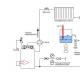
Homemade woodworking machines, created with your own hands. Do-it-yourself wooden machines. Do-it-yourself wood lathe - assembly features Do-it-yourself woodworking machine drawings
The use of a woodworking machine extends far beyond the strictly industrial sphere or carpentry workshops. Quite often you can find such machines in the household of an ordinary person, who with its help can make any piece of furniture or an entire house, if, of course, this person has all the necessary skills. It is quite expensive to purchase woodworking machines in specialized stores, so more and more people are resorting to making their own, based on information and drawings that are presented on the Internet.
However, before starting to describe the work required when making a machine at home, you need to understand the specifics of this device, as well as some nuances that may be useful in the future.
The structure of a woodworking machine includes several main working areas, as well as additional elements. The main ones include:
- bed;
- work plate;
- shaft mechanism;
- cutting tools;
- a motor that transmits motion to other components of the device.
Additional machine parts
include
- areas with fencing of potentially dangerous places;
- lubricating device;
- unit that starts the machine;
- the point that is responsible for the supply of wood.
For the manufacture of the frame, as a rule, a solid alloy or other massive material is used. This is not surprising, because all other components of the woodworking machine are located on it. As a rule, the frame should be installed on a stable reinforced concrete surface.
The work table in a woodworking machine is responsible for fixing all working components. It is made of cast iron, which is pre-polished. The designs of desktops can be different, movable or not.
The cutting element of the machine is attached to it using a shaft mechanism. Depending on the type of cutting element, the shaft mechanism can be of several types: knife, saw and spindle type.
Regarding cutting elements  they are always made of high quality carbon steel. In addition, these elements can be of various types:
they are always made of high quality carbon steel. In addition, these elements can be of various types:
- Circular saws have a cutting device in the shape of a round disk.
- The saw blade is used in band saw woodworking machines.
- Milling and tenoning machines use flat knives.
- Drills are used accordingly on drilling machines.
- Slotting chains.
- In milling and tenoning machines, in addition to flat knives, hooks, cutters and slotting discs are used.
- Sanding knives on appropriate machines.
- Rolled sandpaper is used in sanding machines.
Video
Available materials
Before you start making a woodworking machine at home, you need to make sure that you have all the necessary tools and materials. In particular, we will need:
- drill chucks;
- engine of sufficient power;
- shaft mechanism;
- adjustable bed.
Naturally, to manufacture various parts we will need a sufficient amount of steel and metal. It is necessary to stock up on metal corners that will be used in the manufacture of the frame structure, various bolts, and, of course, a welding machine, without which connecting the main components is impossible.
There are also certain requirements for the engine used. In particular, its power should be in the range of 1.3-1.5 kW, and the shaft rotation speed should be about 2500 rpm.
Regarding cutting elements, many experts agree that when making a machine yourself, it is better to take factory parts, because they are made of tool steel, which is characterized by increased strength. At home, making the same cutter will hardly be possible, so it is better not to complicate this process, but to purchase finished products.
Design of a multi-discipline machine
In principle, making a woodworking machine yourself is quite possible at home. However, in order for the work process to be completed in the correct sequence, it is necessary at the initial stage to make an accurate drawing of the future machine. This kind of design is one of the most difficult tasks in the entire work, so you need to be extremely careful at this stage.
Regarding woodworking machines, when designing them there are certain recommendations regarding the preparation of technical documentation. In the drawing, it is important to indicate the configuration of the future machine, indicating all the main working areas, i.e. bed, cutting elements, etc.
Also at the project stage, it is possible to provide for the presence of certain equipment, the installation of which is optional, but for certain reasons it may be justified. For example, it is possible to provide lighting for the working area, or the presence of various measuring instruments, etc.
DIY assembly
A factory woodworking machine is a rather complex technical structure that performs several jobs:
Carrying out trimming
Such processing allows you to form a primary blank of some part, or to prepare firewood.
Milling and grinding
After the initial trimming, the wood is subjected to grinding and other work aimed at removing various defects - burrs, irregularities, etc.
Carrying out turning works
It is considered the most complex process that can be performed on a machine. This is explained by the fact that their implementation requires certain knowledge and skills of the person doing this work, as well as accompanying hand tools.
As for homemade woodworking machines, in most cases their functionality is not so wide. As a rule, it is limited to ordinary pruning, as well as minimal wood processing. This is quite understandable, because the fewer functions a device has, the easier it is to make, and a woodworking machine, as mentioned earlier, is quite technically complex. Therefore, it is almost impossible to make a full-fledged machine at home that is no different from the factory one.
The process of assembling the machine
It starts with a drawing, which you can make yourself, with a sufficient understanding of the issue, or use those that are publicly available, i.e. in the Internet. However, no matter what the drawing is, the work always begins with the manufacture of the frame, on which the main working parts will be located in the future.
For making a bed
We will need a metal pipe or corner. For example, we take six corners with a cross-section of 25 by 25 mm, as well as one metal corner, the cross-section of which is 40 by 40 mm. The length of the mentioned components should be about 300 mm. They are connected in an elementary way by welding, but you need to carefully check the seams, because during operation of the device significant vibration appears, which can weaken the structure.
Having made the bed, you need to place it on a flat surface. It is best to fill its base with concrete so that the stability of the machine is sufficient to carry out work on it.
For machine design
We will need a shaft mechanism, which we can make ourselves or purchase in a store. It must have a hole in it for installing a drill chuck. To do this, we sharpen the end of the shaft with a regular file. It is necessary to make the diameter of the mount slightly larger than the diameter of the cartridge itself. Then we sharpen the cartridge until it is securely attached to the shaft mechanism. The cartridge is adjusted to the shaft using a needle file and a special composition of sandpaper abrasive and oil. In this case, the shaft diameter should be about 300 mm.
At the end of the shaft there should be a V-belt pulley, and at the other end there should be corresponding devices, thanks to which the functionality of the machine becomes wider. The cutting element in the form of a circular saw must be secured between the pressure washer and the thrust washer.
Table design
It is made of steel, the thickness of which should be 10 mm. In order to be able to change the planing parameters, you need to make a folding table, the upper part of which is adjustable, and the lower part, on the contrary, must be rigidly fixed.
It is necessary to install our electric motor at the bottom of the machine structure. We pull the belt over it and onto the shaft located on top. You can also make an additional corner, with which you can align the wooden material in relation to the cutting elements.
Work and safety
Operation of a woodworking machine should only be carried out by persons who are familiar with certain safety regulations. Otherwise, such work can end very disastrously for the one who carries it out.
- Before starting to work on the machine, you need to carefully check your appearance, i.e. Are there any sleeves or other parts sticking out that could get under the cutting elements?
- We inspect the woodworking machine. We check the reliability of the washers securing the cutting element to the shaft. You also need to check the degree of sharpening of the knives and circular saw, because their insufficient sharpening can lead to unpleasant moments in the process of sawing wood.
- The wood must be fed progressively, without unnecessary jerks. If there are knots on the workpiece, then when the cutting element approaches them, you need to slow down the feed slightly.
- You need to start working only after the engine reaches its maximum speed.
- Much attention must be paid to the material that will be processed on the machine. There should not be any metal staples, nails or other similar elements on it.
Compliance with basic safety precautions allows you to avoid many tragic incidents, which, unfortunately, are not uncommon when working with woodworking machines. It is clear that it is quite difficult to avoid all emergency situations, but reducing the risk of their occurrence is entirely within the power of the individual.
Perhaps the only advice when working with a woodworking machine is to strictly adhere to the safety precautions outlined above. To this list I would like to add a few points regarding direct work. In particular, you need to know in what cases you need to turn off the machine so that emergency situations do not arise:
- If you notice that the machine makes unusual noises and increased vibration.
- If the cutting element or its fastenings fail.
- In case of various debris getting under the cutting elements.
- In case of overheating of the electric motor and shaft bearings.
- Naturally, if you move away from the machine, you also need to turn it off.
Every person, regardless of which machine he works on - homemade or factory-made, must not forget that this work is potentially dangerous to his life if he does not follow the rules that are directly stated in the safety instructions .
Our article is devoted to nostalgia for school labor training workshops. Many people know how to do wood turning, but not everyone can afford to buy and maintain equipment for this. Is it possible to assemble a machine with your own hands that meets technology and safety requirements? Let’s figure it out together.
What GOST says
The good news is that you don't have to reinvent the wheel. The entire assembly process and drawings of each machine module are described in TU3872-477-02077099-2002, and although this document is not publicly available, it can be obtained upon individual request. Although this is unlikely to be needed: the device of the machine is so primitive that you can easily navigate the intricacies of its manufacture even from images from school textbooks.

Another positive fact is that the STD-120M was apparently designed for on-site production, so you can either find almost all components for assembly on sale or make and modify it yourself. Naturally, if you have the opportunity to inexpensively purchase components for this machine or its younger brother TD-120, do so. Factory-produced parts are more reliable, easier to adjust, and the unified frame design allows you to assemble one machine from many donors.

Please also note that standardization of modules largely determines the safety of equipment operation. The basic principles of industrial safety are stated in GOST 12.2.026.0-93, and the rules of electrical protection are set out in GOST R IEC 60204-1. Harmonize any part or machine module you manufacture with these standards.
Manufacturing of the bed
Instead of a cast iron frame, we offer a lighter welded structure. It consists of two pieces of 72-gauge angle steel, each 1250 mm long. There is a great temptation to make the bed larger to process more massive products, but remember that such changes require intervention in other components of the machine. Perhaps you should take the TT-10460 as a sample for a meter-long workpiece.

We place the corners on a flat horizontal plane with shelves facing each other. We insert calibrated inserts between them so that the frame guides are positioned strictly parallel with a distance of 45 mm. To fasten the guides, we use two corners, the same as on the frame, 190 mm each, which we place on the front and rear edges. Before welding parts, it is recommended to squeeze them with clamps so that the metal does not move when it cools.
The guides are fastened with another 190 mm jumper, in the bottom shelf of which there are cutouts for each corner. This part is installed to form a cell, the dimensions exactly corresponding to the landing pin of the headstock, in the standard version it is 45x165 mm.

Such a frame can be attached in any way to a workbench or deck, but it is recommended to weld all fastening elements without compromising the integrity of the base. If a separate corner is allocated for the machine, weld pipe legs perpendicular to the corners of the frame and, for greater stability, make a small “brace” for them with a sledgehammer. Ultimately, the weight of the frame attached to the workbench should not be less than 60-70 kg.

Podruchnik
This element conditionally consists of two parts. For both, you need one type of workpiece - a 50 mm corner, inside of which another, 30 mm wide, is inserted. They are welded along the edges, in the end you should get two sections of 260 and 600 mm.

The short part is the adjustable base of the hand rest. One of the shelves is cut off, but not completely, leaving a 110 mm long section with an inclined cut. The other shelf is cut at a right angle 60 mm from the rear edge. You need to make a counter frame from a thick steel plate that will clamp the guide of the tool rest.

To make a guide with a clamp, take a regular inch pipe and make a longitudinal cut in it with a grinder. The resulting sleeve should be about 150 mm long; we insert it into a 25 mm corner, orienting the slot outward perpendicular to one of the shelves. We tighten the parts with a clamp and weld along the entire length closest to the shelf slot. We cover the workpiece with a second corner of the same length and attach it to the tube from the back side.

The guide is welded flat to the protruding flange of the adjustment rail on its inner side. For fixation, a screw with a long handle and a nut welded to the rail are used. On the reverse side, the strike plate is fastened with a cotter pin or even a welded rod.

The handrail is mounted on a 20 mm smooth reinforcement rod, which is located centrally on the outside of the corner blank. The rod fits tightly into the tube of the guide system, and when the screw is tightened, it is securely pressed on all sides. A long corner piece 600 mm long is welded to the rod with a slight inclination toward itself and a slightly “sharpened” leading edge.


Drive and transmission
The standard drive option is an asynchronous three-phase motor with a power of up to 2 kW (usually 1.2 kW), connected to the headstock shaft by a V-belt drive on two-belt pulleys. The bed for fastening the engine can be located between the legs of the frame, or on an additional scaffold behind the headstock, which will complicate the assembly, but will make it more convenient to transfer the belt.

It is not always possible to use the engine at the required shaft speed, so reaching the final speed is achieved by adjusting the diameter of the pulleys. For example, if you have a blood pressure at 1480 rpm, then in order to reach the coveted 1100 and 2150 rpm, the diameters of the leading and driven streams must be in a ratio of 1:1.5 and 1.3:1.
When placing the engine, it is useful to provide the frame with a plate attached to the gate canopies. An engine installed using such a system will be in a suspended state all the time and will ensure that the belt is tightly pressed by its own weight. And if you equip the platform with a pedal, the speed can be changed even on the go.

There are no problems with the electrical part either. Switching is performed by a standard three-phase starting button with reverse; for such a low-power motor there is no need to install a starter. The only point is to turn on DC braking while holding the stop button, for which you will need a powerful diode bridge (on the KD203D) according to the standard switching circuit.
The frequency-controlled motor can be used as a direct drive, eliminating the need to construct the headstock. To do this, you need to fix the engine on the transition platform, in the lower part of which there is a longitudinal mounting spike 45 mm wide as a standard means of adjustment for the STD120 frame.

Headstock
Looking ahead, we note that both the front and tailstock include parts that can only be made with access to a metal lathe. Otherwise, it makes sense to think about purchasing ready-made modules, or at least their cast consoles.
At the base of the headstock there are two bearing housings of types S, V or U, permanently mounted on an angle steel frame. Unfortunately, it is impossible to predict which sizes will be available, but in general, the height of the spindle axis above the bed should be at least 120 mm. Given that the diameter of the spindle shaft is about 25 mm, the most interesting would be the standard size of the bearing unit with a total height dimension of about 70 mm.

The shaft is machined from round carbon steel with a diameter of 40 mm with a tolerance of no more than 0.05 mm. There are two main variations of the shaft. The first is the simplest: the shaft pillar remains in the center, then descents are made to the landing diameter of the bearing units, then threads are cut at the ends. For axial fixation, four grooves are machined on the shaft for retaining rings.
 1 — seats for bearings; 2 — grooves for retaining rings
1 — seats for bearings; 2 — grooves for retaining rings
The second variation has an extension in the form of a skirt immediately behind the cartridge thread. It is designed to install a flanged thrust bearing mounted on the boss of the headstock base. This approach allows you to reduce bearing wear if massive parts are processed on the machine.
The base of the headstock is two pairs of corners or two channels turned towards each other. By moving the vertical shelves together, you can adjust the height of the base to the axial height of the existing bearing units. A 45 mm strip is welded to the base below, which acts as an adjustment groove. The order of assembly is important: first, bearings are pressed onto the spindle, then the shaft is mounted on a frame with a backing of adjusting steel plates.

Tailstock
Making a tailstock is much easier. It consists of four parts:
- The base is made from angle steel, 100mm high, using the same principle as for the headstock. Two 50 mm corners are bolted across the top; in their shelves in the center there are cutouts with squares 40 mm wide.
- The guide (external) thick-walled square tube is 40 mm wide, 150 mm long and has an internal clearance of 20x20 mm. In the rear part you need to install a plug 6-8 mm thick and with a hole in the center of 8 mm, it is secured with two screws through the walls of the tube.
- The inner tube, also known as the quill, is made from a 20 mm profile tube, preferably thick-walled and milled exactly to fit the guide clearance. An M14 nut is welded in the rear part of the quill; a metal rod, widened to 5 mm, is inserted and welded into the front part, widened to 5 mm to fit a double-row bearing.
- The drive screw has a thread for a nut in the quill (it is advisable to make it trapezoidal); in the rear part there is a transition to an 8 mm thread for attaching the flywheel.

The principle of operation and assembly diagram of the quill are quite obvious, but special attention must be paid to the alignment of the axes. The guide tube, fixed by welding in the cutouts of the corners, can rise higher or lower due to linings made of transformer steel. The headstock and tailstock must be absolutely aligned, the tolerance is only a couple of tenths.

As for the method of attachment to the bed, it is the same for both the headstocks and the tool rest. M14 or M16 studs are welded to the bottom of the headstocks, and a large plowshare bolt is inserted into the slot of the tool rest. The modules are tightened from below with nuts with rods welded to them like levers. For uniform, tight pressing from below, a 50 mm channel is placed as a counter strip.
The author is the host of the youtube channel “Zhelezjaka”. This is a drill stand modified in a certain way. First, let's put it on its side and turn off the drill chuck. Instead of a chuck, a drill is screwed in, which will act as a headstock. A toothed attachment for fixing wooden workpieces on a DIY lathe. The stand frame performs the function of the tailstock. We screw a sharpened bolt with a locknut into a specially drilled hole. We clamp the wooden piece, moving the carriage and clamp the two screws that fix it in this position. Everything is working. There is not enough support for the incisors. Consists of two halves. Made specially collapsible to be adjusted for different workpieces.
On the machine, it is inserted into the bracket and adjusted both in direction, reach and height in relation to the workpiece. To carry out turning work you need a special tool. But in his absence, the master used sharpened old files, of which there are many in the garage. This is necessary to simply show the machine in operation. Turning something on a machine is not a very difficult job. It's even very interesting. The main condition here is not to rush anywhere. After turning the workpiece and sanding it with sandpaper, we got two handles for files.
This homemade woodworking machine can be used as a drilling machine. You just need to lift it up. Remove the tenon from the headstock. Place the chuck with the drill. Remove the spike from the bottom.
Wooden blanks can be sharpened to the full length of the stand. With a diameter much larger than when making a handle. The power of this drill mixer is enough to process such a workpiece.
DIY milling machine from a drill
No matter what test the master subjected his drill stand to. Drill a 19 mm hole in the metal. After that I worked with a 2 mm drill. Rotated a workpiece 70 cm long. I used a drill as a mixer at a construction site. In this video, a standard cutter from a router with an 8 mm shank is installed on a drill. For securing the guides and the workpiece, the table that the master made in advance turned out to be very convenient. The ability to smoothly lower and raise the drill was not superfluous. I tried using a different cutter. I came to the conclusion that there are not enough high spindle speeds. Although, for rough woodwork, in the absence of a router, you can get by with such a tool mounted on a stand.
Homemade drill stand
Workpieces can be drilled to any height without complicated adjustments. We take a twenty, put a 5 mm thick strip, drilled with a seven, to make it easier to make a large hole. I made it from metal corners, a square pipe, and used a strip in the eyes. Corner on the carriage. Square pipe on a stand. The band used is narrow. Square pipe on brackets. It's all cooked. The machine is dismountable, the rod and carriage, adapters for drills are removed. They can be done additionally.
Second part
Woodworking machine Planer-thicknesser with automatic board feed
Homemade woodworking machine
What parts does it consist of? Angle bed 40 x 40. If you can find 35 x 35, that will also work. Required four corners 450 mm long. 9 – 550 mm. Two more corners 270 mm long. Sold at hardware stores. A 12 m pin is used. They are also available in stores. Nuts, washers. At the city flea market you can buy a drum for little money. Knives 200 millimeters long can be found at a hardware store. You need two brackets for the electric motor. Two small tables for planing. Size 300 x 220. Sawing table 600 mm long. Tables can even be made of wood, textolite, or from any suitable material. It is not necessary to make iron ones.
Tools for woodworking.
Purchasing ready-made equipment for industrial production is certainly easier and faster, but it does not always satisfy all the needs of the craftsman, and the cost of such pleasure is very noticeable - this makes you think about the feasibility of such investments. After all, if you have skillful hands and some work skills, it is quite possible to make a woodworking machine according to drawings found on the Internet or developed independently.
At the same time, a homemade woodworking machine will turn out to be quite universal and multifunctional - it will satisfy the needs of a specific person.
Woodworking machines for the home have a standard set of basic design components.

The machine consists of:
- beds (support base);
- work plate (table);
- shaft mechanism;
- cutting tools (circular saw, etc.);
- drive mechanism (motor, gearbox, etc.)

Additionally, a homemade universal woodworking machine is equipped with guards for hazardous areas, a lubrication system, a starter, etc.
Material and tools
To make a universal woodworking machine at home with your own hands, you must first make sure that you have a sufficient amount of material and the necessary tools for processing it. First of all, this concerns metal: angles, channels, steel sheets and strips, as well as fasteners (bolts, screws, nuts, studs). You will definitely need a drill and grinder, a welding machine, files, screwdrivers, pliers, etc.

Most of the structural elements of the machine can be made with your own hands without any problems, but it is better to purchase the engine and cutting tools (for the drill head, circular saw, router, etc.) from a factory.
Design stages
For a craftsman who is intimately familiar with the design of elements, making a woodworking machine according to his own drawings will not be a problem; for others, a huge number of ready-made drawings are available online today that can be used in their work.

The design stage can be called the most crucial moment in the process of creating a woodworking machine with your own hands at home - the slightest error that creeps in will negate even the perfect assembly, the device will not function as intended. Therefore, the drawings should be made in the most careful and responsible manner so that during the further assembly process the current questions of “how”, “where” and “what” do not arise.
Main functions
During design and manufacturing, the equipment can accommodate a very wide range of woodworking work. Depending on the needs and desires of the home craftsman, he can include any combination of them in the design drawings - this will allow the work plans of a particular person to be implemented.

Machine functions:
- Pruning is the simplest operation, but it is necessary for everyone and always.
- Milling and grinding - creating grooves, cuts, grooves and other things is also a very common task in the home workshop.
- Turning is the most complex type of processing, but deservedly popular and in demand.

Important! Making a homemade universal machine is a complex process even if you have detailed drawings, so in the absence of sufficient experience, it is better to carry out such a process as making a device yourself using a simplified scheme - limit yourself to a sawing table, or sawing plus milling/grinding.

The most complex complex of turning should be done with full confidence in your abilities.
Versatile woodworking machine and safety
When working at home on a home-made device, you should follow safety precautions. How to make work not only productive, but also safe?
To do this you should:
- keep an eye on clothing (protruding parts);
- check the device fastenings;
- control the degree of sharpening of the tool;
- When working, do not feed the material “in jerks”;
- start processing only when the engine has reached full speed;
- inspect the material for the presence of metal elements.
With sufficient skills, a self-made unit will serve its owner for many years, you just need to be careful about work and safety.
High-quality processing of wooden blanks is quite a complex job, which is performed using special equipment. But, often, home craftsmen cannot afford to spend a lot of money on an expensive device that is needed for a one-time job. And professional workers prefer to assemble such a machine themselves. In this article you will learn how to make a homemade wood lathe quickly and without much hassle.
A hand-made device will not be inferior in quality to a branded machine for wood turning, because every detail can be selected independently. In addition, using scrap materials when making a wood lathe with your own hands, you will significantly save your budget.
To determine the scope of the upcoming work, you need to familiarize yourself with the structure of a wood lathe.
The standard tool has the following components:
- bed;
- headstock;
- tailstock;
- caliper
The base, or bed, is a supporting structure that ensures a stable arrangement of all parts of the mechanism. The stop for a wood lathe at home is made from a flat board or a wide channel.
The front and tailstocks allow you to securely fasten the element being processed. Unlike the front, the back is movable.
The caliper is responsible for moving the cutting tool along the main axis. If it is not possible to make a support for a wood lathe, a tool rest will play its role.
In order for a self-made device to work well, you must first draw a plan. A diagram is necessary for each design detail in order to visualize not only the location of the parts relative to each other, but also to eliminate errors in the design of the component elements.
Machine capabilities
Woodworking machines for working with solid wood are universal, as they allow you to perform a large number of operations. By making a wood lathe, you will be able to carry out a full range of work on mechanical wood processing:
- drilling;
- creating grooves;
- figured turning;
- end processing.
With proper assembly of a mini turning device for woodworking, a home craftsman will be able to produce not only functional pieces of furniture (table legs, counters, elements for stair railings), but also decorative elements. Even with a simple machine you can make beautiful dishes, gift boxes and children's toys. And having done this, you will be able to make more complex shaped wood products.
Material and components
All main working parts of the turning mechanism must be made of reliable materials. The main rotating element of the engine from the washing machine can be used as a drive. Some craftsmen use motors from machines to sharpen knives, but finding a working motor from a washing machine is much easier. To operate the mechanism, you will also need a set of drive belts.
For the tailstock, you need to find or make your own screw with the ability to fix it horizontally. One of the elements of the front clamp of a wooden workpiece can be a rotary chuck (head) from an old hammer drill or drill.
To avoid movement of the structure during operation, the base is made of a thick metal profile.
It is impossible to make a woodworking lathe with your own hands without using tools. To complete all the work you will need:
- drilling machine;
- files and sandpaper;
- Angle grinder (grinder) and a set of discs for cutting metal;
- welding machine.
You should also prepare screws, bolts and nuts for fastening the elements.
Base, frame and spindle box
Before you start making a wood lathe with your own hands, you need to decide what type of equipment is needed - portable or stationary. Portable can be used in any convenient place and, if necessary, transported. The stationary turning mechanism has high legs and can only be carried indoors.
It is on the frame that the drive, the headstock and tailstock, as well as the tool rest will be attached, so you should pay close attention to its design.
A simpler design for the headstock is to make a faceplate that will fit directly onto the motor screw and fix it. To do this, you need to cut out a circle with a diameter of 15-20 cm from a dense material (wood, plywood or iron sheet), and drill 5 holes in it - the central one and 4 at the intersection of two diagonals. Angles are attached to the four holes, and retaining screws are attached to the opposite side of them. By adjusting the screws, you can clamp a workpiece of any diameter.
Making a tailstock for a wood turning mechanism is much easier. This will require a wide screw with a tapered end. You can make such an element yourself by sharpening an ordinary wide screw at one end using a grinding machine. The spike is attached to the post using lock nuts - from the front and back of the support.
A more reliable design would be a screw support welded from two plates and a pipe. Nuts suitable for the size of the tenon are welded into the pipe on both sides. For quick fixation, a small handle is welded to the opposite end of the screw.
If the headstock is a fixed structural element, then the rear clamp must be able to move along the base, adjusting to the size of the wooden workpiece. Therefore, the tailstock post must have a hole for a fixing screw.
This structural element is necessary for fixing wood cutters. Since the tool rest has direct contact with the worker’s hands, flaws in its manufacture can lead to serious injury.
A reliable homemade product is made from a durable corner 5 cm wide. The length of the hand rest is calculated using the formula 1/4 of the length of the base.
For manufacturing you will also need 2 smaller corners, two tubes of different diameters, a small steel plate and a screw. The two corners are welded together so that there is 3-4 cm of distance left in the middle. A larger diameter tube with a hole for a pressure screw is welded on one edge, into which the tool rest will be inserted. A plate with a hole for a screw is installed at the ends of the corners. This is a fastening element to the base of the machine.
The tool rest (corner) itself is welded to a pipe of smaller diameter. The finished part is inserted into the holder and secured with bolts.
Making a wood lathe is easy - you just need a little time and patience!
You may also be interested in the following articles:
DIY metal lathe How to make a wood planer with your own hands