

Main types of greenhouses
Most often, greenhouse structures are designed for the cultivation of a certain type of plant, taking into account their botanical characteristics, including lighting and temperature conditions inside.
- Single-pitched greenhouse the roof is an ideal option for creating a winter garden or greenhouse, due to the presence of an internal passage into the building. In this case, the greenhouse will be easy to maintain regardless of the time of year. It is best to install a lean-to greenhouse on the south side of the house.
- Gable greenhouses or “house” structures have proven themselves well in most regions of our country and deservedly belong to the category of the most common classic protected ground structures.

- teardrop-shaped options very durable, have excellent light transmission and do not retain snow mass on the surface, but they are difficult to install, so they are extremely rarely made independently at home.
- Dome view not only looks original, but also has some functional characteristics, including the possibility of construction in earthquake-prone areas, as well as reducing the consumption of building materials. When creating such a structure, special attention should be paid to its high-quality sealing and insulation.

- Polygonal design combines good light transmittance, attractive appearance, and high resistance to gusty winds. It should be taken into account that the installation of such a structure is quite complex and proper organization of space is necessary for uniform heating of the air masses.
- Dutch greenhouses are distinguished by reliability and durability. Sloping walls allow for maximum illumination, which has a positive effect on the yield of crops grown. In addition, the construction of such a greenhouse will be inexpensive.
Which greenhouse to choose (video)
In recent years, tunnel structures – “booths” – have become popular. This design perfectly protects plants from bad weather and gusty winds, and as a result, with minimal investment in construction, it is possible to obtain a stable and high yield. This allows us to evaluate this option as optimal for construction at the dacha with our own hands. Most often, a tunnel greenhouse is used for growing peppers and tomatoes.
Collapsible and stationary products
All greenhouses erected and used on household plots and garden plots are divided into stationary and collapsible (folding).
The folding greenhouse began to be used in home garden vegetable growing relatively recently. Its basis is a lightweight, collapsible frame, and its small dimensions allow the greenhouse to be moved to a new location if necessary. A small structure is quite cheap for summer residents, and it is not difficult to assemble it yourself.
A stationary greenhouse, on the contrary, has been used by vegetable growers for many years. The design features of such a building include the presence of a metal frame on which the covering is installed and a foundation base. Most summer residents prefer just such greenhouses, due to their reliability and durability, as well as ease of use in the structure and ease of maintenance.

Choice of material for the frame
The frame base and door must be rigid and strong, which will allow them to withstand repeated seasonal temperature fluctuations, as well as wind and a fairly large weight of snow mass. At the same time, the number of massive elements that reduce illumination should be kept to a minimum. The implementation of a collapsible structure involves the use of materials with low weight and ease of dismantling work. Today, several types of materials differing in characteristics and price are used to create the frame of greenhouses.
- Tree is the most accessible and cheapest option that does not require special skills or the use of professional equipment. The wooden frame is environmentally friendly and lightweight, but is susceptible to rotting and therefore needs to be treated with antiseptics.
- Aluminum allows you to create lightweight and durable structures with a high level of rigidity that can withstand significant loads. To connect the parts, a household riveter is used or nuts are mounted in specially drilled holes. The popularity of the option is somewhat reduced by the high price of the aluminum frame.

- Plastic has such unique characteristics as lightness and strength, as well as resistance to rotting and corrosive changes. The flexibility of the material helps to create structures of different shapes, which is especially important when constructing arched or gable greenhouses. However, it should be taken into account that the significant lightness of plastic requires mandatory attachment to the foundation or soil.
- Steel used to create a greenhouse frame quite often and requires a strip foundation. Galvanized steel frames are characterized by resistance to corrosion, which increases the service life of the greenhouse.

- Profile for drywall successfully combines such advantages as light weight and ease of installation work. As practice shows, a frame made of metal profiles turns out to be easy to use, durable, dismountable and quite affordable. Perfect for creating gable and single-pitch buildings, as well as arched structures and Mittlaider greenhouses.
- Window frames as a material for a greenhouse frame, they allow you to create a structure with acceptable thermal insulation performance in the shortest possible time and with significant savings. However, one should take into account the fragility of such a frame: the average service life, even when wood is processed, does not exceed five years.
Other materials for creating a frame are not popular in home greenhouse construction.

Types of foundation for a greenhouse
The low weight and large windage of a greenhouse structure often causes the structure to overturn under the influence of gusty winds, so the frame should be installed on the most reliable and durable foundation. The choice of foundation type depends in most cases on the weight of the structure.
- Brick foundation easy to install, quite reliable and suitable for most greenhouses. However, it should be borne in mind that the manufacture of such a foundation is a rather labor-intensive and expensive process.
- Stone base very reliable and durable. A properly executed stone foundation can support heavy metal structures made of rolled profiles and fiberglass. Most often used when creating permanent greenhouses and is not a budget option.

- Concrete foundation is one of the inexpensive and quickly erected capital foundations and involves the creation of formwork, subsequent pouring of concrete mixture and installation of rod anchors for fastening the frame.
- The simplest and most affordable option is wooden base. However, the operation of such a foundation made of boards or timber, even when treated with high-quality antiseptic compounds, is limited to five seasons, which makes its installation under a permanent frame impractical.

Greenhouse covering materials
Glass, polyethylene film or translucent cellular polycarbonate can be used as coating material. Each type of material has advantages, but is also not without its disadvantages, which must be taken into account when choosing.
- Film It is one of the cheapest and most accessible materials, but in terms of durability it is not able to compete with polycarbonate or glass. Even the highest quality film coating should be changed every three years. An arched greenhouse is most often covered with two layers of film at once, which allows us to provide plants with the most comfortable conditions for growth and development. The material has a good level of light transmittance, but under the influence of sunlight it quickly wears out and light transmittance indicators decrease. Disadvantages also include the formation of condensation on the inside of the coating.

- Glass refers to traditional materials for greenhouses and is characterized as a durable coating with a high level of light transmission and good thermal insulation. When using it to create protected ground structures, you should remember the rapid heating of glass and the significant weight of the material. In addition, it is important to consider that replacing broken or damaged glass will not be cheap.
- Polycarbonate It is a hard translucent plastic with a cellular structure. The material is characterized by durability, a high level of impact resistance and good light transmittance, as well as excellent flexibility, which makes it possible to use it in arched and tunnel-type structures.

Sometimes other covering materials are used. Some amateur vegetable growers perform a combined covering of greenhouses, in which the roof of the structure is covered with film and the side parts of the frame are glazed.
When a foundation is not needed
The foundation is the basis that provides a high level of stability, integrity, and maximum strength of the greenhouse building. However, there are types of protected ground structures that do not require the creation of a foundation. These are lightweight, portable and collapsible structures, the weight of which is insignificant, and protection against windage is achieved by attaching the greenhouse to the ground using pegs.

Schemes and drawings
Before you start building a greenhouse or greenhouse structure with your own hands, you need to correctly draw up drawings and diagrams of the structure. Greenhouse drawings can be varied. Currently, diagrams of Soviet classic wooden models, as well as modern and rational diagrams of the Mittlaider greenhouse can be found in the public domain.
The choice of a diagram and drawing of a greenhouse or greenhouse structure should be based on the requirements, features and characteristics of the materials used in the independent construction of the structure, as well as the purposes of using the structure of the protected soil in the conditions of homestead or dacha plant growing.
You can create a diagram of the future structure yourself or use ready-made options. The second option is more preferable and can reduce the cost of time and effort.

Stages of making a greenhouse with your own hands
Independent production of a greenhouse or greenhouse structure includes several sequential steps:
- choosing the type of structure;
- creation of drawings and diagrams;
- frame manufacturing;
- carrying out excavation work, including the construction of a foundation;
- installation of the supporting frame;
- installation of translucent coating.
The features of each stage depend on the type of materials used, as well as the characteristics of the structure itself, including size and season of use.

Greenhouse equipment
Creating a microclimate favorable for the growth and development of plants in most cases depends on the use of special greenhouse equipment. In order to increase the productivity of cultivated crops and the quality of the harvest, it is necessary to take care in advance of modernizing the protected ground space. Growing vegetables, berries or green crops in protected soil involves installing heating, watering, additional lighting, and ventilation systems.
- Irrigation system using drip or subsurface irrigation equipment can relieve gardeners and gardeners from heavy manual labor, and also saves time and water.
- Heating can be carried out in several ways, and the choice of equipment depends on the communications system that exists on the personal or garden plot. You can choose stove, electric or gas heating.

- Ventilation very important at all stages of growth and development of garden crops. It helps protect plants from overheating and ensures complete air exchange. For natural ventilation, open doors and vents are sufficient, and if it is necessary to increase air circulation, an exhaust or circulation fan should be installed.
- Additional lighting necessary not only for seedlings, but also for almost any garden plants cultivated in conditions of too short daylight hours. Special lamps make it possible to provide the crop with optimal comfortable illumination in early spring, as well as in winter and late autumn.
How to build a greenhouse with your own hands (video)
Today, many gardeners cannot imagine their plot without a greenhouse. And for the first time in our country, the famous scientist K. Timiryazev grew crops in this way. His merit was the construction in 1872 of a growing house for cultivated plants on the territory of the Petrovsky Academy of Sciences. This prototype of a modern greenhouse made it possible in subsequent years, right up to the present day, to develop various types of protected ground structures that make it possible to lengthen the fruiting period of plants and improve the quality and volume of the harvest.
First of all, the greenhouse is designed to protect various garden and vegetable plants from the effects of negative atmospheric factors (hail, rain, snow, wind, and so on).
A favorable atmosphere is created inside the structure, which makes it possible to grow various fruit crops, and their yield in such conditions increases several times.

As for vegetables and herbs, their harvest time comes much earlier compared to the same types if they are grown in open ground.

A huge advantage of installing greenhouses on a garden plot is the fact that an excellent harvest, and in the case of some crops more than once, can provide vegetables and herbs throughout the entire winter-spring period.
This can be very cost-effective, especially considering that the price of these products in stores during the designated period of time is quite high.

Place for installing a greenhouse
The idea of building a greenhouse with your own hands comes to the minds of many gardeners and gardeners. But before starting work, you must first become familiar with the stages of construction of this structure and, most importantly, determine the shape of the greenhouse and its location.

It must be remembered that it is not for one year. The average time of its operation can be almost ten years.

The best option in this matter would be consultation with specialists. You can get their advice either directly (if such a master is part of your social circle) or via the Internet.

- The place where the greenhouse will be installed must be level and protected from wind loads. At the same time, the sun's rays must completely cover and heat the structure.
- There is no need to set up a greenhouse in dark places, near a fence or trees.

- In the case of a winter version of the greenhouse and growing plants in the cold season, you need to take into account that snow that has fallen on the structure’s cover can prevent the penetration of sunlight. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that this does not happen and remove snow caps in a timely manner.
In addition, due to insufficient heat, light and water entering the greenhouse, it is possible to organize the supply of electricity and arrange watering in the greenhouse by installing an irrigation system.

Where to start building a greenhouse?
When building any structure, including a greenhouse, it is best to start the process with design. Create drawings of the greenhouse, reflecting its external forms and the main materials that will be used for its construction.

The structure itself can be small, with an area of approximately two by three meters and a height of two and a half meters. Or large, three by six meters in area with a similar height.

The most popular configurations used when installing greenhouses include arched and gable greenhouses. When choosing one of the species, not the least, and perhaps the most important role is played by the factor of choosing the types of crops that will be grown in the greenhouse in the future.

For example, the arched type is more suitable for planting low-growing crops, that is, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers. The gable type will contribute to better growth of tall crops (tomatoes of this type, cucumbers and flowers).
In general, creating a good greenhouse project is not difficult. If you can’t do this yourself, then the Internet always offers various standard designs for similar structures.

Selection of materials for coating and frame
One of the most common basic materials used in the construction of greenhouses is polycarbonate. Its attractiveness comes from a number of characteristics and advantages of this material in comparison with other types of materials used in the construction of similar garden structures, for example, film or glass.

Note!

Among the main characteristics are: light transmission, thermal conductivity and strength. One of the main advantages of the material is its lightness and ductility. The internal composition of polycarbonate allows sheets to be bent without the risk of destruction.

In addition, an additional advantage is the price component. Polycarbonate is considered a cheap material, which further increases its demand.

Already during the direct process of installing polycarbonate sheets, it is best to use a double sheet fastening system. Rigid and with opening. Thus, a ventilation system is formed in the greenhouse.

Having decided on the material for covering the greenhouse, you can begin selecting the frame. There is a wide selection of profiles that can be used when installing the frame system. This includes metal pipes with a round, rectangular or square cross-section.

Each designated type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Galvanized square pipes are considered the most suitable. This profile is excellently characterized by high strength, as well as the presence of galvanization, which protects the structure from corrosion.
However, plastic is gaining wide popularity among materials today. Metal pipes are in many ways inferior to plastic pipes, and many have already appreciated this.
Note!


A plastic greenhouse is a modern, high-quality structure, characterized by many positive qualities due to the special properties of the material.

Of these, it is worth noting that plastic pipes are easy to cut, glue and weld. This is an environmentally friendly material, not susceptible to corrosion, mold, and can withstand various atmospheric loads.

Considering the appearance of the greenhouse, you can choose either rigid PVC pipes for gable or single-pitch structures, or flexible PP or PVC for arched types.

In the end, whatever the choice of someone for whom a do-it-yourself pipe greenhouse is an already made decision, he can always compare and choose the most optimal frame option.

Construction of a foundation for a greenhouse
Of course, it is not worth installing the greenhouse on clean soil. A foundation is needed. Taking into account that the structure itself is of a lightweight type, but nevertheless requires stability, the base for it is made as follows:
Note!


- A trench is dug.
- A sand bedding with compaction 20 centimeters thick is installed.
- Formwork is placed along the entire perimeter of the trench on both sides.
- A reinforcing mesh is laid at the bottom of the trench over the entire area of the sand base.
- The trench is filled with concrete. The upper concrete level is equal to the width of the installed formwork board.
When performing these works, you must remember that if the greenhouse itself is installed very quickly (within one or two days), then when laying the foundation it will take almost a month for a good setting. Therefore, such work should be done in advance.

Final stage
When the structure is completely ready, it will be possible to begin the internal equipment. Placing beds and passages, determining where to lay pipes for irrigation, and so on.

Many people like to photograph their work. Some people prefer to film the entire work process, while others prefer to take pictures of the results of the work.

But with special pride, friends and acquaintances are always presented with photos of a greenhouse made with their own hands, where tomatoes, eggplants and other various vegetables and herbs are already ripening to their full potential.

DIY greenhouse photo






As a rule, planting is done in the spring, but you need to take care of the conditions, in particular we are talking about protection from low temperatures. Especially when it comes to vegetables.
Greenhouses and greenhouses do an excellent job with this task. Let's see how to make it from almost improvised materials below.
How is a greenhouse different from a greenhouse?
Before delving into the question of how to make a greenhouse, let's determine the difference between a greenhouse and a greenhouse:

- A greenhouse is used for growing seedlings and further planting them in open beds; plants can be kept in a greenhouse all year round;
- The required level of temperature in the greenhouse is maintained due to the presence of compost or manure in the soil; in the greenhouse there is an additional, third-party source of heating;
- It is possible to grow trees in a greenhouse, but this cannot be done in a greenhouse.

What types of greenhouses are there?
The greenhouse can be stationary or portable (a photo of a greenhouse at the dacha is presented below).

A stationary greenhouse can have all sorts of shapes; the most common model is the butterfly (it got its name due to the doors that open on both sides).

Portable, often in the form of a tunnel. The main material in both cases is polymer film.

From all this it follows that it is quite possible to make a greenhouse with your own hands; this is the same creative process as growing cucumbers, tomatoes, etc.

Material selection
Before we consider how to make a greenhouse with our own hands, we will deal with the issue of choosing a material.
When choosing a material, it must be taken into account that it must meet the following requirements:

- Good light transmission;
- Resistance to various types of deformation, such as strong gusts of wind;
- Easy to install and assemble the entire structure;
- Durability.

As for the materials used, the cheapest, and most importantly practical, is film, and here are its types:

- polyethylene;
- stabilized film;
- polyvinyl chloride

Covering materials include:

- agril;
- lutrasil.

In order to finally decide and understand which material is preferable, it is necessary to compare them and consider the pros and cons of each.

Glass
The advantages of glass include: it transmits approximately 94% of light, lasts a long time, and retains heat.
The disadvantages: it gets very hot in the summer, there is a heavy load on the main frame.

Film
The advantages of this material include: low cost, low weight, no foundation required.
Note!


Disadvantages: fragility, difficult to wash.

Polycarbonate
Pros: transmits light well, high level of thermal insulation, lightweight and durable.

What to use to make a greenhouse frame
The frame is a kind of base for a greenhouse; most often it is made of wood or plastic, less often of metal pipes.

Wooden frame
The main advantage is its environmental friendliness. It is also worth noting that it is very simple in terms of installation.

For installation you will need the following tools: hammer, screwdriver, saw, nails, rubber as a sealing element, wooden beams, ruler.
Note!


It is advisable to cover the wooden elements of the future structure with drying oil before the installation process.
Execution Sequence
First of all, a beam is attached to the mortgage fastening; it will then become the base. Then the main beam is placed around the perimeter of the foundation, and everything is temporarily secured with nails.

Side and corner beams are fastened diagonally with timber. The door frame is installed to the side posts. The cornice is attached to the top of the side and corner beams.

Roof
In the area of the points where the vertical beams are fixed, it is necessary to remove a beam, the length of which is 2 m. The roofing beams must be fastened at an angle of 30 degrees, they are connected to each other by a beam. In the area of the end points they must be supported by vertical guides.

The final fastening of the roof frame is done using corners and strips on self-tapping screws.

Note!

Doorway
First the door frame is attached. Do not forget that in the middle and upper parts the opening is secured with special stiffeners.

Application of metal pipes
A greenhouse, as mentioned above, can be made from metal pipes, and also with your own hands. This design is more wear-resistant.

You will need: a welding machine, a hammer, a grinder, a special attachment for working with metal (disk).
The pipe is divided into two equal parts. Tees are welded to the edges of the base pipe, and crosspieces are welded every half meter. The cut elements must be welded to the crosspieces.

Special tees are attached to the arch to secure the door pillar.

Covering the greenhouse
Once the frame is ready, you can start covering.

Film
The easiest material to use is film. It is necessary to cover the entire structure, leaving a margin of 15 cm, and then cut it off.

Polycarbonate
The front side of the polycarbonate is the one where the drawing is depicted. First you need to cut the sheets. Seal the sections with sealing tape on top and perforated tape on the bottom.

First, the polycarbonate is attached to the top, then to the sides. It is attached to the frame with a special profile, as well as rubber gaskets.

Finally, the seal and door hardware are installed.
Ventilation
In greenhouses, in order to create ventilation (ventilation), you just need to open the doors, but it is advisable to do this in warm weather.

A greenhouse is an indispensable thing for a gardener who is going to harvest a large harvest of tomatoes, cucumbers and other vegetables in the future. By approaching the design wisely and following all the instructions, everything will definitely work out.

DIY greenhouse photo

The presence of a greenhouse on a summer cottage is a common occurrence. Using different materials, you can build greenhouses of a wide variety of shapes and sizes. Work in them begins in early spring and ends in autumn. Having your own vegetables is not only economical, but also safe, since you can be confident in their quality. That is why many people have a desire to equip a winter greenhouse. You can grow vegetables and fruits in it all year round, even if it’s frosty outside.
Can an amateur summer resident build such a structure? In fact, the construction and arrangement of a winter greenhouse does not require much time and money, so you can handle the tasks yourself. In this article we will tell you how to build a winter greenhouse with your own hands, demonstrate the necessary drawings, as well as photo and video instructions.
Features and differences from a summer greenhouse
When constructing a winter greenhouse, unlike a summer greenhouse, a strong and reliable structure is made. It stands on the foundation. In addition, the winter greenhouse has a heating system. The quality and consistency of the temperature inside will depend on the latter. Every winter greenhouse must contain:
- lighting;
- heating;
- ventilation;
- watering.
The size of the greenhouse must be selected in accordance with the number of crops that will be grown. The coating material must be reliable. A simple film will not protect crops from frost and snow. It is also important to provide for the possibility of additional wall insulation.
When developing a winter greenhouse, several conditions must be met for good plant growth: light and temperature conditions, as well as air humidity.
Main types of winter greenhouses

A modern winter greenhouse can be built from various materials. Today, the construction market is filled with innovative materials. They are distinguished by increased strength, lightness and affordable price. This allows you to choose everything you need within even a small planned budget. At the preparatory stage it is necessary to plan the design. Her choice will depend solely on the plants that are planned to be grown.
The types of winter greenhouses are distinguished not only by the materials used, but also by their external forms.
- Single-pitched - wall-mounted and with an earthen fill.
- Gable - with main walls and a glazed roof.
- Polycarbonate arched.

- First of all, the parameters are calculated, since further calculations will depend on this.
- It is also necessary to take into account functionality, that is, to know in advance the features of growing crops. In modern and modernized winter greenhouses, you can grow not only vegetables and fruits, but also mushrooms, herbs, and flowers.
- The microclimate inside the structure will depend on the correct location of the greenhouse at ground level. If desired, the structure can be deepened inside and get the effect of a thermos, or construction can begin on the surface. Some people prefer to set up greenhouses in old buildings (garage or barn).
- A wide variety of architectural solutions allows you to realize any ideas and plans. You can build the structure yourself or buy a ready-made structure. You can also seek help from specialists.
Many people grow flowers of various crops for sale. When choosing exotic plants, it is necessary to calculate all costs, as well as study the requirements for the structure.

When developing a project, it is necessary to take into account the material with which the frame will be sheathed. The winter greenhouse must be durable and airtight, so for arranging the frame choose:
- tree;
- metal.
Both materials are very durable, so it is quite difficult to choose one or the other. Metal is strong and reliable, but wood is much easier to work with. In addition, the wood will not heat up in high summer temperatures. To support the weight of the entire structure, as well as the load of snow on the roof, it is necessary to use strong and thick racks.
Frame covering material:
- film;
- glass;
- cellular polycarbonate.
When choosing a film, it is necessary to sheathe the frame not in one layer, but in several. In addition, you should not use it to arrange the entire structure. Glass also has many disadvantages: heavy weight, fragility and difficulty in installation. The most suitable material for a winter greenhouse is cellular polycarbonate. The advantages include: light weight, light transmission, and ease of installation.
According to experts, the microclimate in a greenhouse made of wood is several times better than one made of metal. When choosing a tree, it must be treated with modern antiseptics and protective agents.

When choosing a site for the construction of a winter greenhouse, it is necessary to take into account three main factors:
- Light. The winter greenhouse should receive the maximum amount of sunlight. The greenhouse is best placed lengthwise from west to east.
- Wind. If the chosen location often experiences gusty and cold winds, it is necessary to consider protection. This will save on heating costs and constantly maintain an acceptable temperature and microclimate.
- Convenience. Access or passage to the greenhouse should be wide and convenient. Thanks to this, it will be very convenient to use the greenhouse for its intended purpose.
When organizing protection from strong winds, you can plant a hedge. It must be remembered that the fence must be placed at a distance of at least 10 m. The distance is calculated depending on the height of the ridge.

The most important thing in a winter greenhouse is heating. This process is the most time-consuming and complex. To organize it, the help of specialists is required. But you can do everything yourself. It is necessary to choose the right type of heating, on which the productivity of the greenhouse will depend. Today there are many ways to heat even a large area. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Sun. Affordable and cheap option. But it is not suitable for winter, since the sun's rays are not so strong and will not be able to heat. It can be combined with other heat sources.
- Biological heating. Biologically active substances decompose, resulting in the release of heat. The simplest biological substance is manure. As with the sun, this method will not be able to completely heat even a small area.
- Electricity. An affordable and popular heating method. It can be installed in any area away from home. You can use different electrical appliances for it: convectors, air heaters, infrared radiation, cable heating, heat pump and water heating.
- Air heating. It is organized at the initial stage of construction of a winter greenhouse, in particular, when pouring the foundation. With the help of heating and ventilation units, warm air is supplied to the middle and upper part of the greenhouse.
- Gas. Gas heaters are installed in the greenhouse, in which direct combustion occurs. To avoid oxygen burnout, it is necessary to provide a good ventilation system.
- Bake. An affordable and economical option involves installing a stove and heating the entire area of the winter greenhouse. Gas, wood and coal can be used as fuel. Among the disadvantages is the heating of the walls, so planting plants next to the stove is not recommended.
It is necessary to choose the type of heating individually for each specific case. You must be guided by such criteria as local climate, planned budget and plant type.
Stages of construction of a winter greenhouse

Since the construction stages and technologies completely depend on the materials and design, there is no need to talk about standards. Using an example, we will look at the construction of a winter greenhouse, which is adjacent to the house. A brick is selected for the foundation. The frame is erected from wooden beams or profile pipes. The entire structure will be covered with polycarbonate.
To create the effect of a thermos, you don’t have to go deep into the ground, but only raise the base. The depth of the foundation is 50 cm, the width is 40 cm. For convenience, it is better to make a strip foundation. Do not forget about the sand cushion or use fine gravel. The execution steps are standard and do not require any professional skills or equipment. After pouring, it is recommended to keep the foundation for a week. On hot days, the surface is moistened with water. A layer of waterproofing should be laid between the foundation and the plinth.
You can use used bricks to build the basement. If the financial side allows, then a new brick is selected. The height of the wall should be about 1 m. The thickness of the walls can be half a brick or a brick, at your own discretion. The frame is constructed from durable and pre-treated wooden beams. Anchors and dowels act as fasteners. Thus, a skeleton is installed that will be a reliable support for heavy loads. The frame for the roof must be made at an angle of 30° from the horizon.
The frame should be sheathed with polycarbonate according to the standard scheme and technology. For a good result, several conditions must be met:
- marking;
- precision cutting;
- accuracy of installation;
- use of special fasteners;
- sealing polycarbonate seams for tightness.

Several vents installed around the entire perimeter can serve as ventilation.
For greater savings, it is recommended to choose a location near your home. Thanks to this, one of the walls is already completely ready, so you don’t have to waste time, effort and money. In order for the main part of the greenhouse to be constantly warm, it is necessary to attach a vestibule at the front door. For high-quality sealing, you can use polyurethane foam and special sealants.

After all construction and sealing work has been completed in full, you can begin arrangement. So, it is necessary to supply water and electricity for lighting to the greenhouse. It is also important to take care of the shut-off valves, which will ensure a high-quality water supply.
When choosing light scattering sources, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of growing the selected crops. An equally important issue is the soil. The substrate is prepared, fertilizers and special additives (feeding) are added. They will ensure fast and proper growth of all vegetables and fruits that have been selected.

Guided by the tips provided, you can build and prepare a winter greenhouse for growing various crops in the winter in just a few days. It is enough to use all available materials and purchase missing ones. You can handle all the work alone, but it is better to have an assistant, especially when it comes to installing the skeleton of a winter greenhouse.
Video
To learn how to make heating in a winter greenhouse, watch the video:
Blueprints











Photo













When building closed ground structures, it is important not only to build a high-quality and durable frame, but also to properly think through the interior space of the room. Arranging the inside of a greenhouse involves using some planning tricks that will help you wisely use the free space to place beds and all the necessary equipment.
You will learn in this article how to set up a polycarbonate greenhouse inside and how to arrange beds for growing vegetables, herbs and other crops.
Arrangement of the greenhouse inside
To successfully grow plants in a greenhouse, it is necessary to ensure a stable indoor microclimate. To do this, it is necessary to carry out thermal insulation, install heating devices in it, and also ensure optimal levels of humidity, lighting and fresh air flow.
Transparent materials that allow sunlight to pass through are used as coverings for greenhouses. Inside the room they are converted into thermal energy. The main task is to limit the transfer of heat from the internal space to the outside. It is necessary to install devices in the building that will evenly distribute the flow of thermal energy. When arranging it, you need to use materials and devices that can absorb and accumulate thermal energy.
For these purposes, you can use ordinary building materials. For example, if you use natural stone as a floor covering, it will absorb heat during the day and release it into the space at night. Brick and concrete, which are most often used for construction, have a low ability to store heat, but if the building has walls and floors of the correct thickness, these materials will also help ensure an optimal microclimate. For example, the thickness of a concrete wall should be 200-250 mm, and a brick wall - 130-150 mm.
Other means can be used as heat storage devices:
- Water containers: their surface must be coated with dark paint so that they better absorb the sun's rays. Large barrels, old paint cans or other containers can be used as water heat accumulators.
- Priming: using ordinary soil as a heat accumulator is the simplest and cheapest way. However, the soil itself has a low ability to accumulate heat, so special mechanical devices must be used to heat it.
- Stone: it can be used as a decorative element and a heat accumulator at the same time. But for the device to operate efficiently, fans are additionally installed to uniformly heat the stones. As a rule, natural stones are laid in one row against the wall, which receives maximum sunlight. They are laid out in one row, leaving small gaps for air circulation. In addition, stones can be placed under the floor.
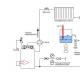
To improve the microclimate, greenhouses are equipped with additional thermal insulation. Recommendations for thermal insulation are shown in Figure 1.
 Figure 1. One of the thermal insulation options
Figure 1. One of the thermal insulation options To do this, you need to reduce the transparency of the coating by attaching the greenhouse to a residential building or using shading. In addition, to reduce heat loss they use:
- Thermal insulation of windows: It is better to install windows with double frames indoors. This will not only reduce heat loss, but also prevent the formation of condensation.
- Movable heat insulating means: Shutters, blinds, curtains or curtains can be used as such means. Advantage should be given to sliding structures to save internal space. Rigid and flexible thermal insulation materials can be used both inside and outside the building.
- Thermal insulation of the base part: It is through the floor of a protected ground structure that the most heat is lost, so the base of the building must be insulated.
It is also important to protect the structure from wind, which creates a pressure difference and leads to heat loss. Therefore, the greenhouse must be placed so that it is protected from the prevailing winds by another building, fence or hedge.
How to make beds in a polycarbonate greenhouse
Arrangement of the building inside with planning tricks first of all involves the proper placement of beds.
Note: It is better to build a greenhouse from polycarbonate, as it is a lightweight and durable material that allows you to create optimal climatic conditions inside.
To know how to make beds in a polycarbonate greenhouse, you first need to decide on the type of structure of the protected soil. They can be ground or racked, respectively, and the plants are placed either on ground beds or on special racks. At home, ground greenhouses are considered more popular.
When planning the placement of beds, it is necessary to take into account the location of the structure itself relative to the cardinal directions, the expected number and size of beds and the characteristics of the crops that will be grown indoors.
The standard arrangement of beds in a 6*3 meter greenhouse includes the following nuances(Figure 2):
- The number of beds is 2-3 pieces, depending on the width of the structure;
- The optimal width is 120 cm, since in this case the plants are easy to care for by moving along the paths;
- To have free access to all plants, you need to make not only longitudinal, but also transverse passes;
- The width of the longitudinal passage should be at least 50 cm, since in this case you can move freely along the passage with the necessary tools.
 Figure 2. Options for location of beds
Figure 2. Options for location of beds Another option that is considered convenient is that there is a wide bed in the middle and two narrow ones near the walls. This arrangement allows you to gain access to all the plants, but at the same time maintain useful soil area.
Many greenhouse owners have long appreciated the benefits of raised beds. Firstly, they save usable space, and secondly, they make caring for plants much easier, since a person does not need to bend too low to weed, water or loosen the soil.
Note: Raised beds also allow for early harvests, as the soil warms up faster and retains heat longer.
There are several options for creating raised beds(Figure 3):
- A frame is made from wooden boards into which the soil mixture is poured. To prevent wood from rotting in high humidity conditions, it must be treated with special antiseptics. The disadvantage of this method is that ants often infest the wood, and if this happens, the material will have to be changed to another.
- A raised bed can also be made from compressed polystyrene foam. It is better to take sheets 4 cm wide: they are quite durable and retain heat well.
- Asbestos-cement slabs are also often used to build high beds. They are cut into pieces and attached to metal rods. This is a durable material, but it is considered harmful, so it is better to choose only chrysolite asbestos, which is less toxic.
- Brick sides are the simplest, strongest and most durable option. For construction, you can use any bricks that will last for a long time.
 Figure 3. Arranging high beds in a greenhouse
Figure 3. Arranging high beds in a greenhouse It is better not to use slate for the construction of high beds, as it releases carcinogens into the air that are harmful to human health.
Fencing and covering paths in a greenhouse
When arranging the inside of a greenhouse, it is necessary to provide a covering and fencing for the paths so that the soil does not crumble from the beds.
 Figure 4. Arrangement of paths in the greenhouse
Figure 4. Arrangement of paths in the greenhouse For this purpose, it is best to use boards treated with special agents against rotting and fungus (Figure 4). The boards are buried in the ground so that they protrude several centimeters above the ground level. It is not recommended to make the sides high, as they will complicate the care of plants.
Soil preparation and quality
For rapid growth of crops, the soil must be more fertile than in open areas. There is no need to change the soil every year; it is enough to just add manure or compost, the amount of which is a tenth of the total amount of soil. To further saturate the soil with nutrients, add bone meal, dolomite mixture, peat and wood ash. Figure 5 outlines the procedure for preparing soil for beds in protected soil structures.
All soil components must be thoroughly mixed. Since the soil for the greenhouse contains peat, the soil will be quite porous. This mixture retains moisture well and contains a minimal amount of weed seeds and roots. Before planting and after harvesting, the soil should be fertilized with compost.
Are common soil requirements for a greenhouse include:
- The composition must include organic components with living beneficial microorganisms;
- The soil should be saturated with minerals that are easily absorbed by the root system of plants;
- Acidity should be optimal (6.5-7 pH), and the soil itself should have good air permeability and retain moisture.
Different soil mixtures have their own characteristics, and they are selected depending on the crops that will be grown indoors. For example, for seedlings you need to take hygroscopic soil, consisting of garden soil, sand and peat in equal quantities. Additionally, the beds are fertilized with compost, which is prepared using household waste or leaves. The material is placed in a wooden box, covered with earth and periodically watered. Sometimes a special nutritious compost with worms (based on a mixture of kitchen waste and seaweed meal) is prepared for protected ground structures.
 Figure 5. Preparation of soil mixture for the greenhouse
Figure 5. Preparation of soil mixture for the greenhouse Other components are also used to prepare a plant base for greenhouse soil.:
- Chicken manure concentrate. It must be prepared a year before use, as chicken manure contains too much nitrogen;
- Green mass from medicinal herbs;
- A liquid solution of soot and wood ash is used for irrigation.
In addition, during operation, mineral fertilizers are added to the soil to improve the quality of seeds and fruits.
How to prepare the soil for various vegetables and fruits
When deciding how to arrange a polycarbonate greenhouse inside, you should pay attention not only to the location of the beds, but also to the soil that will be used for growing crops.
Note: It is better to use a special soil mixture that does not contain weed seeds and bacteria, and the soil itself is well ventilated and does not retain much moisture.
For large buildings, it is not economically profitable to buy special soil for each type of vegetable, so you can prepare the soil mixture yourself.
Recipes for preparing soil for different crops are as follows::
- For tomatoes and peppers take 1 part of rotted humus, forest or garden soil and sand. The composition is thoroughly mixed and sifted through a coarse sieve. To saturate the soil with nutrients, add 100 grams of chalk or eggshells and 100 grams of ash per bucket of the finished mixture. At the end of cooking, the mixture is steamed to kill bacteria.
- For cucumbers and zucchini take 3 parts humus, 4 parts loamy soil and 3 parts peat. You can also add sawdust to the mixture. Such soil turns out to be light and quite nutritious.
In one greenhouse it is better to grow crops with similar characteristics and requirements for soil conditions. But, if this is impossible, high partitions are installed between beds with different soils.
Preparing the southern wall
During the summer, too much sunlight enters the greenhouse. This can cause overheating and death of plants, so protected ground structures must be shaded.
Note: When arranging high-quality ventilation, shading may not be used, since the flows of warm and cool air are distributed evenly. The main sign that signals the need for shading is reddening of plant leaves.
There are several types of plant protection from excess light. You can apply paint, a special protective liquid, or attach a dense material to the transparent surface. Previously, for shading, glass was coated with lime or emulsion paint diluted with water. However, this method has one significant drawback: in the fall the coating must be removed with a brush, and this is a rather labor-intensive process.
 Figure 6. Options for shading greenhouses
Figure 6. Options for shading greenhouses Modern industry produces special liquids that are quickly and easily applied, are not washed off by rain, but at the same time they can be washed off without much difficulty in the fall. The only drawback is that on cloudy days the cover cannot be removed and the plants will lack light. That is why preference should be given to special materials that, if necessary, cover the transparent part on sunny days and open on cloudy days. Such devices are called external and internal shading screens. Options for shading materials are shown in Figure 6.
Blinds are used as internal screens. They roll up easily and protect plants from direct sunlight. External screens perform the same function, but also give plants additional protection from spring frosts.
Note: External screens are more convenient to use. When installing shutters inside a greenhouse, the temperature in the room will increase, and if ornamental plants with large leaves are grown in the building, the shutters may damage them.
To prevent external shading screens from being torn off by a gust of wind, they must be securely attached to the frame. It is best to give preference to products made of wooden or plastic slats located horizontally. They are quite durable, easy to install and remove, and allow some of the sunlight that plants need to pass through. In addition, regular burlap or other dense fabric can be used as a shading screen. In some cases, light-sensitive sensors are installed on external screens to automate the shading process.
Arrangement of beds in a 3 x 6 greenhouse
In a greenhouse measuring 3*6 meters, it is best to make two beds along the walls with a central passage between them. In this case, it is desirable that the width of the passage be 50 cm, so that it is convenient to move around the room with equipment.
In some cases, it is possible to place three small beds: one central and two side ones. This option reduces the usable area, but allows you to grow crops with different requirements for soil conditions.
Organization of space inside
The sun's rays penetrating into the building create a greenhouse effect. The air inside stagnates and becomes an ideal environment for the development of pathogens and pests. Therefore, it is important to equip the greenhouse with a ventilation system and devices to maintain humidity.
Note: When installing automatic ventilation systems, their operation must be coordinated with the operation of heating devices and shading devices.
To ventilate protected ground shelters, ventilation is most often used using open windows, vents and doors (Figure 7). Basic requirements for arrangement include:
- In order for enough air to get inside, the area of windows and vents should be less than 20% of the total area of the structure. Ventilation is very beneficial for plants, especially for seedlings that will later be transferred to open ground. About two weeks before transplantation, ventilation is carried out not only during the day, but also at night. However, you need to make sure that there are no drafts inside.
- It is best to place windows under the ceiling. The air, heating up, rises and exits through the open window. As a rule, for small greenhouses, two vents located on opposite sides of the roof are sufficient. But for large structures, ventilation holes must be installed every two meters, and if alpine plants are grown in the greenhouse, a continuous row of windows will be installed on both sides of the roof.
- To speed up ventilation, additionally install side windows located at the level of the shelving or slightly above ground level. They can be made ordinary, but it is better to install blinds that will allow air to pass through and disperse. The side openings are located on both sides so that during strong winds only those located on the leeward side can be opened.
 Figure 7. Ventilation using open vents
Figure 7. Ventilation using open vents When arranging ventilation, it is important to remember that for normal development plants need not only oxygen, but also carbon dioxide, which is formed in the soil and compost. In small rooms, the ventilation regime is often disrupted due to thermal energy savings. The best solution to this problem would be to install automatic ventilation systems. As a rule, they are installed in large industrial greenhouses, where opening and closing windows manually is difficult.
There are others heat ventilation methods c (Figure 8):
- Installation of fans allows for constant air circulation. It is important to select devices of suitable power depending on the size of the building. The smaller the fan, the higher above ground level it is located. For example, in small greenhouses they usually install only one fan, hanging it above the door.
- Ventilation pipes They draw fresh air in and send warm air out. It is recommended to make the southern side of the pipe from glass, and the internal parts from metal. This will improve the heating of the pipe and increase traction.
 Figure 8. Installation of fans in the greenhouse
Figure 8. Installation of fans in the greenhouse In small greenhouses, it is enough to equip a ventilation pipe, and if additional ventilation is necessary, simply open the front door (Figure 9). You can learn more about greenhouse ventilation from the video.
 Figure 9. Greenhouse ventilation using pipes and automatic systems
Figure 9. Greenhouse ventilation using pipes and automatic systems In addition to natural heating, additional heating devices are also used in closed ground structures.
Note: It is better to install several types of heating at once in order to maximize the use of the greenhouse.
 Figure 10. Organization of solar heating of protected ground structures
Figure 10. Organization of solar heating of protected ground structures Figure 10 shows a diagram that can be used to provide natural solar heating in a greenhouse. The type of heating devices is selected individually depending on the plants that will be grown. For example, tropical and potted crops require more intense heating than vegetables.
There are several types of heating:
- Using a solar system: The device consists of a solar collector and a heat accumulator. The collector is a glass-covered box with a heating coil inside. An ordinary barrel with a layer of thermal insulation can serve as a heat accumulator. A radiator is installed next to the collector and battery, and all parts of the solar installation are connected to each other by insulated pipes.
- Biofuel: Most often, manure is used for heating. As organic fertilizers decompose, they generate heat. Household compost, garbage or wood waste (bark, sawdust) can be used as biofuel. Biofuel can be burned in special stoves or placed on beds after removing the top layer of soil. After burning biofuel in the beds, the soil needs to be leveled and after a few days, when the ground has warmed up, you can start planting.
- Water heating(Figure 11): a boiler is installed in the vestibule of the greenhouse, the water in which is heated with gas, electricity or solid fuel. When selecting a boiler, key attention should be paid to the power of the device, since the heating area will depend on it. Hot water from the boiler is distributed throughout the building through pipes located around the perimeter. They need to be equipped with regulators to reduce or increase the temperature in the building.
- Gas heating: Such heating devices are distinguished by high technology and reliability. However, during the combustion process, natural gas emits too much carbon dioxide, so additional hoods are installed. In addition, heating a greenhouse with gas is expensive and is not always suitable for small farms.
- in this case, a stove with a chimney is installed in the building. Despite the fact that ovens take up a lot of space, they are able to maintain a stable temperature for a long time. As a rule, stove heating is installed in the vestibule so as not to pollute the internal space of the protected ground structure with soot and smoke. Figure 12 shows drawings for installing stove heating with your own hands.
In addition, the greenhouse can be heated with electric heating devices: portable fans with an air heating function or static units. In this case, it is necessary to equip the building with a fan to circulate heated air.
 Figure 11. Arrangement of water heating
Figure 11. Arrangement of water heating Operating a greenhouse in spring and fall can be quite successful with natural light, but when the days become cloudier, especially in winter, additional lighting fixtures need to be installed.
In addition, each crop needs a certain lighting intensity. The most light-loving plants are tomatoes, cucumbers, lettuce and peppers. Green crops, onions and biennial plants are less demanding of light. Plant growth is negatively affected by both too little and too much sun.
 Figure 12. Drawings for arranging furnace heating
Figure 12. Drawings for arranging furnace heating To enhance natural lighting, a blank wall can be painted a light color or covered with reflective material. To reduce light, the building is usually shaded.
An important condition for growing plants is maintaining an optimal level of humidity. To determine its level, special devices, hygrographs or psychrometers, which you can make yourself, are hung in the building. To do this, you need two thermometers and a special table that provides data for determining the humidity level. Examples for making a psychrometer are shown in Figure 13.
 Figure 13. Psychometers for measuring humidity
Figure 13. Psychometers for measuring humidity Two thermometers are placed side by side on one board. The ball of one of them should be dry, and the second should be constantly wet. To do this, just wrap the thermometer in gauze and place it in a container of boiled water. Every 10 minutes, instrument readings are recorded and compared using a table. For example, if the temperature difference is 4 degrees, then the humidity corresponds to 57%. Also, using the difference in indicators, you can determine the probability of frost.
In order for a door or window to open automatically, a special device is installed - a “door pump”. It does not consume electricity, but you need to select the device according to the weight and design of the door or window, since if the pump is weak, the door may jam (Figure 14).
 Figure 14. Automatic greenhouse ventilation system
Figure 14. Automatic greenhouse ventilation system The door pump operates based on the hydraulic cylinder principle. A special wax is poured into the working body (pipe) of the device, which expands when heated and opens the frame. When the temperature drops, the wax cools, decreases in volume and the door closes. Sometimes gas (for example, freon) is used for these purposes.
A thermal drive can be used as an automatic ventilation system. This is a device consisting of two plates that have different coefficients of linear expansion (for example, plexiglass and metal). The plates are held together at a certain temperature, and when it gets too hot or cold inside, the plates bend in a certain direction. Examples of drawings for manufacturing a thermal drive are shown in Figure 15.
Note: If you visit the greenhouse site only on weekends, it makes sense to install an automatic temperature control device in the building. The device is a regulator consisting of a sector body, a rotary valve, an inspection cover and a pusher link. An old soccer ball camera is attached to the sector body (tank) and connected to the tank with a regular rubber hose.
An air tank is installed in the building. When the temperature inside exceeds 25 degrees, the air in the tank expands and fills the chamber. When filled, it activates the valve and push link, which opens the window. As the temperature drops, the reverse process occurs and the transom closes under its own weight. Since such a device is mechanical, it does not require special care for successful operation and operates completely autonomously. From the video you will learn how to make an automatic window lifter for a greenhouse with your own hands.
 Figure 15. Drawings of a thermal drive for a greenhouse
Figure 15. Drawings of a thermal drive for a greenhouse When installing wiring for lighting or heating a greenhouse, extreme care must be taken due to the high humidity inside the building.
Note: If the greenhouse is a separate building, the cable from it is taken out, and if it is attached to the house, the electrical wiring is connected to a common power supply system.
The wires inside can be laid underground or pulled from above using poles. If the electrical wiring will be laid underground, you need to choose areas where excavation work will not be carried out. Otherwise, the cable may be damaged. In addition, the wiring must be insulated with pieces of tiles or wooden planks.
The average trench depth for laying cables is 0.75 m, but if the wires will pass under paths or lawns where excavation is not being carried out, the depth can be reduced. Under no circumstances should trenches intersect with drainage channels.
Note: After laying the electrical wiring, be sure to draw up a plan and indicate the location and depth of the trenches. In the future, this will help not to touch the wiring if you decide to redevelop the site.
If the electrical wiring cable will be carried through the air, you need to dig strong poles into the ground and attach the wires to thick wire. It is advisable to lay them so that tree branches do not touch the wires and damage them. Additionally, you need to install a control panel with separate sockets, fuses or switches. Connecting electrical appliances is carried out in the usual way, but it is better to choose rubber plugs rather than plastic ones.
 Figure 16. Lamps for installing artificial lighting in greenhouses
Figure 16. Lamps for installing artificial lighting in greenhouses After the installation of electricity, the possibilities for improving the lighting and heating of the building are significantly expanded. For artificial lighting, it is better to use fluorescent or regular lamps, as they are resistant to high humidity (Figure 16).
Note: The best are considered to be fluorescent lamps, the light of which is close to daylight, and during operation they do not heat the air and cannot cause burns to plants.
Conventional incandescent lamps are placed at some distance from the plants. But this can cause the stems to stretch. In addition, such lamps consume a lot of energy and quickly fail.
Photosynthetic and ultraviolet lamps can be used as an additional light source. They not only accelerate the growth of crops, but also destroy insect pests. For example, to speed up the growth of seedlings in the spring, you can hang frames with several rows of lamps above the racks. In addition, reflective screens can be hung on the walls, and boxes and glasses with seedlings should be periodically rotated so that the stems do not bend or stretch.
Watering plants in greenhouses is carried out in a special way, since insufficient or excessive moisture can lead to the death of plants. For example, crops in pots are watered, filling the entire space between the soil and the top of the pot with water. This is the only way to moisturize the entire root system.
The intensity of watering depends on many indicators: season, type of plant and soil. For example, large crops with branched roots are watered up to twice a day in summer, and only 1-2 times a week in winter and in a state of vegetative dormancy.
You can determine the lack of moisture by looking at the lower leaves. If the plant does not have enough water, they droop. In addition, dry soil is paler in color than wet soil. But if plastic pots are used for growing, the soil may be dry on top and wet inside, so you need to periodically probe the soil with your finger. If peat serves as the basis for the earthen mixture, when it dries out, the soil begins to lag behind the edges of the pot. After watering, the soil will expand and fill the empty space.
To water the beds, use a watering can or hose with a sprinkler. Thanks to this, the water is distributed evenly, and the lower leaves are not covered with a layer of dried earth. When watering the beds, you need to accurately determine whether the soil is evenly moistened. To do this, you need to dig a hole 15 cm deep, and if the soil in it is dry, continue watering.
 Figure 17. Installation diagram of drip irrigation in a greenhouse
Figure 17. Installation diagram of drip irrigation in a greenhouse In large greenhouses, watering is usually automated. For crops grown in pots, a capillary system is installed. A film is placed at the bottom of the rack, covered with a layer of sand and regularly moistened using an automatic device (an inverted bottle attached to a holder). Pots are placed on top of the sand so that the drainage holes are completely immersed in the sand.
But the most common is the drip irrigation system. In this case, water is supplied through pipes, and watering is carried out using special holes located near each bush or pot. Timers are sometimes installed on such a system so that watering turns on automatically at a certain time (Figure 17).
Note: When using drip irrigation, plants need to be inspected periodically. the fact is that such a system introduces moisture regardless of the individual needs of the crops, so some of them may be moistened too much.
To prevent plants from dying, they must be periodically watered by hand if drip irrigation does not provide the necessary moisture, or temporarily disconnected from the system if the soil is too moist. The author of the video will tell you how to properly organize drip irrigation in a greenhouse.
Selecting material for shelving
Shelf-type greenhouses are more suitable for growing seedlings or seedlings. In such a room, the entire internal space is occupied by racks and shelves.
When choosing a material, you should take into account all the advantages and disadvantages of each type:
- Tree- an organic material that has a beneficial effect on the growth of crops and has good thermal insulation. Since wood rots quickly in conditions of high humidity, it must be treated with antiseptics and periodically tinted during use.
- Metal is considered a more durable material for building shelving. In addition, it is much lighter than wood, and the finished structure can be easily disassembled and reassembled.
It is best to use structures made of aluminum: it is lightweight, durable and does not deteriorate when exposed to moisture.
Installation of shelving
There is no strict size of shelving for a greenhouse, since each owner creates structures according to his height and height of the greenhouse. The width of the racks depends on the zone in which they will be located: in the center or on the sides.
There are certain requirements for the construction and installation of shelving(Figure 18):
- The width of the central structures should not exceed one and a half meters;
- Wall racks are no more than 90 cm wide;
- The increased width of the racks makes them inconvenient to use, since it will be difficult for a person to reach distant plants.
A passage up to half a meter wide must be left between the racks so that you can freely walk along it with equipment or drive a wheelbarrow.
Construction of a quarantine zone
Arranging a quarantine zone is another important condition for the proper distribution of space inside the greenhouse.
A quarantine zone is necessary to protect crops from diseases and pests. It contains boxes and pots with new plants that were purchased in stores or other farms. New plants are transferred to the quarantine zone, and if after 10-14 days signs of disease or pest damage do not appear, the crop is transferred to the rest of the plants.
 Figure 18. Options for arranging shelving in a greenhouse
Figure 18. Options for arranging shelving in a greenhouse The quarantine zone may be small. The optimal size is considered to be sufficient to accommodate 4 pots of seedlings. It is advisable to enclose the area with glass, for example, install an old aquarium with a tight lid on one of the shelves.
Proper division of space
When planning the division of space in a greenhouse, calculate in advance the number of crops and beds, the need for the location of equipment (heating systems, drip irrigation, etc.), and also provide space for equipment.
If crops with different requirements for temperature and humidity conditions will be grown in the same greenhouse, the internal space is divided with plastic film, glass or a piece of polycarbonate. A similar division is practiced when growing cucumbers and tomatoes at the same time.
Arrangement of the adjacent vestibule
It is advisable to build a vestibule near the entrance to the greenhouse for several reasons. Firstly, this room can be used to store equipment. Secondly, the air gap in the vestibule will create the necessary smooth transition between warm air inside the greenhouse and cool air outside.
In the vestibule you can put a cabinet or rack for storing fertilizers, fertilizers and chemicals. To prevent pets from getting inside, it is better to lock the cabinet with a key.