Do-it-yourself heating installation in a private house. Heating installation in a private house. Water heating structure
Modern materials and proven technologies make it possible to competently organize autonomous heating in a private home. And the main advantage of this is that the homeowner independently determines the beginning and duration of the heating season. The modern market offers affordable options for heating systems. At the same time, the correct choice of one of them depends on the design features and dimensions of the house, the number of heating elements and types of energy carriers.
Types of heating systems
Existing systems involve the use of various types of coolant for heating rooms, so there are:
- Mermen.
- Steam.
- Air.
- Electric.
- Underfloor heating systems.
- Combined.
All of them are capable of providing fast and efficient heating of residential buildings of various sizes.
Water heating
One of the most common and popular types of heating for apartments and private houses. It works on the principle of a closed heating circuit, inside which the coolant circulates. Hot water from the heating boiler naturally or forcedly moves through pipes and heating radiators, evenly distributed within the system.
The body of the radiators heats up, causing heat exchange in the room. The cooled coolant is returned to the boiler equipment and the heating process is repeated.
The water heating system is equipped with special valves to regulate internal pressure. For such a scheme, various types of boilers are used - gas, solid fuel, electric.
Steam heating
It is rational to use hot steam heating for heating industrial premises. For heating houses, such a system is practically not used due to the large dimensions of steam boiler equipment, which requires large areas and also has a high heating temperature of the body, reaching 120 degrees.
Hot steam obtained by heating water to a boil is used as a coolant, after which the steam cloud is transported through a pipeline to the radiators. As the steam cools, it condenses into liquid and enters the boiler.
There are two types of steam heating:
- Open. Equipped with a storage tank to collect condensate after cooling the steam and feeding it into the boiler.
- Closed. Condensate enters the boiler equipment independently through pipes of larger diameter.
Air heating
A fairly popular option for organizing heating of retail and industrial areas. The advantage lies in the resistance of system elements to corrosion, temperature changes and leaks. It is used extremely rarely for heating a country house.
The main components of an air heating system include:
- Heat generator for heating air.
- Air channels for the transmission of air masses.
- Fan for uniform air distribution.
The principle of operation of air heating is simple: the heat generator provides rapid heating of the air, which is transmitted through air ducts and enters the premises through ventilation grilles. Channels can be laid in wall or ceiling surfaces. Cooled air enters the heat generator through air ducts, after which the heating process is repeated.
The system uses a heat generator using various fuels: diesel, kerosene, gas (cylinder and main).
Electric heating
A good alternative to traditional water heating is an electric heating system that is safe, convenient and easy to use.
Electric heating of a house is beneficial in cases where there is no possibility of connecting to a gas pipeline or using other energy sources.
To organize it, the following can be used: an electric boiler, electric convectors, film heaters, thermal panels, infrared ceiling-type heaters.
The most popular and easy to use are electric convectors, equipped with a thermostat to maintain a comfortable air heating temperature.
Heating under warm floors
The underfloor heating system provides uniform underfloor heating for rooms of various sizes. The installation of heated floors under porcelain stoneware and ceramic tiles is most effective, characterized by high heat transfer and low energy consumption.
There are two types of underfloor heating:
- Vodyany. Pipes with coolant are laid on a perfectly flat heat-insulating surface and connected to the heating boiler. Next, cement screed and laying of decorative coating are performed.
- Electric. The film is laid on the prepared surface, after which the decorative coating is installed. Another option is a heating cable on a substrate, with a screed or floor covering laid on top.
The principle of operation is the same - heat transfer is carried out through the floor covering.
Combined heating
The combined heating method involves the use of several types of heating and coolants. In damp functional rooms: kitchen, bathroom, corridor - underfloor heating. In living areas: living room, bedroom, children's room - water or electric. The main rooms of the house have water heating, and the rest - electric heating.
Schemes for organizing the heating system of a house
Choosing the most suitable scheme for organizing water heating in a house is quite difficult, so it is recommended to obtain additional advice from a specialist.
There are several common schemes for laying pipes in a private home, which allow for quick and uniform heating. According to the method of movement, heating systems are divided into:
- Single-pipe.
- Two-pipe.
- Collector.
- Leningradsky.
Single-pipe system diagram
The one-pipe system is considered simple and accessible for independent organization. It involves sequential installation of radiators to the pipeline through which the coolant moves. The full cycle consists of heating the coolant, supplying it to all heating circuits and returning it to the boiler.
Despite its practicality and low cost, single-pipe heating has some disadvantages. If a system uses a large number of radiators, the likelihood increases that the furthest ones will remain practically cold. In other words, the heating temperature in distant rooms will be lower than in the one where the heating boiler is located.
In addition, such a system is difficult to carry out repair work. Repairing any radiator will require stopping the entire heating system.
Diagram of a two-pipe system
A two-pipe heating scheme for a private house is more difficult to organize, but easier to maintain. It involves connecting two pipes to the boiler. In this case, one pipe is used to supply coolant to the radiators, the second is used to drain it to the boiler. Radiators can be mounted parallel to each other.
For convenient operation, the pipe for a separate radiator is mounted with an additional inlet valve. The return pipeline is laid under the floor in any room where there is a heating circuit.
Collector system diagram
In a collector heating system, the pipes for the supply and removal of coolant are laid independently of each other. Each radiator is connected to a common collector by separate pipes: for supplying hot water and for returning cooled water.
This option for laying the pipeline ensures maintaining a comfortable temperature in all rooms, and also allows you to repair or replace the heating element in any part of the system.
The disadvantages include the need to install a cabinet under the collector, the high cost of structural elements and installation.

Scheme of the Leningrad system
Leningradka is a perfect version of a single-pipe heating system. It provides more uniform heating of rooms and is easy to install and maintain. In addition, such a piping layout makes it possible to reduce heat loss when the coolant moves between heating circuits.
The system is equipped with special bypass jumpers located under the heating devices. They ensure the return of coolant through pipes, bypassing the radiators, which allows maintaining the heating temperature at the inlet and outlet without significant heat loss.
Basic elements of the heating system
A modern heating system for a private home consists of important elements, each of which performs special functions. These include: heat generators (boiler, circulation pump), distribution pipeline, expansion tank, heating radiators, thermostats and air valves.
The efficiency and safety of the heating system depends on their proper location.
Boiler
The most common type of heating system used in a home is a boiler. The choice of suitable equipment depends on the type of energy carrier. Modern boilers run on gas, wood, kerosene, coal, briquettes and electricity.
Small-sized boilers with a power of up to 25 kW can be installed in utility rooms and utility rooms. It is better to move volumetric heat generators with a power of over 70 kW into special buildings with limited access.
Structurally, the boiler is divided into two compartments - fuel and heat exchanger. The first compartment is intended for combustion of fuel, the second - for heating the coolant used.
Distribution pipeline
Pipes are provided for transporting coolant from the boiler to heating devices. For piping, pipes of various diameters and materials are used.
The following types of pipes are suitable for the heating system:
- Metal - steel, stainless steel, copper, galvanized alloy. A metal pipeline is difficult to install, susceptible to corrosion, and less practical and durable. More reliable are copper pipes, which can withstand water hammer and temperature changes. The only drawback is the high cost of the material.
- Plastic – metal-plastic, polyethylene, polypropylene. The plastic pipeline has high performance characteristics. It is safe, durable, practical, inert to rotting and corrosion. Metal-plastic pipes are the most affordable and time-tested, easy to install and operate.
Heating radiators
To organize heating of a private house, the following types of radiators are used:
- Cast iron radiators. They are characterized by low cost, high heat transfer, large volume and weight.
- Aluminum and bimetallic sectional convectors. They are distinguished by fast heating of rooms due to natural convection, compact dimensions, relatively low weight and attractive appearance.
- Metal panel radiators. A combined type of device that features a long service life, high inertia, attractive design and affordable cost.
Thermostatic devices
For reliable and safe operation of any heating system, a thermostat is required.
The thermostat for heating radiators allows you to correctly set a comfortable heating temperature in the room. Structurally, it consists of a thermal head and a bypass valve.
Thermostats can be direct-acting (installed in the pipeline) or electrically controlled (installed next to the manifold).
Expansion tank
An important functional element in the autonomous heating system of a private house is the expansion tank. It is intended to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant in order to prevent possible pipeline ruptures.
Expansion tanks are either closed or open. Open tanks can be installed at the highest point of the system, closed tanks can be installed in any convenient location.
Air release valve
The air valve is used to quickly remove air from the heating system and the devices that are used for its operation. It can also be used in the following cases:
- During the process of filling the pipeline and radiators with coolant.
- To suck in air from outside if there are problems with the system.
- When air pockets form during system operation.
Features of installing a heating system in a private house
To make heating in your house with your own hands, you need to choose a suitable system. The optimal solution is to install a system with an accessible and economical coolant.
If the house is gasified, you can organize water heating with boilers: gas (as the main one), electric or solid fuel (as the auxiliary one).
The next stage is the creation of a detailed design, carrying out the appropriate calculations, preparing design documentation and a drawing of the system. Next, you should purchase heating equipment and additional materials for installation.
First, a boiler for the heating system is installed. All types of boilers (except for electrical devices) are installed in a special room - a boiler room. The room has special requirements: a reliable ventilation system and separate wiring. The equipment is mounted at a safe distance from wall surfaces lined with fire-retardant material. A separate chimney is also installed.
A pipeline is drawn from the installed boiler to the installation sites of heating radiators. When laying pipes through walls or floors, gating is performed. The connection of individual pipeline elements is carried out taking into account the material from which it is made.
Finally, radiators are installed. Brackets are used for secure fixation. When installing radiators, it is important to maintain the following distances to the radiator: from the floor - 12 cm, from the walls - 4 cm, from the window sill - 11 cm.
Valves (shut-off and control) are installed at the output and input of each, as well as thermal sensors to regulate the heating temperature of the coolant.
After completing the installation of the main and auxiliary elements, pressure testing of the heating system should be carried out. A test run of boiler equipment should be carried out by specialists.
Frequent errors when installing the system
Making mistakes during installation work can lead to a decrease in the efficiency of the finished heating system. The following errors are common:
- Wrong choice of energy carrier.
- Incorrect boiler power calculations.
- Irrational choice of heating system.
- Incorrect selection of the appropriate pipe diameter.
- Poorly made slopes when laying pipes.
- Incorrect choice of shut-off valves and control devices.
- General violation of installation technology.
An effective heating system for a private home requires the correct choice of cheap and accessible energy sources and proper installation of all functional elements.
Any owner of country property sooner or later is faced with the need to create comfortable living conditions. Water heating of a country house is a fairly simple system, but there are many different options for its implementation. The reason is that it must not only be reliable and easy to operate, but also economical and efficient. Therefore, when creating it, it is important to choose the right type and all its elements.
Types of heating systems for a private home
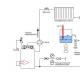
The water heating system of a private house can be of two types: open (gravity) and closed.
The open system consists of a heating boiler, radiators and an expansion tank. All elements are connected to each other by pipes. Hot water, heated by the boiler, rises up the riser to the supply pipe and, under the influence of gravity, spreads by gravity over the radiators.
The movement of water is ensured by the difference in density between hot (heated by the boiler) and cold (heat released in the radiators) water. An expansion tank is necessary to compensate for the increase in water volume when heated. In this case, the tank is used as an open type to reduce hydraulic resistance.

Fig.1.
Water heating in a private house without a pump is energy independent. It only needs a source of fuel to run the boiler.
This scheme has many disadvantages and they are all related to the gravitational principle of operation. Here are some of them:
- slow warm-up;
- the need to install an expansion tank at the highest point of the system while the boiler must be at the lowest point;
- constant evaporation of coolant from the expansion tank (since it communicates with the atmosphere);
- difficulty balancing;
- impossibility of installing heated floors, etc.
The disadvantage of high inertia can be eliminated and productivity can be increased by installing a circulation pump. It is connected according to a bypass circuit, which provides two operating modes. Such a heating system at home can operate both with the gravitational principle of coolant circulation and with forced pumping. However, all its other shortcomings remain.

Fig.2.
Despite the energy independence of an open system, they most often choose a closed system. It differs from an open one by the presence of a circulation pump and the use of a sealed expansion tank.

Fig.3.
The coolant circulates using a special pump. Therefore, there are no restrictions on the installation of elements (a certain slope of pipes and arrangement of elements, etc.), it is possible to install water heated floors, the entire wiring becomes more compact and takes up less space.
Heating schemes for a country house
A closed heating system for a private house can be implemented in various ways, depending on the number of floors and area, as well as on the type of heating devices. The most widely used are single-pipe, double-pipe, beam circuits and their combinations.
Single-pipe heating systems are a scheme in which the supply and return of radiators are connected to one pipe.

Fig.4.
The advantage of this scheme is that it is compact, easy to install and does not require much material consumption. The main disadvantage is that the further the radiator is from the boiler, the less heat it transfers to the room, because colder water enters it than the previous ones.
To eliminate this drawback, an accurate calculation of the heating of the house is required, i.e. pipelines (pipe diameter) and heating devices (number of sections) during design. However, it is often very difficult to balance a single-pipe design.
The two-pipe heating system of a private house has no disadvantages. In this scheme, the coolant is supplied to the radiators from the supply pipe, and the cooled water is drained into the return pipe.
This way, all heaters are connected in parallel, and it is much easier to ensure the same heat transfer from heating devices. Thermostatic valves are used for this purpose.

Fig.5.
Both schemes can be used in houses of different heights. Depending on the number of radiators on the floor, horizontal or vertical wiring can be used.
A two-pipe heating system for a one-story house with a small area must have horizontal wiring. For a multi-story building, you should prefer a vertical layout of risers. This option will allow you to more evenly distribute heat throughout all rooms, thanks to simpler balancing.

Fig.6.
Efficient heating of a house is achieved through the use of a radial (collector) circuit. In it, each radiator is connected individually. Water heated floors work according to the same scheme.

Fig.7.
The collector heating system of a private house is more expensive to install than the previous ones, but they more than pay off in savings in operation. The fact is that you can fine-tune not only the entire system, but also each radiator individually. Thus, it is easy to maintain a low temperature in non-residential premises, thereby significantly reducing fuel consumption for the boiler.
Boiler selection
Heating boilers for a private home can be divided into several groups according to the type of fuel used, power, installation method and functionality. Given their diversity, the choice of one type or another must be made based on the operating characteristics and type of heating system.
Based on the type of fuel consumed, they are divided into electric, diesel, solid fuel and gas. Heating boilers are listed in order of lower energy costs, i.e. gas ones are the most economical. Naturally, the choice in favor of one type or another primarily depends on this characteristic.
Although you can create heating in your home using any energy source, most often you have access to gas. For this reason, the gas heating boiler is most popular. Therefore, we will consider this group in more detail.
Gas boilers for heating can be of two types: floor-mounted and wall-mounted.
Floor-standing ones have great power and are capable of heating a house with an area of more than 150 sq.m. They are simpler in design and can operate in both gravitational and closed systems. Most models are non-volatile, i.e. do not require connection to electricity.

Fig.8.
Wall-mounted heating boilers have lower power and are more compact. They have an aesthetic appearance and can be installed anywhere. They are mainly intended for use in a closed circuit. For this reason, wall-mounted gas boilers are already equipped with a circulation pump, an expansion tank and all the necessary automation. They are energy dependent, but thanks to electronic control they are able to fully automate the heating of a country house.

Fig.9.
They can be of open or closed type. The difference between them is that with an open chamber, air is taken from the room for work. This imposes requirements on ventilation and chimney installation. Boilers with a closed combustion chamber are equipped with a special fan (turbine), thanks to which air is forced in from the street, and exhaust gases are removed through a coaxial chimney, which is very easy to install.
A wall-mounted gas boiler can be single-circuit or double-circuit. Single-circuit only works to heat the room. Double-circuit gas boilers also provide hot water supply. However, they will cope well with the task if there are no more than 2 hot water consumers.
If the number of water points that can be used simultaneously is greater, then it is advisable to choose a single-circuit boiler and install an indirect heating boiler. A boiler is a barrel in which a coil is installed, through which the coolant circulates and thereby heats the water.

Fig. 10.
The most important characteristic of a gas boiler is its power. Designing home heating begins with calculating the boiler power, taking into account many parameters. However, with ceiling heights of up to 3 m and good insulation of walls and roofs, you can follow a simple rule: 1 kW of power is needed to heat 10 sq.m. area of the house.
Expansion tank and circulation pump
An expansion tank is necessary to compensate for the increase in coolant volume when heated. So for water, when heated to a temperature of 80 degrees, its volume increases by about 5%. Therefore, it is necessary to install an expansion tank, and different designs are used for open and closed systems.
A tank for an open system is a container, the volume of which is completely used to fill it with coolant when it expands. Therefore, its volume should be approximately 7% of the total coolant volume.

Fig. 11.
The heating system of a private house with a pump involves the use of a sealed tank. Such containers are structurally divided into 2 parts by an elastic membrane, on one side of which there is air under pressure of usually 1.5 atmospheres, and on the other there is a coolant. In this case, a tank with a volume of 10–12% of the total volume is required.

Fig. 12.
The circulation pump is selected based on the calculated flow and pressure values. Flow rate is the volume of liquid per unit of time that the pump must pump. Pressure is the hydraulic resistance that the pump must overcome.
Formula for calculating consumption:
Q=0.86 x P / dT,
where Q is the design pressure, P is the thermal power (boiler power), dT is the temperature difference between the supply and return (usually 20 degrees).
Formula for calculating pressure:
H=N x K,
where H is the pressure value, N is the number of floors including the basement, K is the coefficient of average hydraulic losses, accepted 0.7 - 1.1 for two-pipe systems, 1.16 - 1.85 for radial schemes.
The given formulas are an approximate calculation of a heating system for a private house; to accurately calculate the characteristics, it is necessary to use special techniques that allow you to take into account all possible factors and accurately determine operating modes.
Pipes and automation
Heating and water supply systems for cottages and summer cottages have a low coolant temperature, usually up to 90 degrees. Therefore, any type of pipe can be used to connect all heating devices: steel pipes, metal-plastic, polypropylene.
Steel ones are strong and durable. However, their use is associated with installation complexity, which is impossible to perform without welding skills. In addition, so that they do not spoil the appearance of the room, they must be painted periodically.
Metal-plastic pipes are very popular. Installing a country house heating system with their help is very simple, especially if you use threaded fittings. However, as practice shows, due to seasonal temperature changes, the fitting clamp can become loose and cause a coolant leak. Therefore, connections must be regularly checked for leaks.
Polypropylene pipes (reinforced) do not have the disadvantages of steel and metal-plastic ones. They are mounted by welding, which makes the connections very strong and durable, and you can do it yourself even without having experience in this kind of work.

Fig. 13.
The most important element is the air vents. These are simple mechanical devices that allow you to remove air from the system that is blocking its operation. Their other name is Mayevsky crane. These devices must be installed not only at the highest point, but also on distribution manifolds and heating devices.

Fig. 14.
If heating radiators are used to heat the room, then it is advisable to install a thermostatic valve on each one. With its help you can accurately set the required temperature.

Fig. 15.
Heating a private house with heated floors
Radiators or heated floors, as well as a combination of both, can be used as heating elements. Quite often they do combined heating at home, i.e. The first floor is heated with heated floors, and the second floor with radiators.
Underfloor heating has a number of advantages:
- allows you to create more uniform heating of the room, thereby making the climatic conditions more comfortable, and the system becomes simpler;
- radiators must be installed along all external walls, which is not always provided for by the layout, while heated floors are free of this limitation;
- ease of adjustment.
However, despite all the advantages, installation of heated floors is more labor-intensive and expensive. The main contribution is made by the costs of materials and labor.

Fig. 16.
Fundamentally, this system is not very different from the traditional one. The main difference lies in the need to install special mixing and distribution manifolds.
The fact is that the air temperature of a heated floor usually does not exceed 35 degrees, while the boiler produces a coolant temperature of more than 50 degrees. The mixing manifold is designed to solve three problems:
- setting a low temperature of the coolant due to mixing hot with cooled;
- distribution of water along the contours;
- ensuring circulation.

Fig. 17.
The heated floor system is built according to a radial scheme. Thanks to this, it is very easy to set up and adjust, which in turn simplifies the creation of comfortable conditions and at the same time allows you to save on heating.
The considered options for creating a heating system can be used for a house of any size and number of floors. It is important to find a compromise between the required climatic factors, the cost of elements, the complexity of maintenance and energy costs. If you correctly correlate all of the above parameters, then the house will always be warm and cozy, and heating costs will not greatly burden the family budget.
If you live in a region where winter temperatures drop below zero, the issue of heating in private homes becomes extremely important. When creating a space heating system in a private house, one of the following heating schemes is used (the design, cost, advantages and disadvantages of each of them will be discussed below).
The most common types of home heating systems
The most ancient means of heating, known since time immemorial, is the Russian stove, the disadvantage of which is that the floor always remains cold, as warm air rises. Fireplaces, which also came to us from antiquity, have changed in many ways, but mainly play an auxiliary role in heating the house. The most popular are water heating systems based on the circulation of water heated from a boiler in pipes. There are boilers heated by different types of fuel. More rare, but no less effective, is air heating. Electric heating in homes is a relatively new type of heating, while the room can be heated without a coolant, and electrical energy is converted into heat.
Water heating
This system is considered the most reliable and simple: the boiler heats the water, which then flows through pipes to the room radiators, from there, giving off heat to the room through the radiators, and returns again to the boiler.

Scheme of water heating of a private house
Water circulation is maintained by a circulation pump. A water heating system is a closed chain consisting of a boiler-heat generator, pipeline, and batteries. Water or antifreeze constantly circulates through it. The fuel for heating the boiler can be coal, firewood, natural gas, kerosene, etc.; centralized power supply or alternative electricity: solar and wind converters, mini-hydro stations, etc.
In addition to the boiler, pipes and batteries, the water heating system includes devices for regulating the system: an expansion tank, where excess water or antifreeze that occurs during heating is discharged; thermostats, circulation pump, pressure gauge, shut-off, automatic air vent, safety valves.
Table 1: Selection of boiler power depending on the heated area of the house

For areas from 30 to 1000 sq. meters, you can also use electric boilers with a power of 3-105 kW, respectively. Restrictions on the use of electric boilers may be for the following reasons: there is not always enough electricity capacity supplied to the house, the high cost of electricity, taking into account the cost of 1 kW of energy per 10 sq.m. with ceiling heights up to 3 m, possible power outages.

Diagram of a water heating system for a private two-story house
Pipes made of different materials are used in a water heating system:
1.Steel, galvanized steel, stainless steel;
They are welded during installation.Steel pipes have a significant drawback: low corrosion resistance. Galvanized and stainless steel pipes do not have this drawback; it is advisable to use threaded connections in their installation. When assembling a pipeline from metal pipes, skill and qualifications are needed. Currently, in new construction of cottages, such pipes are used less.
2. Copper;
Copper pipes are reliable and can withstand very high temperatures and high pressures. They are connected by high-temperature soldering using silver-containing solder. They can be hidden in the walls of the house and then sealed. Working with such pipes requires high qualifications. Copper pipes are the most expensive of all, and are used mainly in exclusive construction.
3. Polymer(metal-plastic, polyethylene, polypropylene reinforced with aluminum).
Polymer pipes are convenient for installation and do not require special professional skills of the assembler. Metal-plastic pipes (aluminum is coated with plastic on both sides) are durable, resistant to corrosion, and do not allow sediment to be deposited on the inner surface. Metal-plastic pipes are installed using press or threaded connections without welding, which reduces the cost of installation work. However, they also have a drawback: a large coefficient of thermal expansion. If only hot water flowed in the pipe for a long time, and then cold water flowed, then they may leak. Therefore, temporarily stopping the boiler in winter and defrosting the heating systems leads to irreversible damage. Another reason for a possible leak: if you bend it at an acute angle, the aluminum layer may simply break.
The choice of material for pipes should be coordinated with the designers, taking into account the possibility of alternative or “emergency” heating of the house, as well as your material capabilities. Experts note that practically the only way to get an absolutely reliable system is to use a copper pipeline that will last for more than one generation.
Water heating system
The water heating system can be single-circuit or double-circuit. A single-circuit system is intended only for heating the room. A two-circuit system is created for both heating and heating water for domestic needs. Often two single-circuit systems are used, one of which is responsible for heating, the other for heating water, then in the warm season only one system can be used, taking into account that 25% of the boiler power is spent on heating water for domestic needs.
There are three options for installing pipes indoors: one-pipe and two-pipe, manifold. Two-pipe heating systems are considered optimal for individual houses.
2.jpg)
Single-pipe water heating for a private house
Heated water from the boiler passes sequentially from one battery to another. The last battery in this chain will be colder than the first. This system is more often used in apartment buildings.
Note: It is difficult to control a system with a single-pipe wiring: without special techniques it is impossible to block the access of the coolant to one of the radiators, since this will block access to all the others.
It is easier to regulate the temperature in the premises if two-pipe wiring. With this type of wiring, two pipes are connected to each heating device: with hot and cold water. Such pipes can be routed in a star shape.

Scheme of two-pipe heating distribution for a private house
A pipe with hot water comes to the battery and leaves with cold water. The temperature of each battery is the same.

Scheme of a two-office "loop" system
In this case, the batteries located closer to the heat producer are warmer.
There is also a radial or collector wiring, when two pipes are supplied from the collector to each heating device - forward and return.
Note: A collector in a water heating system is a device that collects coolant - water.

Scheme of collector heating for heating a private house
Collector systems are universal; they allow you to create heating systems with hidden pipe wiring. Installation can be carried out by people without special skills. This wiring diagram makes it possible to regulate the system and install special electric motors that maintain a given temperature in the rooms. The advantage is easy temperature control in each room, relative ease of installation, and the ability to replace a damaged section of pipe without destroying the floor structure. On each floor, in a special cabinet there are collectors, from which pipes go to the heating radiators, independently connected to each radiator. All shut-off valves are located in the cabinet. The need to install cabinets and high pipe costs are among the disadvantages of the collector system.
Note: The cost of the pipes will depend on the selected wiring diagram (two-pipe or single-pipe). The single-pipe scheme has a lower cost.
Calculation of the cost of a heating water system

Calculation diagram for heating water system
It is believed that to heat a room with an area of 10 square meters. you need 1 kW of heating power.
There are also correction factors:
From 2 windows facing north - 1.3;
From 2 windows facing south and east - 1.2;
1 window facing north or west - 1.1.
Example: Area 10 x 10 sq.m., two floors. 4 rooms with 2 windows each.
Based on the footage, you need a single-circuit boiler with a capacity of 25 kW (let’s say it runs on gas) or a double-circuit boiler of 28 kW to heat domestic water. On average, such a boiler can cost approximately $800. You can also choose an electric boiler, which can also cost about $800-850 for a house of this size.
Equipment:
- batteries (we will choose steel ones: 8 batteries on the first floor, two for each window, size 500x800, power 1645 W; and 4 batteries on the second floor, one under the window, size 600x1000, power 2353 W);
- polypropylene pipes about 200 m;
- brackets;
- corners;
- taps and other elements;
- system installation;
- system design;
- approvals will be about $11,000.
If you need a gas supply for a gas boiler, you need a project with approvals, which will cost about $400. Then it is necessary to install a gas pipeline, which can cost about $1,500. When choosing an electric boiler, costs are reduced due to the fact that no additional wiring is required (unlike gas boilers); therefore, a chimney and boiler room are not needed.
Note: Water heating systems have the disadvantage of labor-intensive and expensive installation and the need for preventive maintenance. If antifreeze is used in the system, then you need to remember that all antifreeze can lead to leaks in the system; after five years, the antifreeze needs to be changed, as they age and their freezing point increases.
Air heating

Air heating scheme in a private house
Air heating systems come in gravity and forced ventilation systems. With a gravity heating system, air moves due to natural circulation due to temperature differences. At different temperatures, different air densities arise, due to which natural air movement occurs in the system.
Warm air exits through the air ducts under the ceiling and, occupying a significant volume, displaces colder air (for example, near windows and doors) down and towards the air intake, thereby creating air circulation in the heated room. The disadvantage of gravitational (natural) circulation is that due to the intake of cold air from open windows, doors, and drafts, air circulation is disrupted and overheating occurs in the upper part of the room and cooling of its working part. The advantage is independence from electricity.
A forced ventilation system uses an electrically driven fan to increase air pressure and distribute it throughout the ducts and rooms. The heat carrier is air, which is heated by a heat generator, the main elements of which are a burner and a heat exchanger. The air supplied by the fan blows the heated the heat exchanger, where the combustion products exit, is heated to 45-60 degrees, then supplied through the air duct system to the rooms. Through return air ducts or through grilles, the cooled air is returned to the heat generator. The speed of air movement in systems with forced circulation is much higher. But there is a problem of noise in air ducts and distribution grilles.
The air heating system allows you to do without boilers, radiators, pipes and other elements that are used in water heating. Heat generators can operate on different types of fuel from the burner.
Operating principle and design of the system:
Heating of the premises occurs by supplying heated air there. The system operates in fully automatic mode. The main element of the system is the heat generator. Heat generators can be both stationary and mobile.

Design of a heat generator for an air heating system
In the combustion chamber of the heat generator, liquid fuel (diesel, kerosene) or gas supplied from the burner burns (gas and diesel burners have standard sizes and connections, therefore they are interchangeable). A diesel burner requires an additional tank, filters, and fuel lines for liquid fuel. Household gas heat generators can operate both on natural gas and bottled liquefied propane-butane.
Note: heating a residential building with an area of 100 sq. meters for a month at a temperature of + 24 degrees C, approximately 6 fifty-kilogram cylinders of liquefied propane will be required. An alternative to cylinders: propane tanks (sizes 2500-5000 liters) - gas holders buried in the ground; they do not require special heating).
A fan is located at the bottom of the combustion chamber; air from the room enters here, which is directed to the heat exchanger (heat generators can also carry out a small mixture of outside air). Next, the heated air is directed through the air ducts into the room, and the combustion products go into the chimney. Heated air (usually up to 45-60 degrees) and pumped directly or through air ducts, moving, creates uniform heating throughout the entire volume of the room. Through return ducts or through grates on the floor, the air returns back to the heat generator. Exhaust gases are removed through a chimney. To heat a house, an air flow rate of 1000 to 3800 m3/hour at a pressure of 150 Pa is sufficient.
If the room area is large, long air ducts can lead to heat loss, so sometimes it is possible to install several heat generators without air ducts instead of one heat generator with air ducts connected to it. The maximum length of the main air duct should be no more than 30 m, branches - no more than 15 m.
Air ducts vary:
1. According to the form: round And rectangular;
Round ducts usually have a circular cross-section with an internal diameter of 100-200 mm, they are durable and create little aerodynamic drag. Attached with a clampthe required diameter and studs.
Rectangular ducts in the form of boxes with dimensions from 100x150 mm to 3200x4000 mm. They have advantages when a large cross-sectional area is needed, or installation is carried out in difficult conditions; they fit better into the interior of rooms, save space, which is why they are more often used in private homes. They are fastened using a special profile and studs.
Both round and rectangular ducts are attached to the ceiling using drive-in anchors.
2. By hardness: hard And flexible;
Rigid ones are made of galvanized or stainless steel (both round and rectangular cross-sections). They are used in rooms of any layout and complexity. Flexible and semi-flexible air ducts of only circular cross-section are made of thermoplastic material using a spiral steel frame. They are easy to install, however, they increase aerodynamic drag
3. According to the material: metal And non-metallic;
Metal:
- Chimneys are made from black steel (1.0-2.0 mm) with a primer;
- Air ducts are made of copper in wet rooms: kitchens, bathrooms, bathrooms, swimming pools. This is the most expensive material;
- Made of aluminum alloys: able to withstand high temperatures and do not corrode. Most often installed in kitchens;
- Made from galvanized or stainless steel: produced with a thickness of 0.5-1.0 mm. Such air ducts have a low price, they have anti-corrosion properties, durability and increased fire resistance. (Air ducts made of galvanized steel are most often used).
Non-metallic:
- Plastic air ducts have a low cost, are made of polyethylene, vinyl plastic, etc. They are light in weight, easy to install, are not subject to corrosion, and have antistatic properties. However, they have low fire resistance. Attached using metal or plastic mounting brackets.
- Textile air ducts for transporting air are made of airtight fabric - polyamide, and permeable polyester fabrics are used for air supply (they are also an air filter). To ensure fire resistance, fiberglass is used. They are economical, easy to transport, easy to attach and install. However, textile air ducts only provide air flow.
Air ducts passing through unheated rooms or adjacent to an external wall must be insulated. If you plan to hide the air duct between the ceilings, then you need to place it in a metal frame and insulate it. In order to disinfect the air and refresh it, filters, humidifiers and fresheners can be built into the system. Air distributors and air intake devices are attached to the ends of the air ducts leading into the premises.
Calculation of the cost of an air heating device

Heating air system calculation diagram
Example: two-story private house with an insulated attic and basement with a total area of 300 sq. meters. Equipment and ductwork will cost approximately $8,000; consumables will be $550. (pipes and air duct wiring will cost $10-15 per p/m). Installation and commissioning works - $2300. Design and estimate work - $700.
In general, air heating without automation can cost approximately $11,000. Some companies offer the cost of installing air heating at 26-36 USD. for 1 sq. turnkey meter. Comparing these calculations with calculations for water heating, it is clear that the cost of wiring air heating, calculated at a minimum, will be lower than when creating water heating. Thanks to automation, the air heater can be turned on 3-4 times a day for 10-15 minutes to maintain the temperature. Fuel consumption during the heating season can be 30-40% lower compared to water heating.
The disadvantages of air heating include the fact that it is difficult to modify it, it requires competent calculation of air ducts and network topology, labor-intensive routing of air ducts, and installation must be done during new construction. It is necessary to condition and humidify the air in the room.
Electric heating
Among the various options for electric heating of private houses: electric convectors, ceiling infrared long-wave heaters, cable and film systems for heating floors and ceilings.
Let's consider the use of electric convectors. They are popular in low-rise suburban construction, especially in those regions where there are no gas mains.
Operating principle of electric convectors
The operation of an electric convector is based on the phenomenon of air convection (circulation), as a result of which over 80% of the heat is released into the air. The high moisture resistance and reliability of convectors allows them to be installed in bathrooms and children's rooms, since the temperature on their surface does not exceed +60 C. There are models of electric convectors that do not dehumidify the air in the room and do not burn oxygen. The operation of electric convectors is based on heating the cold air entering the device from the room. Heating is produced by a heating element made of a conductive component. After heating, the air increases in volume and rises through the louvers of the outlet grille. Additionally, the air is heated due to heat radiation from the surface of the electric convector.

Electric converter operation diagram
The level of comfort is ensured by an electronic system for maintaining the desired temperature. There are models with a built-in thermostat and with a remote thermostat. The thermostat saves energy. The air temperature sensor records the temperature in the room over a short period of time and sends a signal to the thermostat, which turns the heating element on or off. The presence of a thermostat allows you to set the operating mode once, and disconnect the device from the network only during a long absence. The built-in thermostat is affected by the temperature of the convector body, so its data may be inaccurate. The remote thermostat regulator takes into account the temperature of the point in the space in which it is installed. The remote thermostat is attached to the wall at a height of 1-1.5 m from the floor, away from drafts.
Electric convectors can be divided by size into two main groups: high - up to 45 cm high and baseboard - up to 20 cm high. High electric convectors are either placed on the floor or mounted using a special frame on the wall. Skirting convectors are convenient for installation under low windows and stained glass windows. Their power is 0.5-3.0 kW (in increments of 250 W). Dimensions in length, depending on the power, can be up to 2.5 m with a thickness of about 80 mm. For the greatest effect, it is recommended to install the electric convector at a height of up to 1 m, or under window openings. To ensure normal air flow circulation, the electric convector must not be obscured by objects at a distance of up to 0.1 m.
In terms of operating costs, this type of heating is inferior only to gas, but it is more reliable and safe. The control units are equipped with overheating protection. No grounding required. The devices are insensitive to voltage surges. The mains voltage is sufficient for operation of the device -220 V.
Calculation of the number of electric convectors

Diagram of the number of electric converters in a private house
The number and power of convectors are determined based on the volume of the room that will be heated.
The calculations can be based on the required heating power 1m3 of room: 20 W/m3 - for rooms with good thermal insulation (according to energy-saving standards of Scandinavian countries); 30 W/m3 - houses with insulated walls and ceilings, double-glazed windows; 40 W/m3. - poorly insulated houses; 50 W/m3 - poorly insulated buildings.
Example: The requirement for the main heating of a house with an area of 100 m2 and a height of 3 m (volume 300 m3) of a poorly insulated house, that is, with a need of 40 W/m3, is 12,000 W. Thus, it is possible to place four convectors with a power of 2.5 kW and one with a power of 2.0 kW in this area. Depending on the company and the availability of additional functions, the price of a convector can range from $100 to $200-250. Thus, the cost of electric convectors for this case (seven pieces) can be $1,250.
One can add to the advantages of electric convectors that, despite the generally low costs of equipment, there are no costs for maintenance and prevention.
Note: The disadvantage of electric convectors is that they heat the room unevenly in height: warm air accumulates under the ceiling, and the air temperature at the floor remains low, which is also typical for water heating; dependence on electricity can also become problematic when it is turned off; In addition, circulating flows carry dust with them. However, now some companies offer models of electric convectors that help reduce the collection of dust around the devices. If the room is large, you need to install a fan to speed up heating.
How to choose the type of heating for a private home
Based on the experience of various construction projects, we can say with confidence that the most correct choice of heating system for a particular house depends on what type of energy is most accessible, the distance of the home from populated areas, and the material capabilities of the owner. There are pros and cons to any heating system, so consult with the designers before making a decision.
Of course, if there is a gas supply to the house or even to the area, then it is best to choose water heating with a gas heat generator (boiler). Gas is currently the cheapest form of energy. However, in winter there are drops in gas pressure to 100-120 mm of water. Art., with a norm for boilers of 180 mm water. Art., which can lead to shutdown of the heating system.
For heating you can use electric convectors. If it is possible to supply electricity of sufficient power (if you have installed equipment with a power higher than 10 kW, you need to connect a three-phase wire and agree with the energy sales authorities), then you can use other types of electric heating. However, you will then be completely dependent on the electricity supply.
Owners of houses remote from civilization will have to think about creating an independent heating system.
For example: installation of solid fuel stoves and fireplaces in the house. The main danger with improperly installed stoves is the possibility of carbon dioxide entering the room, so good stove makers are needed. As an alternative to stoves, you can install a solid fuel boiler: wood and coal for water heating. By installing sensors, such boilers will be able to maintain the desired temperature without the use of electricity. Or use liquid fuel boilers, however, taking into account that emissions from burning diesel fuel are harmful to health, and also that 1 kW of energy will cost 4-5 times more than when using solid fuel.
In order to be sure that your home will always be warm, it may be worth making sure that you can use different energy sources. For example, to have a solid fuel fireplace or to purchase a boiler that runs on different types of fuel, which is produced by European manufacturers, however, its price will exceed the total price of single boilers that run on different fuels.
The most important characteristic of current costs is the cost of fuel and its consumption per unit of time.
Currently, fuel prices are approximately:
1 liter of diesel fuel - $0.4. The cost of 1 kWh of energy is $0.04.
1 m3 of natural gas for a private owner - $0.04. The cost of 1 kWh of energy is $0.005.
1 liter of propane-butane mixture - $0.2. The cost of 1 kWh of energy is $0.018.
1 kWh of electrical energy for a private owner - $0.03.
1 kg of coal averages $0.2. The cost of obtaining 1 kWh of energy ($0.04).
Attention! In this article, all prices are presented for the period 2009.
Every home in the Russian climate requires an efficient heating system. For a private home, which, as a rule, is absent, there are quite a lot of options for its arrangement. Differing from each other in design, types of wiring and coolants, all these systems have their advantages and disadvantages.
Classification of heating systems for a private home
First of all, heating systems differ in the type of coolant and are:
- water, the most common and practical;
- air, a type of which is an open fire system (i.e. a classic fireplace);
- electric, the most convenient to use.
In turn, in a private house they are classified according to the type of wiring and are single-pipe, collector and two-pipe. In addition, there is also a classification for them according to the energy carrier required to operate the heating device (gas, solid or liquid fuel, electricity), and according to the number of circuits (1 or 2). These systems are also divided by pipe material (copper, steel, polymers).
Water heating of a private house
Water heating in a private house is carried out using a closed circuit filled with hot water circulating through it. In this case, the heating device is a boiler, from which it is necessary to run pipes throughout the house to each radiator. The water passes through the radiators, gives off heat to the rooms and returns to the boiler. There it heats up again and enters the system. Antifreeze can also be used as a coolant.

Most often, the heating system consists of copper pipes, the most reliable, however, also the most expensive.
Steel is used less often, and water heating is almost never made from polymer materials that do not tolerate temperature changes well.
In addition to pipes, the circuits must be equipped with additional elements:
- an expansion tank that collects excess liquid;
- thermostats that control the temperature in front of the radiators;
- a circulation pump that ensures forced movement of liquid through pipelines;
- shut-off and safety valves.
Subspecies
A system of this type can be:
- single-circuit, providing only air heating;
- double-circuit, which also allows you to get hot water.

Based on the principle of fluid movement in pipes, one-pipe, two-pipe and manifold systems are distinguished. The first involves a sequential transfer of coolant from one battery to another. Its advantages include ease of wiring, while its disadvantages include low efficiency, impossibility of regulation and difficulty in replacing individual elements.
Two-pipe
A two-pipe system is better, as it is more maintainable and ensures minimal heat loss.

But the most convenient and effective way to set up a water heating circuit will be achieved if you carry out one that provides both quick replacement of a worn-out element and simple temperature control, but also costs more.
Pros and cons
The main advantage of all water heating systems in a private home is the efficient transfer of heat throughout all serviced rooms. Among the disadvantages are:

- complexity and labor intensity of installation;
- the need for regular maintenance of pipes and the boiler, which can be carried out either by yourself or using the services of specialists.
Application of gas boilers
Boilers used in a water system can use different types of fuel. The most common and convenient to use is gas equipment - although it can only be installed if a central gas supply is connected to the house. In addition, among the disadvantages of gas boilers is the need for their regular monitoring by the relevant utility services.

But such a system has the following advantages over others:
- Easy to install and operate.
- High efficiency in the use of energy resources. On average, gas costs are 30–40% lower than using liquid fuel or electricity.
- Fast heating of rooms with coolant. Within an hour, the temperature in rooms with a water heating system, in which the heat source is a gas boiler, will increase noticeably.
- Environmentally friendly use of gas.
- The ability to automate the process, including programming the required temperature and hot water heating.
If there is no gas supply in a private home, it is necessary to use boilers that run on other types of fuel. For example, on wood, pellets or coal. Such a solid fuel boiler will be completely autonomous and independent of the supply of electricity or gas.

However, its environmental friendliness is significantly less compared to other options. And to store energy, you will need an additional storage device protected from moisture.
Heating using liquid fuel
Liquid fuel equipment should be installed correctly in buildings where the use of both gas and electricity is impossible or simply impractical (for example, the electrical network will not support such a powerful boiler). Its advantage can also be called independence from electricity and gas supplies. Although the disadvantages of such boilers usually outweigh the advantages:

- for fuel it is necessary to install a special fireproof tank;
- the energy carrier is very expensive, and this option turns out to be the most unprofitable;
- large volumes of fuel combustion products are released.
Electric boilers
Using electric boilers in water heating systems is convenient and quite profitable. And at the same time, high automation of the process is ensured.

However, the rate of heating of the coolant by most electric boilers is not too high - and if more powerful equipment is installed, the electrical network may be overloaded.
In addition, electricity is best used as both an energy carrier and a coolant, without the intermediary role of water.
Air system
The principle of operation of the air system is to heat the air directly near the unit (usually a stove, boiler or fireplace). Next, hot air currents are forced (using a ventilation system) or under the influence of gravity to spread throughout the house, providing it with heat. The disadvantages of the forced method are the cost of electricity, while the gravitational method is the possibility of disruption of the air movement pattern due to open doors and drafts.

A wood, gas or liquid fuel unit can be installed as a heat generator in a private home. The advantages of the system include relatively simple maintenance and maximum energy independence (especially in the case of gravitational heat distribution). At the same time, it also has disadvantages:
- the need to correctly design and install air ducts at the construction stage of the building. It is almost impossible to integrate them into already built housing;
- mandatory thermal insulation of air ducts;
- high cost of installation, even if you do the work yourself.
Electric heating
You can heat your home with electricity not only by installing a water system. Using electricity to directly heat rooms will be more correct and profitable. There are two device options:

- electric convectors;
- underfloor heating system;
- infrared long-wave heaters.
Heating with electric convectors
Electric convectors are less profitable compared to water heating, which uses gas as an energy carrier. However, compared to other options, their use will be cost-effective.

In addition, installing such devices is much faster than water radiators, and no pipes are required - only wires and an electrical network capable of withstanding the required power.
"Warm floor"
The use of heated floors will allow you not to use indoor shoes even in the coldest time of the year. Their advantage compared to convectors is more uniform heating of rooms.
However, “warm floors” cannot be used as the main source of heat – but there is no better option for additional heating.
Using infrared heaters
Almost the only disadvantages of using infrared radiation to heat a private home are the discomfort caused by the luminous panel and the low accuracy of power control. At the same time, among its advantages are:

- high heating rate;
- an increase in the temperature not of the air, but of the interior items;
- full automation of the equipment operation process.
The issue of replacing stove heating with a more modern one, sooner or later, has to be decided by the owner of a private house. It is clear that the task is very difficult for a non-professional, but doable. There are many specific subtleties in this work that only professionals in their field - designers and installers of heating systems - know about. We can't do it without their help. But if the owner of a private house wants to do the heating with his own hands, he can easily do some of the work himself. And entrust the important stages of work to professionals.
This article will give the novice home craftsman an idea of what cycle of work needs to be done.
Heating options
First you need to choose a heating system. And there is plenty to choose from - there are several of them and They differ from each other by the type of coolant:
- Water heating system;
- Steam heating system;
- Air heating system;
- Electric heating system.
Let's look at each of them separately.
Water heating
It works on the principle of a closed loop of pipes containing hot water. The central element in this system is the boiler, where water is heated and distributed through pipes throughout the entire system (). Installed water heating radiators, through which the coolant passes, heat up and warm the rooms. The cooled water flows back into the boiler and the process repeats again.

All heating boilers fit into a similar scheme, but the most popular are economical gas boilers.
Important! Gas boilers require regular inspection and adjustment by gas company specialists.
Steam heating
Steam from heated water acts as a heat carrier. In the boiler, the water is heated to a boiling point and, in the form of steam, is distributed through the mains to the radiators. Cooling, the steam turns back into water and goes back through the pipes to the heating boiler.
There are two types of steam systems:
- Open;
- Closed.
In the first case, the system has a storage tank for condensate. And in the second, the condensate formed after cooling flows back into the boiler through pipes of increased diameter.
Steam heating is used mainly in industrial premises in large industries, where steam is needed for their own needs. For home use, steam heating has not become widespread due to the large areas for placing boiler equipment. And the steam boiler itself is quite difficult to operate, and due to the high steam temperature of 115°, it is also dangerous.
Air heating
In a finished residential building, it is almost impossible to deploy equipment with your own hands to organize air heating. Only at the stage of construction of a new house is it possible to install the entire system (). And this despite the fact that the principle of operation of such a system is quite simple.
A heat generator located at the lowest point of the steam heating system, for example in the basement, heats the air. And already heated, it disperses through the air ducts throughout the rooms of the house and exits through the grilles under the ceiling of the rooms. Warm air displaces cold air into return air ducts laid to the heat generator. That is, it turns out to be a closed cycle of work.
To improve performance, a fan is included in the heating system, which increases the air pressure in the air duct.
An example of the operation of air heating is shown in Fig:

The heat generator can operate autonomously on diesel fuel or kerosene. You can also use gas - both natural gas from the main gas pipeline and bottled gas.
To equip a private house with this type of heating, it is necessary to carry out design work. Specialists will calculate what material the air ducts will be made of (metal, plastic or textile), what size they will be, and build the correct topology of the heating network for the entire building.
Electric heating
Provided there is a constant power supply, electric converters, hanging infrared heaters, and an electrical “warm floor” system will help maintain heat in the house.

This system does an excellent job of heating the house, but high electricity bills make you think about the cost-effectiveness of this heating method.
But if you install it as a spare, in addition to the main one (for example, a gas boiler), then this heating method is quite in demand.
Mounted heating electric convectors have one feature - uneven heating of the room space. The lower zone at floor level is cold, and the upper zone under the ceiling is warm.
An electrical “warm floor” system will help correct the situation:

Heating system elements
The entire electrical heating system in a house can be compared to a person’s circulatory system. The heart is a boiler, from which heat is distributed through veins (pipes) to the heating elements throughout the house.
This is, of course, a figurative representation. In fact, there are many more elements that ensure the efficient operation of the entire electric heating system - from pipe connectors to expansion tanks.
Electric heating can be organized in different ways:
- Forced water circulation;
- Natural circulation of water.
A pump is included in the forced circulation system. But there is a small drawback - the pump requires electricity to operate. If it is turned off, the entire heating system will stop working.

Systems with natural circulation, in terms of independence from electricity, are more convenient. Water circulation occurs due to the fact that the water temperature at the outlet and inlet of the heating boiler is different. But in this case, pipes with different diameters are selected, and it is difficult to adjust. The advantage is that such a system does not depend on electricity.

Systems are also divided into open and closed.
In open electrical systems, an expansion tank is installed to relieve excess pressure. As a rule, this is the highest point of the system. To relieve pressure in closed systems, a closed-type membrane tank is installed. It is small-sized, sealed and can be mounted anywhere in the electrical system, which avoids the formation of air locks.
Calculation of the system and selection of boiler power
Of course, store managers can also select equipment. But there are two ways in which you can do this completely independently with your own hands.
A simple approximate method is used by equipment sellers: the area of one room is multiplied by 100 W. By summing the obtained values for all rooms, the required power of the heating devices is obtained.
- If only one wall faces the street, the area is multiplied by 100 W;
- For a corner room, the measured area is multiplied by 120 W;
- If there are 2 external walls and two windows, the area of the room is multiplied by 130 W.
For a more accurate calculation, use the formula:
W cat.=(S*W spec.):10
Where,
- S – room area;
- W beat – specific power of the heater used per 10 m² of room area.
W beat is selected depending on the region.
For example, if the area of all heated premises is 100 m², with a specific power for the Moscow region of 1.2 kW, then the output for the boiler is: W = (100x1.2)/10 = 12 kilowatts.
Heat consumption for ventilation
The flow of fresh air is very important for comfortable living in the house. And therefore, when choosing a heating boiler, it is important to take into account the heat consumption for ventilation. Fresh air indoors is undoubtedly necessary, but the speed at which cold air flows inside the house is equally important. And the lower the speed of fresh air flows, the more comfortable the living conditions become.
Building codes specifically stipulate the presence of exhaust ventilation in the following premises:
- Baths;
- toilet;
- Kitchens.
And the flow of fresh air should be ensured by vents in the windows and supply valves in living rooms (Fig.):

Thus, the supply air is divided into three zones:
- Air flow.
- Air flow.
- Air hoods.
When organizing any heating system, it is necessary to take into account the heat consumption not only for heating the house, but also for its ventilation. If the work is carried out according to the project, then it must include a calculation of heat loss due to the entry of cold air masses into the room.

Only after calculating the nominal air exchange in the house can conclusions be drawn about the final heat requirement for both heating the house and its ventilation.
Before choosing and buying a boiler for your heating system, You need to decide several parameters for yourself:
- The most important thing is to purchase exactly the type of boiler that will effectively heat the entire house;
- Choose a heating boiler that will constantly operate on the selected type of fuel;
- And lastly, the boiler will only work for space heating or also heat water for everyday needs.
For reference! If the boiler operates primarily for heating, it is single-circuit, and if it also produces hot water, it is double-circuit.
Solid fuel boilers
It makes sense to opt for solid fuel heating boilers either if there is no way to connect to gas in the region or if there is fairly inexpensive coal or firewood.

You can install a solid fuel boiler with your own hands using solid fuel as a backup heat source. The cost of such boilers is relatively low, but The heating system will not work without:
- Expansion tank;
- Security groups;
- More reliable pipes and radiators.
This is due to the fact that boilers of this type operate at higher temperatures.
Such boilers are very reliable if a number of conditions are met:
- The fuel for the boiler must be consistent in both quality and humidity.
- Mandatory daily cleaning of the solid fuel boiler.
Gas boilers

The most popular, if connected to gas mains, are gas boilers (). Its main advantage is that, despite its simplicity, it is also easy to use. Most modern models of gas boilers are also equipped with a thermostat. And this is very convenient - you select the desired temperature for your home, and the device will automatically maintain comfortable warmth throughout the entire house.
Gas heating boilers have a wide range of prices to choose from.
The price is affected by:
- Manufacturer;
- Power;
- Boiler type.
But the big advantage of boilers of this type is that they already come complete with a circulation pump and an expansion tank.
And the material from which gas heating pipes and radiators are made is completely different and much cheaper than, for example, for boilers running on solid fuel (coal, etc.).
Electric boilers

This is the most expensive way to heat a house ().
But! Electric heating boilers have some advantages:
- Wide choice of power – from 2 to 40 kW;
- Stability in work;
- Do not pollute the atmosphere in the house;
- Very easy to use;
- Built-in circulation pump;
- Supplied with expansion tank and temperature sensor;
- They are reliable in operation;
- Inexpensive repairs and maintenance.
Electric boilers are comparable in price to gas boilers.
Liquid fuel boilers
Most consumers have no idea that traditional liquid fuel heating boilers now have the opportunity to work not only on diesel fuel, but also:
- Kerosene;
- Light grades of oil;
- Used oils (including synthetic origin);
- Fuel oil.

It is enough to change the burners for the desired type of fuel.
For reference! There are universal liquid fuel boilers without burners on sale. The consumer has the opportunity to choose a burner for diesel fuel or gas independently.
But when using liquid fuel heating boilers, it is necessary to take into account a number of features:
- Compared to gas boilers, fuel costs will increase significantly.
- Equipment purchase and installation costs are higher than other types of heating.
- On the site near the house it is necessary to leave space for the installation of a large tank for storing fuel reserves.
- To prevent the specific smell of diesel fuel and the noise from the operation of burners from spreading into the living areas of the house, it is better to install heating equipment in a separate building.
- Since the burner requires the operation of automation and pumps powered by electricity, to ensure uninterrupted operation, install a backup generator.
- For stable operation of liquid fuel boilers, only good quality fuel is required.
For convenience, the table combines the estimated characteristics of heating boilers using different types of fuel:

Heating system diagrams
A water heating system can be organized into two types:
- Single-circuit;
- Double circuit.
And according to the principle of movement of the system there are:
- Single-pipe;
- Double-pipe;
- Collector;
- Leningradskaya.
Single-pipe

A single-pipe heating system is installed sequentially - one radiator after another. From the diagram, a significant drawback of this system is immediately noticeable. The coolant, moving from one radiator to another, begins to cool. With a less intensive circulation of water in distant radiators, it not only gives up all the remaining temperature to the metal, but also slowly enters the return line.
Thus, if the number of radiators for heating is too large, then the last radiator may be completely cold.
In addition, such a heating system is not practical to repair. To repair one radiator, you have to stop all heating in a private house.
Conclusion! In single-pipe heating systems, it is impossible to extend the circuit indefinitely.
Two-pipe

In a two-pipe heating system, maintenance is much simpler. Hot water is supplied to the radiator through one pipeline, and through another pipe (waste water) it flows back into the boiler. The radiators in this circuit are connected in parallel.
For ease of operation and repair, each pipe is mounted with a shut-off valve. Here, too, the water at the last radiator in the system will be colder, but significantly hotter than in a single-pipe system.
Collector

The figure shows that the supply and return systems for each heating radiator are organized independently of each other. A significant advantage in such a system is the ability to coordinate the temperature in any room separately. It is also very convenient to repair any section of the pipeline and each radiator separately.
Today, all experts recognize the collector heating system as the most progressive.
But there are also disadvantages:
- Requires installation of a manifold cabinet;
- Pipe consumption during installation of a heating system is sensitive to estimates.
Leningradskaya

A more advanced, single-pipe system, which, combined with ease of installation and low cost, is still very popular.
Despite the fact that the Leningrad heating system began to be introduced many years ago, it is still successfully used in the construction of multi-story buildings. This system has a main feature – simplicity. To construct such a system, you can have a minimum of knowledge and get by with a minimum amount of materials than in two-pipe systems. In addition, such a system has the ability to control each radiator in the system.
System installation
Once the choice of heating system has been made, the most correct step would be to contact the design office. Having a work project and drawings in hand, you can purchase and store the necessary materials, monitoring and control devices, and components.

Installation begins with choosing the location for installing the heating boiler. If combustion products are released during boiler operation, the optimal solution would be to build a separate boiler room. You can place the boiler room in the basement, provided there is good ventilation and sound insulation.
The boiler itself is installed at such a distance from the walls that it is always easily accessible for maintenance.
The covering of the floor and walls near the heating boiler must be made of fire-resistant materials. A chimney system is installed from the boiler to the street.
The following steps for installing the heating system will be carried out according to the project:
- Installation of a circulation pump;
- Distribution manifold unit;
- Measuring instruments;
- Manual or automatic adjustment devices.

After completing the installation of the boiler, they proceed to work on the installation of main pipelines, according to the selected heating scheme, to the places where the radiators will be installed. In residential buildings, you will have to make passages for pipelines in the walls and partitions. Based on the selected material, the pipes are connected to each other by previously prepared elements.

Installation work is completed with the installation of radiators. Typically, the following conditions are adhered to during installation:
- Distance from the floor – 12 cm;
- Distance from walls – up to 5 cm.
Shut-off valves, temperature sensors and other adjusting elements are installed on the pipes at the inlet and outlet of radiators.
The installation work is completed by pressure testing of the entire system.
Boiler connection

Connecting the installed boiler to the heating system according to the following diagram:
- The pipe system laid throughout the house is connected to the terminals on the boiler.
- As a rule, shut-off valves that cut off from the general system are installed at the joints.
- To operate electrical appliances, wires and a ground loop are connected.
- Installation of safety valves, thermostats and other devices (installed before installing shut-off valves).
- For gas heating boilers - connection to the gas pipeline.
- Filling the heating system with water.
- Pressure testing of the system with high pressure. At the same time, leaks in the system are identified and eliminated.
- Relieving pressure in pipes to operating level.
Important! When starting a gas boiler for the first time, the presence of a representative of the gas company is required.

The modern building materials market offers a large selection of pipes from a variety of materials for the installation of a heating system.
Of course, with sufficient welding skills, you can opt for the usual steel pipes. But why doom yourself in advance to guaranteed system repairs due to the fact that the pipes will be susceptible to corrosion?
If there is a desire to use either copper or stainless steel pipes, then it can only be approved if the owner is not limited in financial resources and is not afraid of certain installation difficulties. Such pipes are the most expensive, but they are not afraid of high pressure and high temperature.
The most inexpensive option is polypropylene pipes. But we must take into account that the connection points with the fittings are made by soldering and if the heating of the connection is insufficient, this place will definitely leak. And if overheated, the internal section may overlap with molten material.
Recently, polyethylene or metal-plastic pipes have become very popular. Installation is quite simple, provided that the joints are made using pressed fittings. They can be laid under poured floors when installing a “warm floor” system.
With a large selection of modern radiators, it is at least not rational to opt for traditional cast iron ones (). Due to low thermal conductivity, they have lost their former popularity.
Aluminum radiators
In addition to high heat transfer, aluminum radiators are very lightweight.

Due to the fact that they have a variety of center distances (350-500mm), the installation of a heating system is greatly facilitated. Aluminum radiators have a number of advantages that distinguish them from other heating devices:
- High heat transfer;
- Low weight of the structure;
- High working pressure (18 atm.);
- Beautiful design.
Bimetallic radiators

Systems of this type combine the advantages of both sectional (made of aluminum alloys) and tubular (made of steel):
- Increased strength (up to 40 atmospheres);
- Long service life (up to 20 years);
- Beautiful design;
- High level of heat transfer.
Steel panel radiators
The main advantage of steel radiators is their quick response to changes in coolant temperature.

They heat up instantly and also cool down quickly. Such properties significantly affect energy saving.
The large area of stamped steel panels has a positive effect on high heat transfer, and the presence of a ribbed surface increases the area of the heating device. Such qualities increase comfort and heating efficiency.
Selection by power and methods of connecting radiators
The decision to completely replace the heating system has been finally made. The main elements of the system have been selected, the only question left to solve is: how much power can the radiators themselves produce?
It is this indicator that is actually the most important in determining the properties of the heating system.
Let's take, for example, a room with an area of 10 m² with a ceiling height of 3 m. The volume of the room is correspondingly 10x3 = 30 m³.
But this indicator does not fully describe the characteristics of the radiator. It is known from the standards that to heat 1 m³ of a room, a heating radiator with an output power of at least 40 watts is required.
The result is: 30x40 = 1200 W.
For insurance, you can add 15-20%. This is exactly the amount of heat needed to heat such a room. As you can see, the calculations are quite simple and you can do them yourself before going to the store.
When we figured out the power of the radiator, it remains to choose the method of connecting it to the main line, which is done in several ways, as in the figure:

Lateral connection of heating batteries is used when installing to risers. If the main pipes are laid under the floor covering or at floor level - diagonal.
The figure shows that these two connection methods allow the entire surface of the battery to be used as productively as possible.
The lower versatile connection method also finds its supporters. The figure shows that with this direction of hot water it is impossible to effectively heat the entire space of the radiator.
Errors during installation
Shortcomings and errors in installation work are not uncommon. Their description is a topic for a separate article, but the most common ones can be identified:
- Incorrect selection of heat source;
- Any defects in the boiler circuit;
- Incorrectly selected heating system;
- Negligent attitude of installers.
Choosing a boiler with insufficient power is the most common mistake.
The desire to save on the cost of the boiler, but at the same time power not only the heating system, but also organize the supply of hot water, will lead to the fact that the heat generator will not be able to provide the house with enough heat.
All elements and devices in the boiler piping must be installed according to their functional properties. For example, it is recommended to insert a pump specifically on return pipeline lines and do not forget to take into account the horizontal position of the pump shaft.
If the heating system is incorrectly selected, there is a risk of additional alterations. So, if you “hang” more than five radiators on a one-pipe system, most often the rest will not heat at all.
Examples of shortcomings in do-it-yourself installation include poorly placed slopes, unwelded connections, or installation of incorrectly selected shut-off valves.
For example, if you confuse the installation locations of the valves on the pipes in front of the entrance (ordinary tap) and at the outlet of the radiator (water supply control tap). It also happens that the installation of pipes in the floor occurs without mandatory insulation, so that the water does not cool down on the way to the radiator. I had to change the heating system at the dacha - old cast-iron radiators and a Soviet boiler, for which parts could not be found even during the day with fire. But when we found out the cost of services for replacing and modernizing thermal communications, we were in great shock. In the end, we decided to do everything ourselves - albeit not so quickly, but you can save a good penny. Fortunately, we found this article, where all stages of the work are described in great detail and with examples, with many photographs explaining it. I especially liked the section “Errors during editing” - we learned a lot of useful things from the “what not to do” category, otherwise we would have spent more time, nerves and money on redoing it.
Thanks to the author for the detailed article. It can be safely used as a scientific guide when independently installing a heating system in your home. Thanks also for the many recommendations. They will help, especially for beginners. And on my own behalf I will add that, in my opinion, the most optimal option among those proposed is to install a gas boiler. After all, judge for yourself: it is relatively cheap, familiar and practical. However, the author or anyone else may disagree with me. I'll be looking forward to other people's opinions on this.
Two years ago we just installed heating in the house. So as not to be dependent on the stove, otherwise this fumes and smoke get boring, to be honest. Our specialists and I installed water heating. Quite practical and power is not lost or dissipated. The water is simply heated by the boiler and it is distributed through pipes that are located around the house, such as a battery. And they are already heating the house. For us personally, this method seemed the simplest and most optimal.
A question arose about replacing the heating in a private house, so we decided to throw out the Soviet batteries and boiler and replace it with a new one. The prices are of course terrible, the prices are terrible. So I started searching on the Internet for how to do everything correctly, fortunately I came across you and received information on installing and assembling the system. Everything is explained in detail and it was easy to understand. After reading it, it became more profitable for me to do it myself than to overpay 10 times more to some smart guy who can do the same thing as me.