Do-it-yourself installation of electrical and electrical wiring. Do-it-yourself electrical wiring in an apartment: wiring repair and installation from scratch. Wall work
What should be the electrical wiring diagram in a private house under construction? How to properly distribute wires throughout all rooms? I will tell you what wiring cross-sections modern electrical appliances need, and how to provide protection against electric shock and short circuits. And as a bonus, I’ll clearly explain how to connect a voltage stabilizer and generator to your home panel.
Required elements
Let's start with the main thing - with protective elements. The electrical panel in your home should include:
| Image | Element |
 |
General switch or circuit breaker at the input, breaking the phase and neutral wires. |
 |
Residual current device(RCD), which is triggered when current leaks through damaged insulation, when a person or pet touches the terminals or wires. Its sensitivity should allow it to respond to a leakage current of 30 mA. |
 |
Slot machines for certain consumer groups (sockets in a separate room, lighting, boiler, electric stove, etc.). The circuit breaker is placed on the phase wire and trips when the rated current is exceeded. Its task is to prevent overheating and fire of the wiring. |
The tripping current of the circuit breaker must minimally exceed the calculated peak load on the wiring section. Let's say, for a circuit with a peak power consumption of 5 kW, it is worth choosing a 25 ampere machine (which at a voltage of 220 volts corresponds to a power of 25x220 = 5500 W).
Grounding is provided with a separate terminal block for all sockets and metal housings of electrical appliances. The ground wire must not be interrupted by switches or connectors. The source of ground can be the body of the shield (if there is ground at the input) or electrodes buried in the ground.
Accessories
The following are often connected to the panel:
- Voltage regulator, providing stable parameters of the current supplying household appliances in case of serious deviations from the nominal value at the input.

It makes sense to install a stabilizer only on certain groups of consumers who are most sensitive to power (this includes televisions, computers, audio equipment, refrigerators, etc.). Powerful heating devices (boilers and electric stoves) operate over a wide voltage range and, when it drops, only proportionally reduce power consumption.
- Generator, allowing you to switch to autonomous power supply when the lights are turned off with minimal time.
What will be the wiring diagram in each of these cases?
Stabilizer

The stabilizer is connected to the phase wire break. Zero remains common with the meter and consumers. The stabilizer housing is connected to a common ground.
Generator

The actual power switching is ensured by a reversing switch having three operating positions:
- The consumer is powered from the input;
- The consumer is disconnected from both current sources;
- The consumer is powered by the generator.

The signal lamp (LS-47) is needed to indicate the mains voltage. It will allow you to notice the moment the light turns on without the help of measuring instruments (multimeter or indicator screwdriver).
Normative documents
How to install wiring in a house taking into account all the requirements of regulatory documentation? The source of information for us will be SNiP 31-02 (design of engineering systems of cottages) and the manual of the Ministry of Construction of Russia, which supplements its requirements, released in 1997 and again regulating the construction of engineering systems of single-family houses.
For the convenience of the reader, I will bring together the relevant and most important points of both documents for us.
- Installation of electrical wiring in a private house must be carried out with a grounding loop. The ground must be separate: the neutral wire cannot be used as it;

- Power limit determined by the owner of the house. The minimum values are 5.5 kW in a house without electric heating systems and electric stoves and 8 kW if they are present. If the total area of the house exceeds 60 square meters, the minimum input power increases by one percent for each square meter of area in excess of 60;
The local administration may limit the maximum power depending on the condition of the local power grid and the capabilities of the substation.
- Open wiring can be performed directly on walls and other building structures, as well as in boxes and baseboards with cable ducts. In this case, open wires without protective tubes or ducts are mounted on building structures at a height of at least 2 meters;
- Hidden wiring Can be mounted at any height in ceilings and walls. We allow its installation in structures made of flammable materials;

- For wiring installation Only copper wires can be used. With the same cross-section as aluminum, they provide almost twice the resistivity, which means less heating at high currents;
- Wires and cables in protective sheaths can be passed through walls without bushings and pipes. The output of the unsheathed input cable through external walls is carried out in a plastic tube;
The pipe is installed with a slope towards the street to prevent leakage through the wire into the house.

- Electrical wiring in the house should not experience mechanical stress in places of branches and connections. All wire connections are insulated, and the thickness of the insulation should not be less than the thickness of the insulation of a solid wire;
- At connection points hidden wiring to sockets, junction boxes, switches and lamps, the wire must have at least a 5-centimeter reserve length. The supply will be useful when replacing fittings or repairing wiring;
- If the wiring goes from a dry room to a damp one(shower room, toilet, etc.), all connections are installed from the dry room side. There should be no junction boxes in the bathroom;
- Recommended installation height sockets - 80-100 cm, switches - 1.5 meters from the floor level;
In my opinion, it is much more convenient to adhere to European standards: 90 cm for switches and 25 cm for sockets. Low-lying sockets will allow you to get rid of household appliance wires hanging untidy on the walls, and switches will be accessible even to a child who has recently started walking.

- In a dacha made of timber or logs, in a frame house and on a wooden In the attic, do-it-yourself electrical wiring is done in a metal pipe (steel, copper or corrugated stainless steel). Even if a short circuit occurs, it will not cause a fire: before the pipe has time to heat up to a dangerous temperature, the machine will turn off the power to the circuit;

- Switches are set to phase. Zero does not open;
- When distributing one group line to several outlets, the ground branches off to each of them(either in the junction box or in the socket housing). It is impossible to connect the ground in series to several sockets;

- Metal enclosures in damp areas lamps and other electrical appliances must be grounded. If the lamp is hung on a metal hook, it must be insulated from the body (for example, with a plastic shell) so that in the event of a breakdown on the metal parts of the lamp, a phase does not occur on the entire reinforcement of the reinforced concrete structures of the house;
However: a device with a two-pin plug belonging to electrical safety class zero can be connected to an outlet without grounding, only to zero and phase. In this case, the installation of electrical wiring must be carried out with an RCD on the corresponding line: it will turn off the power in the event of leaks accompanying electric shock to a person or animal.
- If the sockets in the apartment or house are installed at a height accessible to children, they need to be protected with lids or plugs;

- Hidden wiring should not be placed on chimneys and heating panels with an operating temperature above 35 degrees: vinyl insulation of the wiring has limited heat resistance and softens when heated;
- Wires must not cross. The reason is the same: during peak currents, the insulation at the intersection may overheat;
- Switches placed at the entrance to the room, from the side of the door handle.
A number of document requirements specifically stipulate electrical installation in rooms with high humidity:
- If possible, wiring should be routed to adjacent, dry rooms. The lamps are placed on the wall closest to the input;
- For lighting with incandescent lamps, lamps with housings made of dielectric materials (plastic, ceramics, etc.) should be used.

What should the wire cross-section be? SNiP 31-02 specifies only lower limits:
- Copper group lines - not less than 1 mm2;
- Aluminum group lines - not less than 2.5 mm2;
- Copper risers and circuits to which the meter is connected are at least 2.5 mm2;
- The same risers and chains, but aluminum - at least 4 square millimeters.
First, examples of a cottage wiring diagram.



Now - some practical tips on how to do electrical wiring in the house.
Wires
I recommend making connections to the meter and input using single-wire copper wire VVG with a cross-section of at least 4 square millimeters per core with an input power of up to 10 kW and 6 mm2 with an input power of 10 - 15 kW.
In other areas the following are used:
- For wiring sockets - VVG 3x2.5 mm2;
- For lighting distribution - VVG 3x1.5 mm2.

It is better not to use stranded wire: its price is slightly higher than that of single-wire wire, and it provides a smaller area of electrical contact on the terminal blocks.
In general, the cross-section of hidden wiring is calculated as 1 square millimeter of copper per 8 amperes of peak current, open - 1 mm 2 per 10 A.
Connections
Do-it-yourself electricians are most easily mounted on brass blocks: they reliably connect the ends of the wires and, unlike sleeves and welding, leave the connection detachable. If necessary, you can connect an additional socket to the distribution box at any time.

Wiring
In my opinion, it is most convenient to lay the wiring in a baseboard with a cable duct. Why? Here are the arguments:
- Installation of wiring in this case practically does not involve dirty work. In the worst case, you will have to drill a series of holes for dowel-screws securing the baseboard;
- The wiring remains accessible for repair, and there is no need to open the walls to replace a section of it;
- If you need to connect an additional socket, it will not require much effort: you just need to strip the wire and install three blocks on it (zero, ground and phase), making a branch.

Conclusion
Now you know what the wiring diagram might look like and how to install it correctly. As always, the video in this article will provide you with additional materials. I look forward to your comments and additions to it. Good luck, comrades!
Electricity is a serious and responsible matter. If you are going to do all the work yourself, you need to do everything very carefully and diligently. Proper wiring in a private home is a guarantee of safety, because according to statistics, 70% of fires occur due to electrical faults. If you are not confident in your abilities, it is better to entrust the work to proven specialists.
Action plan
Electrical wiring in a private house is done before finishing work begins. The frame of the house is out, the walls and roof are ready - it's time to start work. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- Determination of the input type - single-phase (220 V) or three-phase (380 V).
- Development of a scheme, calculation of the capacity of the planned equipment, submission of documents and receipt of the project. Here it must be said that the technical specifications will not always determine your declared power; most likely they will allocate no more than 5 kW.
- Selection of components and components, purchase of meters, machines, cables, etc.
- . Performed by a specialized organization, you need to decide on the type - overhead or underground, install an input machine and a counter in the right place.
- Install electricity into the house.
- Laying cables inside the house, connecting sockets and switches.
- Ground loop design and its connection.
- Testing the system and obtaining a certificate.
- Electrical connection and operation.
This is only a general plan; each case has its own nuances and features, but you need to start by obtaining the technical conditions for connecting to the electrical network and the project. To do this, you need to decide on the type of input and the planned power consumption. It must be remembered that the preparation of documents can take six months, so it is better to submit them even before the start of construction: two years are given to fulfill the technical conditions. During this time, you will probably be able to build a wall on which you can put a machine and a counter.
How many phases
A private house can be supplied with single-phase voltage (220 V) or three-phase (380 V). According to energy consumption standards for a private house, the maximum consumption per house for a single-phase network can be 10-15 kW, for a three-phase network - 15 kW.

So what's the difference? The fact is that powerful electrical appliances can be directly connected to a three-phase network - electric stoves or heating boilers, ovens and similar equipment. However, the input requirements and wiring of the 380V network are much stricter: higher voltage, greater chance of serious injury. Therefore, if your house is no more than 100 square meters, and you do not think of heating it with electricity, you are better off using 220 V.
Making a plan and receiving a project
Having decided on the type of input, you can begin to develop a plan for electrifying your home. Take a scale plan of the house, and draw where the equipment will be located, figure out where to place the sockets and switches. In this case, you need to take into account where any large-sized furniture will be located, and where it can be rearranged, so that sockets and switches are not placed in these areas.
All lighting fixtures will need to be drawn on the plan: chandeliers, sconces, floor lamps, lamps. Some of them will need switches, some will need sockets. Then you will need to figure out which devices in each room will need to be turned on. For example, in the kitchen there is a lot of equipment that works constantly. It definitely needs sockets. There is also equipment that turns on periodically. All this is plotted on the plan, and the optimal location of the switching points is determined. The same approach applies to each of the rooms.

Determination of total power
Having decided approximately what equipment will be installed in your home, add up its power. The average power can be taken from the table: there is probably no technology yet. Moreover, where there are, take into account starting loads (they are much higher). Add about 20% of the reserve to the found amount. The result will be the required power. You indicate it in papers submitted to obtain permission to connect electricity to the site. If you are given the stated power, you will be very lucky, but you should not hope for it. Most likely, you will have to invest in the standard 5 kW - the most common electricity limit for a private home.

Breakdown of consumers into groups
All these consumers (this is the term of professionals) - lamps, spotlights, switches, sockets - are divided into groups. A separate branch runs electrics to lighting fixtures. Usually one is enough, but this is not a rule; it may be more convenient or expedient to make two branches - for each wing of the house or for each floor - depending on the type and configuration of the building. The lighting of the basement, utility rooms, as well as the light on the street stands out in a separate group.
Then the sockets are divided into groups. How many you can “put” on one wire depends on the diameter of the wire used, but not very much - three to five, no more. It is better to allocate a separate power supply line for connecting each powerful device: this is more reliable from the point of view of fire safety, and will contribute to a longer operation of the devices.
As a result, you may have three to seven lines going to the kitchen - this is where the equipment is most abundant and powerful too: for an electric boiler and electric stove, separate lines are absolutely needed. It is better to “plant” the refrigerator, microwave, electric oven, and washing machine separately. Not so powerful blender, food processor, etc. can be included in one line.

There are usually two to four lines going into the rooms: in a modern home and in any room there is something to plug into the electrical network. One line will go to lighting. On the second there will be sockets into which you will need to plug in your computer, router, TV, and phone charger. All of them are not very powerful and can be combined into one group. If you intend to install an air conditioner or turn on an electric heater, you will need separate lines.
If a private house is small - a dacha, for example, then there may be two or three groups: one for all lighting fixtures, the second for the street and the third for all internal sockets. In general, the number of groups is an individual matter and depends most of all on the size of the house and the amount of electrical equipment in it.

Based on the number of groups received, the number of machines on the distribution panel in the house is determined: to the received number of groups, add two to four for development (suddenly you forgot something important, or you need to turn on something new powerful, divide a group that is too large or far apart into two, etc.). The number of machines in it is also selected based on the number of groups: there is a separate machine for each group. If a private house is large - on several floors, it makes sense to install more powerful machines on each floor, and connect group machines to them.
Where to put the shield
The installation location of the electrical panel is not regulated by regulations. There are only restrictions regarding the distance from the pipelines; it must be at a distance of at least 1 meter. Any pipes are taken into account: water supply, heating, sewerage, internal drains, gas pipelines and even gas meters.
There are no restrictions on premises. Many people place the panel in: since it’s a technical room, it makes sense to collect all communications here. The receiving authorities do not make any claims. Sometimes it is more convenient to place the shield near the front door. If the protection class meets the requirements, there should be no claims.
Selection of cables and components
Today's standard wiring diagram for a private house includes two circuit breakers. One - input - is installed before the meter, usually on the street. It and the meter are sealed upon commissioning. The second RCD machine is placed in the house in front of the panel. The operation (shutdown) current of these devices is selected so that the circuit breaker installed in the house is turned off first (its current value is slightly less). Then, in the event of an emergency, you will not need to crawl under the roof.

If the estimated load is less than 15 kW, the circuit is standard - RCD + automatic circuit breaker, meter and then division into groups. For higher power consumption, it will be necessary to install a transformer; its parameters and the parameters of all equipment will be indicated in the project.
Recently, when connecting a private house to the power grid, they are required to install a meter and a machine on the street. This requirement is not supported by law; it is simply easier for the electricity service to control consumption. If you want, you can fight, if not, choose a meter and machine in a case with increased dust and moisture protection - a protection class of at least IP-55. For installation inside a building, the protection must be less - IP-44, and accordingly the price will be lower.
Cable selection
For electrical wiring in a private home, it is better to use cables rather than wires. Their insulation is at least twice as good, therefore the laying requirements are not so stringent, and they are safer to use. All internal wiring in a private house must be done with. Previously, there were no such requirements, but now many electrical appliances have three-pin plugs and require grounding for safe operation. Therefore, the cable must be three-core.
In electrical cables, the cores are made of copper or aluminum. Although aluminum is cheaper, it is used less often: it is rigid, more likely to break, and more difficult to work with. If you install electrical wiring in a private home yourself and lack experience, this can become a problem. In addition, it cannot be used inside wooden houses at all.
Determination of core cross-section
Once you have decided on the material, you can select the diameter of the cable cores. This is done depending on the planned load on the line according to the table.

Calculation of electrical wiring - the selection of the cross-section of the cable cores is carried out according to this table
The cross-section of the core is selected according to the current or power of all consumers connected to one circuit breaker. This is where your home electrification plan, where you have outlined consumer groups, will come in handy once again. You calculate the sum of the currents or powers of all devices and select the desired cross-section of the cores according to the table.
How to use the table? If you decide to lay copper wires, the input voltage is 220 V, then the left part, the corresponding column, is suitable for internal wiring. The found power of all consumers connected to the group will be compared (it is easier to find and calculate). In the part where we are talking about copper wires laid in trays, voids, channels, in the “220 V” column, find the nearest higher value. Follow this line to the right to the column “Section, sq. mm". The number indicated here will be the required core size. From conductors of this diameter it will be necessary to make electrical wiring from the machine to sockets or switches.
In order not to get confused when counting and laying, designate wires of the same diameter on the plan with a certain color (write it down so as not to forget what color you designated what). After the diameter has been determined for all consumer groups, the length of the required cables for each size is calculated, and a margin of 20-25% is added to the found figures. You have calculated the wiring for your home.
Shell type selection
There are certain requirements for the type of sheath only when laying electrical wiring in wooden houses: it is recommended to use triple (NYM) or double () cable insulation. In houses of less flammable materials, any insulation can be used. The main thing is that it is intact, without cracks, sagging or other damage. If you want to play it safe, you can use conductors with enhanced protection. This makes sense in rooms with high humidity (kitchen, bathroom, swimming pool, bathhouse, etc.).
Selection of sockets and switches
For some powerful devices, sockets are selected according to the maximum (starting) current. For other low-power consumers they are standard. You need to know that they exist:
- External - when the body sticks out from the wall. They are easier to install: a backing is attached to the wall, and a socket is attached to it on top. But few people use such models now, even at their dachas. The reason is aesthetic: not the most attractive sight.
- Internal. A recess is made in the wall for the electrical part, and an installation box is installed and walled up in it. The electrical part of the socket or switch is inserted inside this box.
It is indoor electrical sockets and switches that are most often used today. They are decorated in different styles and painted in different colors. They are selected mainly to match the finish, and if this is not possible, they are installed in white.
Read how to connect pass-through switches (turn on/off lights from two or more places).
DIY wiring
Modern construction trends provide for hidden wiring. It can be laid in specially made grooves in the walls - grooves. After laying and securing the cables, they are covered with putty, comparing them with the surface of the rest of the wall. If the erected walls will then be lined with sheet materials - plasterboard, gypsum plasterboard, etc., then grooves are not needed. The cables are laid in the gap between the wall and the finish, but in this case - only in corrugated sleeves. The shell with laid cables is attached with clamps to the structural elements.

When installing, you need to remember that the internal electrical wiring of a private house is done according to all the rules and recommendations. This is the only way to guarantee safety. The basic rules are:
- laying wiring only vertically and horizontally, no rounded corners or beveled routes;
- all connections must be made in ;
- horizontal transitions must be at a height of at least 2.5 meters, from which the cable runs down to the socket or switch.
A detailed route plan, similar to the one in the photo above, must be saved. It will come in handy during repairs or wiring upgrades. You will need to check with him if somewhere nearby you need to ditch or make a hole or hammer a nail. The main task is not to get caught in the cable.
A large percentage of electrical wiring problems come from poor wire connections. They can be done in several ways:

Still, the most reliable connection methods are welding and soldering. If it is possible to make the connection like this, you can assume that you will not have problems. At least with connections.
Installing electrical wiring in a house with your own hands requires careful fulfillment of all requirements. This is a guarantee of your privacy and the safety of your private property.
After the wires from the machine to the connection point of the socket or switch are laid, they are checked for integrity with a tester - the wires are connected to each other, checking the integrity of the conductors, and each individually to the ground - checking that the insulation is not damaged anywhere. If the cable is not damaged, proceed with the installation of the socket or switch. Once connected, everything is checked again with a tester. Then they can be started on the appropriate machine. Moreover, it is advisable to sign the machine immediately: it will be easier to navigate.
After finishing the electrical wiring throughout the house and checking everything yourself, they call electrical laboratory specialists. They check the condition of the conductors and insulation, measure grounding and zero, and based on the results they give you a test report (protocol). Without it you will not be given permission to put into operation.
Electricity is a serious and responsible matter. If you are going to do all the work yourself, you need to do everything very carefully and diligently. Proper wiring in a private home is a guarantee of safety, because according to statistics, 70% of fires occur due to electrical faults. If you are not confident in your abilities, it is better to entrust the work to proven specialists.
Action plan
Electrical wiring in a private house is done before finishing work begins. The frame of the house is out, the walls and roof are ready - it's time to start work. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- Determination of input type - single-phase (220 V) or three-phase (380 V).
- Development of a scheme, calculation of the capacity of the planned equipment, submission of documents and receipt of the project. Here it must be said that the technical specifications will not always determine your declared power; most likely they will allocate no more than 5 kW.
- Selection of components and components, purchase of meters, machines, cables, etc.
- Input of electrics from the pole into the house. Performed by a specialized organization, you need to decide on the type - overhead or underground, install an input machine and a counter in the right place.
- Install the panel, bring electricity into the house.
- Laying cables inside the house, connecting sockets and switches.
- Ground loop design and its connection.
- Testing the system and obtaining a certificate.
- Electrical connection and operation.
This is only a general plan; each case has its own nuances and features, but you need to start by obtaining the technical conditions for connecting to the electrical network and the project. To do this, you need to decide on the type of input and the planned power consumption. It must be remembered that the preparation of documents can take six months, so it is better to submit them even before the start of construction: two years are given to fulfill the technical conditions. During this time, you will probably be able to build a wall on which you can put a machine and a counter.
How many phases
A private house can be supplied with single-phase voltage (220 V) or three-phase (380 V). According to energy consumption standards for a private house, the maximum consumption per house for a single-phase network can be 10-15 kW, for a three-phase network - 15 kW.
 Three-phase input is needed only when you need to connect powerful equipment operating from a 380 V network
Three-phase input is needed only when you need to connect powerful equipment operating from a 380 V network So what's the difference? The fact is that powerful electrical appliances can be directly connected to a three-phase network - electric stoves or heating boilers, ovens and similar equipment. However, the input requirements and wiring of the 380V network are much stricter: higher voltage, greater chance of serious injury. Therefore, if your house is no more than 100 square meters, and you do not think of heating it with electricity, you are better off using 220 V.
Making a plan and receiving a project
Having decided on the type of input, you can begin to develop a plan for electrifying your home. Take a scale plan of the house, and draw where the equipment will be located, figure out where to place the sockets and switches. In this case, you need to take into account where any large-sized furniture will be located, and where it can be rearranged, so that sockets and switches are not placed in these areas.
All lighting fixtures will need to be drawn on the plan: chandeliers, sconces, floor lamps, lamps. Some of them will need switches, some will need sockets. Then you will need to figure out which devices in each room will need to be turned on.
For example, in the kitchen there is a lot of equipment that works constantly. It definitely needs sockets. There is also equipment that turns on periodically. All this is plotted on the plan, and the optimal location of the switching points is determined. The same approach applies to each of the rooms.
 The result of designing electrical wiring in a private house. You should also get a similar diagram.
The result of designing electrical wiring in a private house. You should also get a similar diagram. Determination of total power
Having decided approximately what equipment will be installed in your home, add up its power. The average power can be taken from the table: there is probably no technology yet. Moreover, where there are, take into account starting loads (they are much higher). Add about 20% of the reserve to the found amount. The result will be the required power.
You indicate it in papers submitted to obtain permission to connect electricity to the site. If you are given the stated power, you will be very lucky, but you should not hope for it. Most likely you will have to invest in the standard 5 kW - the most common electricity limit for a private home.
 Average power values of devices for calculating the total load on the electrical wiring of a private house with your own hands
Average power values of devices for calculating the total load on the electrical wiring of a private house with your own hands Breakdown of consumers into groups
All these consumers (this is the term of professionals) - lamps, spotlights, switches, sockets - are divided into groups. A separate branch runs electrics to lighting fixtures. Usually one is enough, but this is not a rule; it may be more convenient or expedient to make two branches - for each wing of the house or for each floor - depending on the type and configuration of the building. The lighting of the basement, utility rooms, as well as the light on the street stands out in a separate group.
Then the sockets are divided into groups. How much you can “put” on one wire depends on the diameter of the wire used, but not very much - three to five, no more. It is better to allocate a separate power supply line for connecting each powerful device: this is more reliable from the point of view of fire safety, and will contribute to a longer operation of the devices.
As a result, you may have three to seven lines running into the kitchen - this is where the equipment is most abundant and powerful too: for an electric boiler and electric stove, separate lines are absolutely needed. It is better to “plant” the refrigerator, microwave, electric oven, and washing machine separately. Not so powerful blender, food processor, etc. can be included in one line.
 Designing electrical wiring in a private house: counting the number of groups and planning what to connect where
Designing electrical wiring in a private house: counting the number of groups and planning what to connect where There are usually two to four lines going into the rooms: in a modern home and in any room there is something to plug into the electrical network. One line will go to lighting. On the second there will be sockets into which you will need to plug in your computer, router, TV, and phone charger. All of them are not very powerful and can be combined into one group. If you intend to install an air conditioner or turn on an electric heater, you will need separate lines.
If a private house is small - a dacha, for example, then there may be two or three groups: one for all lighting fixtures, the second for the street and the third for all internal sockets. In general, the number of groups is an individual matter and depends most of all on the size of the house and the amount of electrical equipment in it.
 The wiring plan can be quite small if the house is small
The wiring plan can be quite small if the house is small Based on the number of groups received, the number of machines on the distribution panel in the house is determined: to the received number of groups, add two to four for development (suddenly you forgot something important, or you need to turn on something new powerful, divide a group that is too large or far apart into two, etc.).
The distribution panel and the number of machines in it are selected based on the number of groups: there is a separate machine for each group. If a private house is large - on several floors, it makes sense to install more powerful machines on each floor, and connect group machines to them.
Where to put the shield
The installation location of the shield is not regulated by regulations. There are only restrictions regarding the distance from pipelines; it must be at a distance of at least 1 meter. Any pipes are taken into account: water supply, heating, sewerage, internal drains, gas pipelines and even gas meters.
There are no restrictions on premises. Many people install a panel in the boiler room: since it’s a technical room, it makes sense to collect all communications here. The receiving authorities do not make any claims. Sometimes it is more convenient to place the shield near the front door. If the protection class meets the requirements, there should be no claims.
Selection of cables and components
Today's standard wiring diagram for a private house includes two circuit breakers. One - input - is installed before the meter, usually on the street. It and the meter are sealed upon commissioning. The second RCD machine is placed in the house in front of the panel.
The operation (shutdown) current of these devices is selected so that the circuit breaker installed in the house is turned off first (its current value is slightly less). Then, in the event of an emergency, you will not need to crawl under the roof.
 Typical wiring diagram for a private house: there can be many different groups
Typical wiring diagram for a private house: there can be many different groups If the design load is less than 15 kW, the input circuit breaker is set to 25 A. The meter is selected accordingly. For higher power consumption, it will be necessary to install a transformer; its parameters and the parameters of all equipment will be indicated in the project.
Recently, when connecting a private house to the power grid, they are required to install a meter and a machine on the street. This requirement is not supported by law; it is simply easier for the electricity service to control consumption. If you want, you can fight, if not, choose a meter and machine in a case with increased dust and moisture protection - a protection class of at least IP-55. For installation inside a building, the protection must be less - IP-44, and accordingly the price will be lower.
Cable selection
For electrical wiring in a private home, it is better to use cables rather than wires. Their insulation is at least twice as good, therefore the laying requirements are not so stringent, and they are safer to use. All internal wiring in a private home must be made with protective grounding. Previously, there were no such requirements, but now many electrical appliances have three-pin plugs and require grounding for safe operation. Therefore, the cable must be three-core.
In electrical cables, the cores are made of copper or aluminum. Although aluminum is cheaper, it is used less often: it is rigid, more likely to break, and more difficult to work with. If you install electrical wiring in a private home yourself and lack experience, this can become a problem. In addition, it cannot be used inside wooden houses at all.
Determination of core cross-section
Once you have decided on the material, you can select the diameter of the cable cores. This is done depending on the planned load on the line according to the table.
 Calculation of electrical wiring - the selection of the cross-section of the cable cores is carried out according to this table
Calculation of electrical wiring - the selection of the cross-section of the cable cores is carried out according to this table The cross-section of the core is selected according to the current or power of all consumers connected to one circuit breaker. This is where your home electrification plan, where you have outlined consumer groups, will come in handy once again. You calculate the sum of the currents or powers of all devices and select the desired cross-section of the cores according to the table.
How to use the table? If you decide to lay copper wires, the input voltage is 220 V, then the left part, the corresponding column, is suitable for internal wiring. The found power of all consumers connected to the group will be compared (it is easier to find and calculate).
In the part where we are talking about copper wires laid in trays, voids, channels, in the “220 V” column, find the nearest higher value. Follow this line to the right to the column “Section, sq. mm". The number indicated here will be the required core size. From conductors of this diameter it will be necessary to make electrical wiring from the machine to sockets or switches.
In order not to get confused when counting and laying, designate wires of the same diameter on the plan with a certain color (write it down so as not to forget what color you designated what). After the diameter has been determined for all consumer groups, the length of the required cables for each size is calculated, and a margin of 20-25% is added to the found figures. You have calculated the wiring for your home.
Shell type selection
There are certain requirements for the type of sheath only when laying electrical wiring in wooden houses: it is recommended to use triple (NYM) or double (VVG) cable insulation. In houses of less flammable materials, any insulation can be used.
The main thing is that it is intact, without cracks, sagging or other damage. If you want to play it safe, you can use conductors with enhanced protection. This makes sense in rooms with high humidity (kitchen, bathroom, swimming pool, bathhouse, etc.).
Selection of sockets and switches
For some powerful devices, sockets are selected according to the maximum (starting) current. For other low-power consumers they are standard. You need to know that they exist:
- External - when the body sticks out from the wall. They are easier to install: a backing is attached to the wall, and a socket is attached to it on top. But few people use such models now, even at their dachas. The reason is aesthetic: not the most attractive sight.
- Internal. A recess is made in the wall for the electrical part, and an installation box is installed and walled up in it. The electrical part of the socket or switch is inserted inside this box.
It is indoor electrical sockets and switches that are most often used today. They are decorated in different styles and painted in different colors. They are selected mainly to match the finish, and if this is not possible, they are installed in white.
DIY wiring
Modern construction trends provide for hidden wiring. It can be laid in specially made grooves in the walls - grooves. After laying and securing the cables, they are covered with putty, comparing them with the surface of the rest of the wall.
If the erected walls will then be lined with sheet materials - plasterboard, gypsum plasterboard, etc., then grooves are not needed. The cables are laid in the gap between the wall and the finish, but in this case - only in corrugated sleeves. The shell with laid cables is attached with clamps to the structural elements.
 How should internal wiring be laid? In a private home, when installing it yourself, you must follow all the rules
How should internal wiring be laid? In a private home, when installing it yourself, you must follow all the rules When installing, you need to remember that the internal electrical wiring of a private house is done according to all the rules and recommendations. This is the only way to guarantee safety. The basic rules are:
- laying wiring only vertically and horizontally, no rounded corners or beveled routes;
- all connections must be made in installation junction boxes;
- horizontal transitions must be at a height of at least 2.5 meters, from which the cable runs down to the socket or switch.
A detailed route plan, similar to the one in the photo above, must be saved. It will come in handy during repairs or wiring upgrades. You will need to check with him if somewhere nearby you need to ditch or make a hole or hammer a nail. The main task is not to get caught in the cable.
Wire connection methods
A large percentage of electrical wiring problems come from poor wire connections. They can be done in several ways:
- Twisting. Only metals that are homogeneous or do not enter into a chemical reaction can combine in this way. It is strictly forbidden to twist copper and aluminum. In other cases, the length of bare conductors must be at least 40 mm. The two wires are connected to each other as tightly as possible, the turns are laid one next to the other. The connection is wrapped on top with electrical tape and/or packed with heat-shrink tubing. If you want the contact to be 100% and losses to be minimal, do not be too lazy to solder the twist. In general, according to modern standards, this type of wire connection is considered unreliable.
- Connection via terminal box with screw terminals. The housing is made of heat-resistant plastic and contains metal terminals that are tightened with screws. The conductor, stripped of insulation, is inserted into the socket and secured with a screw or a screwdriver. This type of connection is the most reliable.
- Connecting blocks with springs. In these devices, contact is provided by a spring. A bare conductor is inserted into the socket and clamped by a spring. Still, the most reliable connection methods are welding and soldering. If it is possible to make the connection like this, you can assume that you will not have problems. At least with connections.
- Installing electrical wiring in a house with your own hands requires careful fulfillment of all requirements. This is a guarantee of your private security and the safety of your private property. After the wires from the machine to the connection point of the socket or switch are laid, they are checked for integrity with a tester - the wires are connected to each other, checking the integrity of the conductors, and each individually to the ground - checking The insulation is not damaged anywhere. If the cable is not damaged, proceed with the installation of the socket or switch. Once connected, everything is checked again with a tester. Then they can be started on the appropriate machine. Moreover, it is advisable to sign the machine immediately: it will be easier to navigate. After finishing the electrical wiring throughout the house and checking everything yourself, they call electrical laboratory specialists. They check the condition of the conductors and insulation, measure grounding and zero, and based on the results they give you a test report (protocol). Without it you will not be given permission to put into operation.
Reading time ≈ 13 minutes
Everyone knows well what electrical wiring is in their home, but not everyone understands how to do it with their own hands, using diagrams and calculations. But it does not always take many years of study and practice to complete any work, no matter how complex. Sometimes it is enough to concentrate and be extremely attentive, without losing sight of various nuances. It will be the same this time - if you follow all the instructions received in this article, then everything will work out for you.
Installation of a home power supply panel
Before you begin work on wiring and laying electrical wires and cables, you should familiarize yourself with some important provisions, without which high-quality and safe installation is simply impossible. This includes several positions, knowing which you can choose the right wire, install protection and provide for force majeure situations.
Section of cores of cables and wires

Difference between cable and wire
A novice electrician, first of all, needs to distinguish a wire from a cable, since one or the other may be needed. A wire is one insulated or non-insulated strand, while a cable consists of several insulated strands enclosed in a sheath (see photo above). But if we talk about the cross-section, it makes absolutely no difference whether it is a wire or a cable in front of you. Below is a table of cross-sections of copper and aluminum conductors for different voltages - this is the private sector, so you may need not only ≈220V, but also ≈380V. And I also want to clarify, since many people believe that electrical appliances indicate the power they can produce with watts or kilowatts, but this is not a speaker or laptop speaker! Here in W and kW the power consumption is shown, according to which and.
| Section, mm 2 | Copper | Section, mm 2 | Aluminum | ||||||
| ≈220V | ≈380V | ≈220V | ≈380V | ||||||
| A | kW | A | kW | A | kW | A | kW | ||
| 1,5 | 19 | 4,1 | 16 | 10,5 | 2,5 | 22 | 4,4 | 19 | 12,5 |
| 2,5 | 27 | 5,9 | 25 | 16,5 | 4 | 28 | 6,1 | 23 | 15,1 |
| 4 | 38 | 8,3 | 30 | 19,8 | 6 | 36 | 7,9 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 6 | 46 | 10,1 | 40 | 26,4 | 10 | 50 | 11 | 39 | 25,7 |
| 10 | 70 | 15,4 | 50 | 33 | 16 | 60 | 13,2 | 55 | 36,3 |
| 16 | 85 | 18,7 | 75 | 49,5 | 25 | 85 | 18,7 | 770 | 46,2 |
| 25 | 115 | 25,3 | 90 | 59,4 | 35 | 100 | 22 | 85 | 56,1 |
Note. I would, of course, recommend using copper wiring, but different situations happen in life, especially since the house may be old, and you are not going to change some areas. In this case, you just need to check whether the cross-section of the wires corresponds to the power consumption of electrical appliances.
Selection of core cross-section depending on current strength
You may have a wire or cable at home that you want to use, but you don’t know its cross-section, since it has been lying around for a long time or you didn’t buy it at all. Everything is simple here: the section is the area, therefore, S = πr 2. For example, the core diameter is 2 mm, which means S=πr 2 =3.1415*1 2 =3.1415, that is, the cross-section in this case can be determined as 3 mm, but this is a conditional calculation, without reference to a specific wire or cable.
For private houses and apartments, as a rule, the following wires and cables are used:
- PVS – Wire in Vinyl Sheath Connecting;
- VVGng – Vinyl-Vinyl Bare (without special insulation) does not burn (melts);
- PPV – Flat Wire Vinyl insulation (copper);
- APPV – Aluminum Wire Flat Vinyl insulation.

Solid (left) and stranded (right) wires
There are single-core and stranded wires and cables, and on this occasion there are disagreements regarding their choice, that is, which one is better, but everything is simple here. If laying is done in a groove or a fixed cable channel, then it is better to choose a single-wire conductor, but if some movement of the wire is possible, then choose a multi-wire one.

This means that now it is clear which wire can withstand how much, but in practice it looks a little more varied, since different areas may have different loads, so let’s consider such calculations using a conditional example. Let's take the kitchen and estimate how many electrical appliances can be connected there at the same time:
- Oven (electric oven) – 2 kW.
- Mobile phone charging – 0.025 kW.
- Air conditioning – 3 kW.
- Coffee maker – 3 kW.
- Freezer – 0.7 kW.
- Mixer – 0.18 kW.
- Incandescent lamp – 0.02 kW.
The total is: 2+0.025+3+3++0.7+0.18+0.02=8.925 kW
This means that the cross-section of the common wire that will have to withstand such a load, according to the table, must be at least 6 mm 2. This is exactly the wire that should be suitable for the kitchen dose and, although no one will turn on all the appliances at the same time, any normal electrician will make the calculation precisely on this basis. Now in new houses or in new homes they don’t use it at all, and all wiring is done from one power supply panel, and if the house is large, then two such panels are installed, for example, on the first and second floor. But, be that as it may, a cable must be suitable for the switchboard, the cross-section of which can withstand the power consumption of all simultaneously switched on devices. As a rule, Energy Network issues an order regarding the cross-section of the wire that is suitable for the electric meter from the power line. If you use the same cross-section to connect the shield, you can’t go wrong (most often it’s copper 10 mm 2 for copper).

Copper and aluminum conductors are spliced only through blocks
In reality, everything does not always look the way we would like, and in cases where the wiring in a house is partially replaced, it is usually necessary to splice copper with aluminum. This can be called an “explosive mixture”, since these two metals are incompatible and oxidation, loss of contact, and then complete destruction of the aluminum core begins very quickly. Splicing is only permissible through blocks - you cannot make any twists, even if they are well soldered!
What else you need to know when laying electrical wires

Residual current device (RCD) single-phase
When installing or replacing electrical wiring in your home, and if you do it yourself, then in 99% of cases the diagram will also be drawn up by you, that is, this indicates complete awareness of the location of all electrical appliances. This is necessary for the distribution of protective modules that are needed by such devices as a pumping station, an oven, a microwave oven, an automatic washing machine, a dishwasher and an electric water heater (boiler). That is, the connection of such devices, or the installation of sockets for connecting them, will be carried out through an RCD or residual current device. Such protection, at the slightest leak on the housing, simultaneously disconnects the zero and the phase, so that in the event of a short circuit, a person will not feel even a slight tingling sensation.
RCDs are installed after the electrical appliance connection panel, and in some cases, units such as a home pumping station, automatic washing machine, dishwasher and electric water heater are connected from a separate panel, but this depends on several factors - location, aesthetics, desire owner and so on. Currently, there are RCDs on sale paired with a differential circuit breaker, but this does not increase safety, and I simply do not see any other advantages, so I will refrain from recommending the purchase of such a device.
Now about the circuit breakers on the power supply panel. As a rule, representatives of the local power grid standardize power consumption for private homes. Everything is simple here - if they install it themselves or instruct you to install an electric meter on the street for ease of access for inspectors, then they will install the machines and seal them. If, for example, they install 20A circuit breakers (C20) at the meter, then there is simply no point in installing more powerful ones on the internal switchboard - in such situations you can install similar fuses, or 16A ones.
Note. Someone may have a completely reasonable question about the advisability of installing a wire with a cross-section designed for heavy loads, they say, they still limit it. Yes, at the moment this may not be practical, but the situation can always change and the local distribution zone has the right to lift these restrictions.
Grounding

Standard plug with the ability to ground the device
Most modern electrical appliances are manufactured with the possibility of grounding them, and some of them are simply impossible to operate without this function - “they give you an electric shock.” Whether a particular device needs grounding can be determined even without its passport, by looking at the plug - if there is a metal spring between the pins, then this is a grounding contact. For private houses, there are at least five engineering developments of grounding systems, these are TN-C, TN-S, TN-C-S, TT and IT, but all this is complex and confusing, so in the private sector such schemes are considered in one or two cases out of a hundred There are two simpler options that ensure your safety and do not require any engineering tabs - just compliance with basic requirements.

Closed circuit in the form of a triangle
A closed grounding loop is made in the form of an equilateral triangle, where the distance between the corners (pins) is 100-120 cm, but more is possible. The depth of the lower part of the contour should be 200-300 cm (the denser the soil, the shallower the depth), but in any case, the entire contour is recessed underground 30-50 cm from the surface. To do this, use smooth or ribbed reinforcement ø 10-14 mm - the thinner the rod, the easier it is to drive it into the ground. The contour is welded together with steel wire ø 5-6 mm and bolts are welded to each corner. It is possible, of course, only to one corner, but if the grounding wire is screwed along the entire perimeter, then in the event of a break in the steel wire (due to corrosion), the contact will still remain and the circuit will be complete.

Linear ground loop
To make a linear grounding loop, you will need the same reinforcement, which is driven into the ground under the same conditions. In this picture we see that the immersion depth is 150-250 cm, that is, half a meter less than for a closed triangular contour, but in fact this does not change anything. The fact is that the deeper the reinforcement is, the tighter its compression will be, therefore, the contact will improve.
Below you can watch a video about how you can drive a long steel rod into the ground without preliminary drilling. Only in our case, it is first better to dig a trench or pit 30-50 cm deep, and then drive in the reinforcement, so that after connecting it will be possible to hide the circuit underground.
How to drive long reinforcement into the ground without drilling a well
Stages of wiring electrical wires and cables
Next, you can learn how to install electrical wiring in a house with your own hands - these are step-by-step steps and some diagrams that may be useful. Perhaps this approach to work will seem somewhat bureaucratic to you, but there are rules for the construction of electrical installations or PUE, which are immutable instructions that can sometimes save the life of a person who has climbed into the wrong place. The fact is that every point of these Rules is written on someone’s injury or even life, so breaking them not only makes no sense, but is simply tantamount to balancing over an abyss on a rotten rope.
Marking the route in the house plan or on the walls

All routes must be either strictly vertical or strictly horizontal
The purpose of any electrical wiring of wires and cables is to deliver power to the points of consumption by any devices and devices. But at the same time, the laid routes should not interfere with the installation of other accessories used in the room, for example, wall cabinets, paintings or mirrors. In order not to accidentally break the wire when drilling a wall, all routes are laid in a strictly vertical or strictly horizontal direction - this is noted either when designing a house, or simply on the walls if this is a replacement wiring. All sockets and switches are connected vertically. If there are several sockets at the same level along the perimeter of the room, and you do not want to insert each of them into the panel, this is normal, but you should not parallel them with one horizontal wire. It is better to set the dose at the ceiling, raise the connection vertically and place all the wires horizontally in this dose, where there will be a parallel connection with a connection to the common power wire.
Note. We have already talked about choosing the required wire cross-section, so there is no point in creating a special section for this in the step-by-step instructions.
Drilling and scoring walls
If the house does not involve installing plasterboard on the walls or suspended ceilings of any type, then all wiring is laid in grooves or under a layer of plaster. In the second case, everything is somewhat simpler - the wire or cable is nailed to the wall with clips, and the top is covered with a layer of plaster or starting putty. This option is very convenient and does not require laying the wiring in a cable channel - neither straight nor corrugated.

Chasing walls for electrical wiring
It’s another matter if there is already wiring on the walls but not yet installed - it has to be recessed into the grooves, and chiseling them is not always easy, but it is always dusty work. To do this, two parallel lines with a depth of at least 2-4 cm are cut on the wall with a grinder and a diamond-coated disk, and the distance between them depends on the number of wires being laid. Then, with a chisel in impact mode, a strip is knocked out between the two cuts, forming a groove for laying. The holes for the socket boxes are made with a Pobedit hole cutter with a diameter of 60 mm. A passage through the wall for any wires and cables is made with a Pobedit drill of the required diameter (usually such passages are needed for two parallel sockets in different rooms and then a drill ø 6-8 mm is used).
Electrical wiring installation

Laying electrical wiring in grooves
If you run all the cables through grooves, then they will have to be fixed somehow for convenience so that they do not fall out until they are completely sealed with plaster or putty. Here again, you can use clips, but given the width of the groove, this is, at a minimum, inconvenient and, at a maximum, impossible. Therefore, they are spot-fixed with alabaster - namely alabaster, and not with gypsum or polymer putty. The fact is that hardening of the putty takes a relatively long time, but alabaster hardens in a matter of minutes, but in order for it to hold the wire in the groove, 30 seconds is enough.
Schemes are a bonus
At the end I want to leave two connection diagrams: a double switch for the chandelier and a pass-through switch for the corridor.

Connection diagram for a chandelier via a double switch

Pass-through switch diagram (can be assembled without a junction box)
Conclusion
I talked about the basic principles of how to do electrical wiring in a private house with your own hands, but these are only principles, since the specific situation and the diagram, among other things, are determined according to the configuration of the building. But if you understand the essence, you can easily apply this knowledge in your own home.
Due to the need to power the home with electrical energy, it is necessary to install an electrical network indoors. For this purpose, electrical wiring and other elements for connecting, switching and lighting the home are laid. Since this procedure does not require special training, anyone can perform it independently. But first you need to figure out how to install electrical wiring in a house yourself, what stages it consists of, and what needs to be taken into account.
Stages of installing electrical wiring in a house
The entire process can be divided into several stages, the sequence of which will ensure a high-quality result and save time on performing the relevant work. The following installation stages are distinguished:
- Determining the installation method - external or external installation of the cable;
- Drawing up a power supply diagram for the premises;
- Transferring the drawn up diagram directly to the walls;
- Selection of the most suitable elements and materials for installation;
- Preparatory work on processing walls and other structures for installation of electrical wiring, installation of lighting groups, circuit breakers and others;
- The installation work itself;
- Obtaining permission from the power supply organization to connect to its networks, if it is necessary to form a new connection point (if you are replacing the electrical wiring with a new one, this procedure is not required).
Now take a closer look at each of the stages in practice.
Which installation method should I choose?
Of the existing options for laying the cable route, there are two installation methods in relation to wires - internal and external electrical wiring. Internal wiring means that the cable lines are located inside the walls. External electrical wiring is installed on the walls from the outside, and it can be done either with wires or with means of protecting the cable from mechanical damage, for example, cable channels in which the conductor is located.
Advantages and disadvantages of internal lining.
The advantages of hidden electrical wiring include greater reliability and durability due to the inability to cause damage during normal operation. Such electrical wiring requires lower financial costs for armored wires and components for their installation. In addition, hidden installation does not make any changes to the interior of the room.
The disadvantages of internal electrical wiring include labor-intensive preparatory work for producing grooves and poor maintainability in the event of any damage.
Advantages and disadvantages of external gasket.
The advantages of open wiring include a much simpler preparatory process and speed of installation of electrical wiring. During operation, it is easier to repair or change the wiring diagram.
The disadvantages of external electrical wiring are a much greater susceptibility to mechanical damage and an impact on the overall appearance of the interior of the room.
How to create a wiring diagram?
An electrical wiring diagram helps identify switches, lamps, and electrical wiring lines. Therefore, when drawing it up, you need to take into account the connection diagram of electrical appliances in the house. For example, for home electrical wiring, the location of sockets near the TV, electric stove, bed, etc. will be relevant.
Figure 1: Example of wiring diagram in a house
According to the graphical representation method, two-dimensional and three-dimensional wiring diagrams are divided. The first option is the simplest, as it does not require the use of graphic editors and other programs. To do this, take the plan of your own tenant and, on a copy of it, mark the connection points and the number of sockets for each room, wires, switches and electrical wiring lines.
A 3D model is a much more labor-intensive process, but is a great help when creating an electrical project. When, according to a completed assignment, the relevant specialists implement such a project (they are building walls, performing electrical wiring and other electrical installation work).
Rules for installing electrical wiring according to the PUE
When determining the location of wiring and installation of individual elements, you should be guided by the requirements of the PUE. Regarding electrical wiring and the rules for its installation in the PUE, Chapter 2.1 is highlighted. Therefore, the following requirements must be met for the wiring diagram:
- All lines must be installed exclusively in a vertical or horizontal plane, turns are made at an angle of 90º. It is strictly forbidden to shorten the distance diagonally or run wires along a curve.
- In relation to the structural elements of the room, horizontal lines cannot be closer than 20 cm to the ceiling or floor. Vertical lines should be located at a distance of no closer than 10 cm from door and window openings and corners.
- Sockets must be located at a distance of 80 to 100 cm from the floor in accordance with clause 6.6.30 of the PUE; in some situations, this value can vary up to 150 cm. If metal structures (radiators, pipes, stoves) are located near the socket, it is prohibited to bring them closer connection point more than 50 cm.
- Separate requirements are imposed on the arrangement of sockets, switches, electrical wiring in the bathroom and in accordance with clauses 7.1.46 - 7.1.48 PUE
- The switch is installed at a height of up to 1 m, 1.8 m or under the ceiling in accordance with clause 7.1.49 of the PUE.
- The connection of wires must be carried out in boxes; it is forbidden to leave them open or close them in the wall, clause 2.1.21 of the PUE.
Marking on site
To transfer the installation diagram data to an existing wall structure, you need to use measuring instruments (tape measure, angle, etc.), a level, thread and a pencil. To do this, retreat the required distance according to the distances indicated on the diagram and apply the appropriate marks on the building structures (walls or ceiling).
 Figure 2: Wall marking
Figure 2: Wall marking Markings can be done with chalk or a construction pencil. The main requirement for applying an image is to ensure good visibility and the absence of unnecessary details. If you have a laser level, this procedure is greatly simplified.
What elements need to be selected?
Structurally, electrical wiring in a house may include a number of elements:
Wires– for installation in the house, brands such as AVVG, PSV and the like are used. Copper wires are the most preferred due to better technical parameters: long service life, lower resistivity, etc. But, in some situations, aluminum wires can also be used for electrical wiring. The specific option is selected based on the maximum load and insulation requirements.
To determine the maximum currents flowing through electrical wiring, add up the power of electrical appliances that can be connected, and add 20–30% for the safety margin. Based on this, the appropriate cross-section of the core is selected. The insulation resistance must correspond to the characteristics of the room in which the cable is used and the installation method. It should be noted that the cables must be planned with a margin, since at the points of connection or output points they use more than the calculated length of the wire, and the margin must provide the possibility of reconnection.
 Rice. 3. wires for wiring
Rice. 3. wires for wiring – designed for connecting different sections of electrical wiring, separating and distributing electricity. They are divided into models of external and internal placement, which are selected in accordance with the project. Depending on the cross-section of the wires, boxes with the appropriate size of holes are selected.
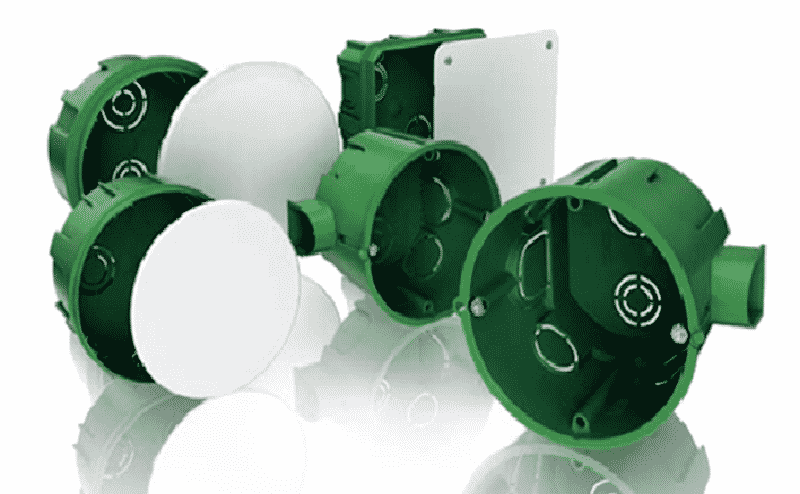 Figure 4: Junction boxes
Figure 4: Junction boxes Sockets– may differ in design features: the presence or absence of a grounding contact, cover, hole size, etc. Also, various models can be designed for indoor or outdoor installation. Some options have paired connection point pins.
Switches– can have a design with one, two or three keys, a rotary mechanism or a sensor. It should be noted that some switches are equipped with a voltage divider, which can affect the operation of lighting fixtures.
Lighting– sold as lamps, chandeliers, spotlights, sconces and others. A wide variety provides the opportunity to choose for installation in certain rooms. By purpose, we can distinguish between high-power and low-power lighting devices for the bathroom, kitchen, etc.
Residual current devices– presented on the basis of electromagnetic, semiconductor or microprocessor circuits. The installation is necessary to protect both the electrical wiring in the house from short circuits and fires with household appliances connected to it, and people who may be harmed in the event of a breakdown.
Metering devices– monitor energy consumption. Their installation is required for a new electricity connection or if this is provided for by the project. Depending on the number of phases, electric meters can be connected to a three-phase or single-phase network.
 Rice. 5: Typical electricity meter
Rice. 5: Typical electricity meter Protective grounding– must be provided for all consumers with a voltage of more than 42 V. Because of this, when connecting new wiring, it is necessary to have a grounding loop to which the PE conductor from all consumers is connected.
Cable channels– required for external installation of wiring; depending on the material of manufacture, they can be plastic or metal boxes. The size is chosen so that when laying the wires, all the necessary conductors can fit freely in them. Structurally, they can have perforations for cooling or be made in one piece.
The procedure for installing electrical wiring in the house step by step
Please note that depending on the specific situation, certain installation operations may not be performed.


First make a small hole in the center with a drill, and then use a hole saw.
 Figure 9: Drilling a hole with a crown
Figure 9: Drilling a hole with a crown 
But at the same time, make sure that excessive force does not damage the insulation.

In addition to those allocated for separate rooms or objects, it is necessary to install an input machine with a higher setting. It is installed at the entrance of electricity into the house. You can also use other protective devices (voltage, differential, etc., if needed).
 Figure 15: Shield with various protections
Figure 15: Shield with various protections 
To do this, apply voltage at the cable input to the electrical panel. Then test the flow of electric current at all connection points using a test lamp or test the presence of potential using an indicator.

If your home is not yet connected to an external network, then you do not need to do this yourself. Since the connection to the air main is carried out by employees of the energy supply organization. Performing this procedure yourself is prohibited and extremely dangerous.